What to expect after gluteus medius tendon repair surgery – The road to recovery after gluteus medius tendon repair surgery can be a journey of both challenges and triumphs. Understanding what to expect after this procedure is crucial for a smooth and successful rehabilitation. This guide will delve into the intricacies of the surgery, from the initial stages of preparation to the long-term outcomes, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate this transformative process.
This journey begins with understanding the gluteus medius tendon, a vital component of hip stability. Tears in this tendon can cause debilitating pain and limit mobility, prompting the need for surgical repair. The surgery itself involves carefully stitching the torn tendon back together, allowing it to heal and restore proper hip function.
But the road to recovery doesn’t end there. A comprehensive rehabilitation plan is essential to regain strength, flexibility, and full range of motion, ensuring a return to an active lifestyle.
Understanding Gluteus Medius Tendon Repair Surgery
Gluteus medius tendon repair surgery is a procedure to fix a torn tendon in the gluteus medius muscle, which plays a crucial role in hip stability and movement. Understanding the anatomy of the gluteus medius tendon and its function, common causes of tears, and the surgical procedure itself can help patients make informed decisions about their treatment options.
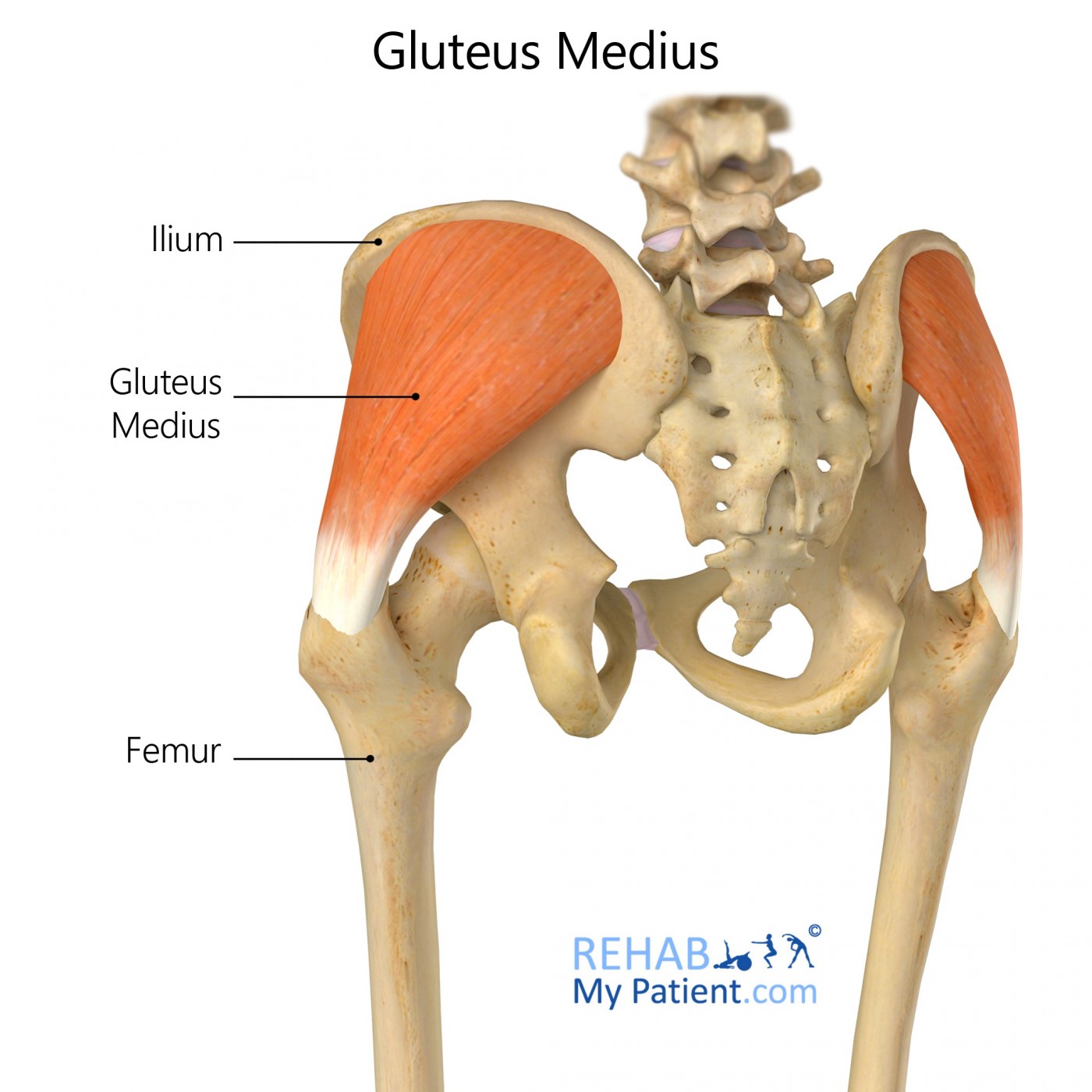
Anatomy and Function of the Gluteus Medius Tendon
The gluteus medius muscle is located on the side of the hip, and its tendon attaches to the greater trochanter, a bony prominence on the upper part of the femur (thigh bone). The gluteus medius muscle is responsible for several important hip functions, including:
- Abduction: Moving the leg away from the midline of the body.
- External rotation: Rotating the leg outward.
- Hip stability: Helping to control the movement and position of the hip joint, especially during walking and running.
A healthy gluteus medius tendon is essential for maintaining proper hip function and preventing injuries.
Causes of Gluteus Medius Tendon Tears
Gluteus medius tendon tears can occur due to various factors, including:
- Overuse injuries: Repetitive movements or high-impact activities can strain the tendon, leading to microscopic tears that eventually progress to a complete tear.
- Direct injury: A direct blow to the hip or a fall can cause a sudden and forceful tear of the tendon.
- Degenerative changes: Over time, the gluteus medius tendon can weaken and degenerate, making it more susceptible to tears, especially in older individuals.
- Underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of tendon tears.
Symptoms of Gluteus Medius Tendon Tears
The symptoms of a gluteus medius tendon tear can vary depending on the severity of the tear. Common symptoms include:
- Pain: Sharp pain in the side of the hip, especially during activities that involve hip abduction or external rotation.
- Weakness: Difficulty lifting the leg away from the body or rotating it outward.
- Limping: A noticeable limp when walking or running.
- Swelling: Swelling or tenderness around the greater trochanter.
- Clicking or popping: A clicking or popping sensation in the hip joint.
Gluteus Medius Tendon Repair Surgery
Gluteus medius tendon repair surgery is typically recommended for patients with significant pain, weakness, and functional limitations despite conservative treatment options. The goal of the surgery is to reattach the torn tendon to the greater trochanter, restoring hip stability and function.
Surgical Techniques for Gluteus Medius Tendon Repair
There are several different surgical techniques that can be used to repair a gluteus medius tendon tear. The specific technique chosen will depend on the size and location of the tear, the patient’s overall health, and the surgeon’s preference. Some common techniques include:
- Open repair: This technique involves making a larger incision over the hip to directly access the torn tendon. The surgeon will then use sutures or other fixation devices to reattach the tendon to the bone.
- Arthroscopic repair: This minimally invasive technique involves making small incisions and inserting a small camera and surgical instruments into the joint. The surgeon can then visualize the torn tendon and repair it using sutures or anchors.
- Tendon transfer: In some cases, the surgeon may transfer another tendon to the greater trochanter to help stabilize the hip. This technique is often used when the gluteus medius tendon is severely damaged or cannot be repaired.
Pre-Surgery Preparation
Preparing for gluteus medius tendon repair surgery is essential for a successful recovery. Your doctor will work with you to ensure you are in the best possible condition before surgery.This section Artikels the pre-operative assessments and tests, provides a list of pre-operative instructions, and discusses potential risks and complications associated with the surgery.
Pre-Operative Assessments and Tests
Before surgery, your doctor will conduct a comprehensive assessment to determine the extent of your injury and develop a personalized surgical plan. This may include:
- Physical Examination:This involves assessing your range of motion, muscle strength, and gait. Your doctor will evaluate the affected area and examine for any other signs or symptoms.
- Imaging Tests:These tests help visualize the tendon injury and surrounding structures. Common imaging tests include:
- X-rays:Provide a clear image of the bones in the hip and surrounding area, helping identify any fractures or other bone abnormalities.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):Creates detailed images of the soft tissues, including the tendons, muscles, and ligaments, allowing for a thorough evaluation of the tendon injury.
- Blood Tests:These tests evaluate your overall health and identify any potential health issues that could increase surgical risks.
- Electrodiagnostic Testing:This test assesses the function of the nerves that control the muscles around the hip, helping to identify any nerve damage.
Pre-Operative Instructions
Your doctor will provide specific instructions to prepare for surgery. These may include:
- Diet:You may be advised to follow a specific diet, such as a clear liquid diet, for a certain period before surgery. This helps to ensure your digestive system is prepared for the procedure.
- Medications:You may need to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, before surgery. Be sure to discuss all medications, both prescription and over-the-counter, with your doctor.
- Activities to Avoid:You may be asked to avoid certain activities, such as strenuous exercise or smoking, before surgery. This helps to minimize the risk of complications.
Potential Risks and Complications, What to expect after gluteus medius tendon repair surgery
Like any surgical procedure, gluteus medius tendon repair surgery carries some potential risks and complications. These may include:
- Infection:As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection. Your doctor will take steps to minimize this risk, such as using sterile techniques and administering antibiotics.
- Bleeding:Bleeding is another potential complication of surgery. Your doctor will take steps to control bleeding during and after the procedure.
- Nerve Damage:In some cases, the nerves in the area may be damaged during surgery. This can lead to numbness, tingling, or weakness.
- Delayed Healing:The tendon may not heal properly, leading to pain, instability, or a need for additional surgery.
- Blood Clot Formation:Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a blood clot that forms in a deep vein, is a possible complication of surgery. Your doctor will take steps to minimize this risk, such as using compression stockings and encouraging movement after surgery.
It’s important to discuss any concerns you have with your doctor before surgery. They can provide more detailed information about the potential risks and complications specific to your situation.
Post-Surgery Recovery and Rehabilitation

Recovering from gluteus medius tendon repair surgery involves a structured rehabilitation process designed to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the affected hip. This process typically involves several stages, each focusing on specific goals and activities.
Recovery Timeline and Stages
The recovery timeline after gluteus medius tendon repair surgery varies depending on individual factors such as age, overall health, and the severity of the injury. However, a general timeline can provide a roadmap for the recovery process.
- Immediate Post-Surgery (Days 1-2):The first few days after surgery focus on pain management and wound care. You will likely experience some pain and swelling, which can be managed with medication. You will also be encouraged to start gentle range-of-motion exercises for your ankle and knee to prevent stiffness.
- Week 1-2:During this period, you will begin gradually increasing your activity level. You may be able to walk with crutches or a walker, and your physical therapist will guide you through exercises to improve your range of motion and strength.
- Week 3-6:As your healing progresses, you will gradually decrease your reliance on crutches and start to bear more weight on your injured leg. Your physical therapist will introduce more challenging exercises, including strengthening exercises for your hip and leg muscles.
- Week 6-12:This stage focuses on regaining full function and strength in your hip. Your physical therapist will continue to guide you through exercises, and you may start to participate in low-impact activities like swimming or cycling.
- Month 3-6:You should be able to return to most activities by this time. Your physical therapist will continue to monitor your progress and adjust your exercise program as needed. You may need to continue with some exercises to maintain your strength and flexibility.
- Month 6-12:This stage focuses on returning to high-impact activities and sports. Your physical therapist will work with you to ensure that you are ready for these activities and to help you prevent further injuries.
Post-Operative Care
Proper post-operative care is crucial for successful recovery. This includes:
- Wound Management:Keep the surgical incision clean and dry. Follow your surgeon’s instructions for dressing changes and wound care.
- Pain Management:Pain medication can help manage discomfort after surgery. Your surgeon will prescribe appropriate pain relievers, and you should follow their instructions for dosage and frequency.
- Activity Restrictions:You will need to follow your surgeon’s instructions for activity restrictions. This may include avoiding certain activities, such as running, jumping, or heavy lifting, for a specific period.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the rehabilitation process after gluteus medius tendon repair surgery. It helps to:
- Improve Range of Motion:Physical therapy exercises help to restore the normal range of motion in your hip joint, reducing stiffness and improving flexibility.
- Strengthen Muscles:Exercises focus on strengthening the muscles around your hip, including the gluteus medius, which helps to stabilize the joint and prevent further injury.
- Improve Balance and Coordination:Exercises designed to improve balance and coordination help to restore your ability to walk, run, and participate in other activities without pain or instability.
- Functional Exercises:Physical therapists incorporate functional exercises into your rehabilitation program to help you regain the ability to perform everyday activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, and getting in and out of a car.
Specific Exercises and Stretches
Physical therapy exercises are tailored to each individual’s needs and recovery progress. Some common exercises and stretches that may be included in your rehabilitation program include:
- Hip Flexor Stretches:These stretches help to improve flexibility in the hip flexor muscles, which can become tight after surgery.
- Gluteus Medius Strengthening Exercises:Exercises that strengthen the gluteus medius muscle, such as hip abductions, help to stabilize the hip joint and prevent further injury.
- Balance Exercises:Exercises that challenge your balance, such as standing on one leg or walking heel-to-toe, help to improve coordination and stability.
- Proprioceptive Exercises:Exercises that involve moving your body in different directions and positions help to improve your sense of where your body is in space.
Expected Outcomes and Potential Complications
Gluteus medius tendon repair surgery aims to alleviate pain, improve function, and restore mobility in the hip. While the surgery offers significant benefits, it is essential to understand both the expected outcomes and potential complications.
Expected Outcomes
The primary goal of gluteus medius tendon repair surgery is to restore the integrity of the tendon, which allows for proper hip function. This leads to improvements in:
- Pain Reduction:The surgery aims to alleviate pain caused by the torn tendon, allowing for greater comfort during activities.
- Improved Function:A successful repair restores the strength and stability of the hip, enabling individuals to engage in activities like walking, running, and climbing stairs with less difficulty.
- Enhanced Mobility:The surgery can improve range of motion in the hip joint, allowing for greater flexibility and a wider range of movement.
Potential Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential complications associated with gluteus medius tendon repair surgery. These can include:
- Infection:As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection at the surgical site. This can be minimized through meticulous surgical techniques and post-operative care.
- Delayed Healing:Some individuals may experience delayed healing of the tendon, which can prolong recovery time and affect long-term outcomes.
- Nerve Injury:Nerves surrounding the hip joint can be damaged during surgery, potentially leading to numbness or weakness in the leg.
- Re-tear:In some cases, the repaired tendon may re-tear, particularly if proper rehabilitation protocols are not followed.
Comparison with Non-Surgical Treatment
Non-surgical treatment options for gluteus medius tendon tears often involve conservative measures like rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), physical therapy, and pain medications. While these options may provide relief for some individuals, they are less effective in restoring full function and may not address the underlying cause of the tear.
Surgical repair is generally considered the preferred treatment option for significant gluteus medius tendon tears, especially those that do not respond to conservative management.
Surgical repair offers a higher likelihood of achieving long-term pain relief, improved function, and restored mobility compared to non-surgical approaches.
Lifestyle Modifications and Prevention

After gluteus medius tendon repair surgery, it’s crucial to make lifestyle changes to prevent future injuries and promote long-term healing. By adopting preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of re-injury and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.
Posture and Ergonomics
Maintaining proper posture and ergonomics is essential to reduce strain on the hip joint and prevent future injuries.
- Sit uprightwith your back straight and shoulders relaxed. Avoid slouching or hunching over, as this can put unnecessary stress on your hip muscles.
- Use a chair with good lumbar supportto maintain the natural curve of your spine. Consider using a lumbar pillow if your chair lacks adequate support.
- Stand tallwith your feet shoulder-width apart and your weight evenly distributed. Avoid standing for long periods in one position, and take breaks to stretch and move around.
- When lifting objects, bend your knees and keep your back straight. Avoid lifting heavy objects with your back bent, as this can strain your hip muscles.
Exercise Techniques
Proper exercise techniques are crucial for preventing future injuries and promoting healing after surgery.
- Warm up properlybefore any physical activity. This helps prepare your muscles for exertion and reduces the risk of injury.
- Use proper formduring exercise. Focus on maintaining a controlled range of motion and avoid overexertion.
- Listen to your bodyand stop if you feel any pain. Pushing yourself too hard can lead to further injury.
- Avoid high-impact activities, such as running or jumping, until your surgeon clears you. These activities can put excessive strain on your hip joint.
- Incorporate strengthening exercisesthat target your gluteus medius and other hip muscles. This will help improve stability and prevent future injuries.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for reducing strain on your hip joint and preventing future injuries.
- Excess weightputs extra stress on your joints, including your hip joint. Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly reduce this stress.
- Consult with a healthcare professionalto determine a healthy weight for your body type and lifestyle.
- Adopt a balanced dietthat includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Engage in regular physical activityto help maintain a healthy weight and improve overall fitness.
Regular Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy weight, improving overall fitness, and reducing the risk of future injuries.
- Engage in low-impact activitiessuch as walking, swimming, or cycling. These activities are easier on your joints and can help strengthen your muscles.
- Avoid activities that put excessive strain on your hip joint, such as running or jumping, until your surgeon clears you.
- Start graduallyand increase the intensity and duration of your workouts as you become stronger.
- Listen to your bodyand stop if you feel any pain.
End of Discussion
Recovering from gluteus medius tendon repair surgery is a process that requires patience, dedication, and a commitment to following your healthcare provider’s instructions. While the journey may have its ups and downs, the potential for regaining hip strength, mobility, and a pain-free life is a powerful motivator.
Remember, with consistent effort and a supportive team, you can achieve your recovery goals and reclaim your active life.
Essential FAQs: What To Expect After Gluteus Medius Tendon Repair Surgery
How long will it take for me to fully recover?
Full recovery after gluteus medius tendon repair surgery typically takes several months. The healing process varies depending on individual factors, but most patients can expect to return to most activities within 6-12 months.
Will I need to use crutches or a walker?
You will likely need to use crutches or a walker for several weeks after surgery to keep weight off the affected hip and allow the tendon to heal properly. Your healthcare provider will guide you on the appropriate use and duration of these assistive devices.
What kind of physical therapy will I need?
Physical therapy is a critical part of your recovery process. Your therapist will design a personalized program that includes exercises to improve range of motion, strength, flexibility, and balance. The therapy will progress gradually, starting with gentle movements and progressing to more challenging exercises as your hip heals.
What are some tips for preventing future injuries?
Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing proper body mechanics, and incorporating regular low-impact exercise into your routine can help prevent future gluteus medius tendon injuries. Your healthcare provider can provide specific recommendations for your individual needs.