How long does it take to repair head gasket – How long does it take to repair a head gasket? It’s a question that often pops up when your engine starts acting up, leaving you wondering about the cost and downtime. A head gasket, that crucial seal between your engine block and cylinder head, can spring a leak, leading to a whole host of problems.
The repair time, however, isn’t a one-size-fits-all situation. It depends on a whole bunch of factors, from the type of engine to the severity of the damage and even the availability of parts.
This article will delve into the factors that influence head gasket repair time, the steps involved in the process, and the average time estimates you can expect. We’ll also explore preventive measures to help avoid this issue in the first place.
Buckle up, because we’re about to get technical!
Factors Influencing Head Gasket Repair Time
The time required to repair a head gasket can vary significantly depending on several factors. Understanding these factors can help you estimate the repair time and prepare for potential costs and inconvenience.
Engine Type, How long does it take to repair head gasket
The type of engine plays a crucial role in determining the repair time. For instance, gasoline engines generally have simpler designs compared to diesel engines, which often require more specialized tools and techniques. This difference in complexity can impact the time needed for disassembly, inspection, and reassembly.
- Gasoline Engines:Typically, gasoline engines have shorter repair times due to their simpler design and easier accessibility.
- Diesel Engines:Diesel engines, with their higher compression ratios and more robust components, often require more time for repair.
Severity of Damage
The extent of the head gasket damage is a primary factor influencing repair time. Minor leaks might only require a simple repair, while severe damage could necessitate a more extensive overhaul.
- Minor Leaks:Minor leaks may only require replacing the head gasket and potentially resurfacing the cylinder head. This can be a relatively quick repair.
- Severe Damage:Severe damage, such as a blown head gasket, may involve removing the cylinder head, inspecting for warping or damage, and potentially replacing other components. This can significantly increase the repair time.
Accessibility
The accessibility of the engine components can significantly affect repair time. Engines in some vehicles are more easily accessible than others, which can influence the time needed for disassembly and reassembly.
- Easy Access:Engines with easily accessible components, such as those in front-wheel drive vehicles, often have shorter repair times.
- Limited Access:Engines in rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive vehicles, especially those with complex engine configurations, can be more challenging to work on, leading to longer repair times.
Availability of Parts
The availability of replacement parts can also impact repair time. If the required parts are readily available, the repair can proceed quickly. However, if parts are not readily available, it may take longer to obtain them, delaying the repair.
- Common Parts:Common parts for popular vehicles are typically readily available, leading to shorter repair times.
- Rare or Specialized Parts:Parts for less common vehicles or specialized components may require ordering and shipping, potentially extending the repair time.
Vehicle Make and Model
The make and model of the vehicle can influence repair time due to variations in engine design, accessibility, and the availability of repair information.
- Popular Models:Popular vehicle models often have readily available repair information and parts, potentially leading to shorter repair times.
- Less Common Models:Less common models may require more time to locate repair information and parts, potentially extending the repair time.
Common Head Gasket Failure Symptoms
Several symptoms indicate a potential head gasket failure, each impacting the repair time.
- Coolant Leak:A coolant leak is a common symptom of a head gasket failure. The leak may be minor or significant, affecting the repair time.
- Engine Overheating:A blown head gasket can cause the engine to overheat as coolant leaks into the combustion chamber. This symptom often indicates a more severe issue, requiring a more extensive repair.
- White Smoke:White smoke from the exhaust is another indication of a head gasket failure. This smoke is caused by coolant entering the combustion chamber, often requiring a more involved repair.
- Engine Misfire:A head gasket failure can lead to engine misfires due to the loss of compression in the cylinders. This symptom can indicate a more severe issue, requiring a more extensive repair.
- Oil in Coolant:A head gasket failure can cause oil to leak into the coolant. This symptom often indicates a more severe issue, requiring a more extensive repair.
Steps Involved in Head Gasket Repair
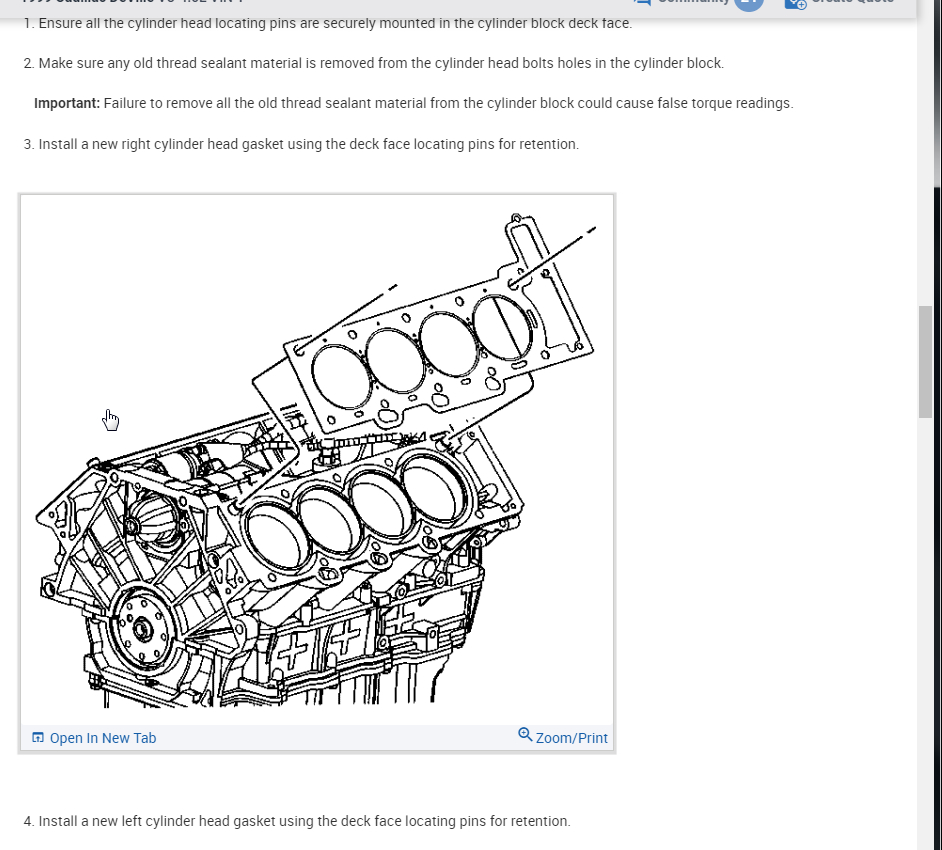
A head gasket repair involves a systematic process of dismantling, inspecting, repairing, and reassembling the engine components. This procedure requires meticulous attention to detail, proper tools, and adherence to manufacturer specifications.
Engine Removal
The engine removal process typically begins with disconnecting the battery to prevent electrical hazards. The next step involves disconnecting various hoses, wires, and components connected to the engine, such as the radiator hoses, throttle cable, fuel lines, and electrical connectors.
Once the engine is sufficiently detached, it is carefully lifted using a hoist or engine crane and placed on a stand for further inspection and repair.
Head Surface Preparation
Before the head gasket can be replaced, the cylinder head and block surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned and inspected for any damage. This involves removing any debris, gasket remnants, or corrosion. The surfaces are then carefully inspected for warping, cracks, or other imperfections.
If any damage is found, the cylinder head may need to be resurfaced or replaced.
Gasket Replacement
The head gasket is the crucial component that seals the combustion chamber from the cooling system. Replacing a damaged head gasket involves carefully removing the old gasket and applying a new one. The new gasket must be properly positioned and torqued to ensure a leak-proof seal.
Reassembly
Once the head gasket is replaced, the cylinder head is reattached to the block, ensuring that the bolts are properly torqued according to the manufacturer’s specifications. The engine is then reassembled, ensuring that all components are correctly installed and connected.
Tools and Equipment
A comprehensive set of tools and equipment is essential for a successful head gasket repair. These include:
- Torque wrench: To ensure proper tightening of bolts and nuts.
- Socket set: To access and loosen/tighten various bolts and nuts.
- Wrenches: For loosening and tightening bolts and nuts.
- Screwdrivers: For removing and installing screws.
- Pliers: For gripping and manipulating small parts.
- Engine hoist: For lifting and lowering the engine.
- Engine stand: To support the engine during repair.
- Cleaning supplies: For cleaning engine parts.
- Head surface machining equipment: For resurfacing the cylinder head.
- Gasket scraper: For removing old gasket material.
- Sealant: For sealing critical areas during reassembly.
Importance of Proper Torque Specifications and Sealant Application
Adhering to proper torque specifications is crucial for a successful head gasket repair. Incorrect torque can lead to leaks, head gasket failure, or even engine damage. Torque specifications are provided by the manufacturer and should be followed precisely. Sealant application is another critical aspect of head gasket repair.
Sealant is used to seal critical areas, such as the cylinder head and block mating surfaces. Applying the sealant correctly ensures a leak-proof seal and prevents fluid leaks.
Head Surface Machining
If the cylinder head is warped or damaged, it needs to be resurfaced to ensure a proper seal with the block. This process involves using a specialized machine to mill the head surface, creating a perfectly flat and smooth surface.
Proper head surface machining is essential for a successful head gasket repair.
Average Repair Time Estimates

Repairing a head gasket can take a varying amount of time, depending on several factors. The complexity of the repair, the vehicle’s make and model, and the mechanic’s expertise all play a role in determining the duration.
Estimated Repair Times for Different Head Gasket Repair Scenarios
The severity of the head gasket failure significantly impacts the repair time. Here’s a table outlining estimated repair times for different scenarios:| Scenario | Estimated Repair Time ||—|—|| Minor leak (no overheating) | 8-12 hours || Major leak (overheating) | 12-18 hours || Head gasket replacement with additional repairs (e.g., warped head) | 18-24 hours || Engine rebuild (severe damage) | 24+ hours |
Estimated Repair Times for Various Vehicle Makes and Models
The vehicle’s make and model can also influence the repair time. Certain vehicles have more complex engine designs, requiring longer repair times.| Vehicle Make and Model | Estimated Repair Time ||—|—|| Honda Civic (2006-2011) | 10-14 hours || Toyota Camry (2012-2017) | 12-16 hours || Ford F-150 (2015-2020) | 14-18 hours || Chevrolet Silverado (2014-2019) | 16-20 hours |
Comparison of Repair Times for Different Repair Shops and Mechanics
The experience and efficiency of the repair shop and mechanic can significantly impact the repair time. Some shops may have specialized equipment and technicians, allowing them to complete the repair faster.| Repair Shop | Estimated Repair Time ||—|—|| Independent Mechanic | 12-18 hours || Dealership | 14-20 hours || Specialized Head Gasket Repair Shop | 10-16 hours |
Factors Influencing Repair Time Estimates
Several factors can influence the estimated repair time, including:
Vehicle accessibility
Some vehicles have engines that are more difficult to access, requiring more time for disassembly and reassembly.
Complexity of the repair
Replacing a head gasket on a vehicle with a complex engine design may take longer than a simpler engine.
Availability of parts
If the required parts are not readily available, it may delay the repair.
Mechanic’s experience
A more experienced mechanic may be able to complete the repair faster than a less experienced one.
Shop workload
If the repair shop is busy, it may take longer to schedule and complete the repair.
Preventive Measures for Head Gasket Issues
A proactive approach to engine maintenance is crucial for preventing head gasket failures. By addressing potential issues before they escalate, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your engine and avoid costly repairs.
Regular Engine Maintenance
Regular engine maintenance plays a vital role in preventing head gasket failures. By adhering to a schedule of routine inspections and service, you can identify and address potential problems before they lead to serious damage.
- Oil Changes:Regularly changing the engine oil helps maintain lubrication, reducing friction and wear on engine components, including the head gasket.
- Coolant Flushes:Coolant helps regulate engine temperature, preventing overheating. Regularly flushing the cooling system ensures proper coolant flow and prevents corrosion, which can weaken the head gasket.
- Timing Belt/Chain Inspection:A worn or broken timing belt or chain can cause engine damage, including head gasket failure. Inspecting and replacing them according to the manufacturer’s recommendations is crucial.
Common Causes of Head Gasket Failure and Preventive Measures
Understanding the common causes of head gasket failure allows you to take preventive measures to mitigate the risk.
- Overheating:Overheating is a primary cause of head gasket failure. When the engine overheats, the pressure inside the combustion chamber increases, putting stress on the head gasket. To prevent overheating, ensure the cooling system is functioning properly, including the radiator, thermostat, water pump, and fan.
- Improper Torque:The head bolts must be tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure a proper seal. Incorrect torque can lead to leaks and head gasket failure. Consult the vehicle’s repair manual for the correct torque settings.
- Contamination:Contamination of the cooling system with oil, debris, or rust can weaken the head gasket. Regularly flushing the cooling system and using the correct coolant can prevent this.
- Age and Wear:Head gaskets, like any engine component, are subject to wear and tear over time. Even with proper maintenance, head gaskets can eventually fail due to age. Regular inspections and replacement as needed can help prevent premature failure.
Role of Coolant and Oil Levels
Maintaining proper coolant and oil levels is crucial for head gasket health.
- Coolant:Coolant plays a vital role in regulating engine temperature. Low coolant levels can lead to overheating, putting stress on the head gasket. Regularly check the coolant level and top it off as needed.
- Oil:Oil lubricates engine components, reducing friction and wear. Low oil levels can lead to increased friction and heat, potentially damaging the head gasket. Regularly check the oil level and top it off as needed.
Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Here is a checklist of preventive maintenance steps to help prevent head gasket issues:
- Regular Oil Changes:Change the oil according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Coolant Flush:Flush the cooling system every 2-3 years or as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Timing Belt/Chain Inspection:Inspect and replace the timing belt or chain according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Coolant Level Check:Regularly check the coolant level and top it off as needed.
- Oil Level Check:Regularly check the oil level and top it off as needed.
- Head Gasket Inspection:Inspect the head gasket for leaks or signs of wear during regular maintenance.
Potential Complications and Risks
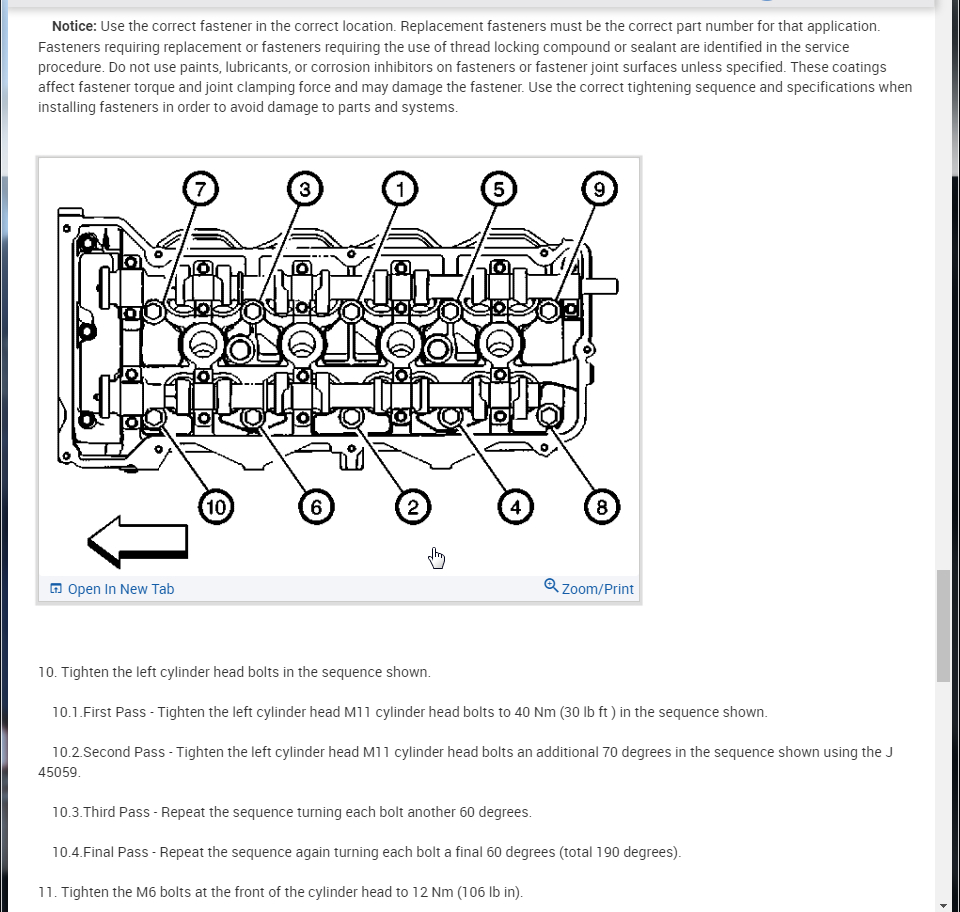
While head gasket repair is a common automotive procedure, it can sometimes lead to complications if not performed correctly. Understanding these potential issues is crucial for making informed decisions regarding your vehicle’s repair.
Improper repair techniques can result in further damage to the engine, leading to costly and time-consuming repairs. It’s important to be aware of the potential risks associated with head gasket repair and to seek professional help for complex repairs.
Potential Complications During Head Gasket Repair
Several factors can complicate head gasket repair, potentially leading to additional issues or the need for further repairs. These complications can arise from various sources, including improper installation, pre-existing engine damage, or unforeseen circumstances during the repair process.
- Damaged Cylinder Head:The cylinder head might be warped or cracked, requiring replacement or machining.
- Damaged Engine Block:The engine block could be damaged, requiring replacement or repair.
- Improper Torque Application:Incorrectly tightening the head bolts can lead to cylinder head warping or damage to the engine block.
- Cooling System Issues:Problems with the cooling system, such as a clogged radiator or a faulty thermostat, can contribute to head gasket failure.
- Oil Contamination:Improper sealing of the head gasket can result in oil leaking into the cooling system or vice versa.
Risks Associated with Improper Repair Techniques
Improper repair techniques can lead to various risks, including:
- Further Engine Damage:Incorrectly repairing a head gasket can worsen existing damage or cause new problems, potentially leading to engine failure.
- Increased Repair Costs:Improper repairs often require additional work to rectify the mistakes, leading to higher repair costs.
- Safety Hazards:A poorly repaired head gasket can cause overheating, leading to engine damage and potentially unsafe driving conditions.
Common Mistakes Made During Head Gasket Repair
Common mistakes during head gasket repair can lead to complications and increase the risk of further engine damage. These mistakes often stem from a lack of experience or improper procedures.
- Insufficient Cleaning:Failing to thoroughly clean the cylinder head and engine block surfaces before installing the new gasket can lead to leaks.
- Incorrect Gasket Selection:Using the wrong type of head gasket can lead to improper sealing and leaks.
- Improper Torque Sequence:Tightening the head bolts in the wrong sequence can cause uneven pressure distribution and damage to the cylinder head or engine block.
- Over-tightening Head Bolts:Excessively tightening the head bolts can warp the cylinder head or damage the engine block.
Importance of Seeking Professional Help for Complex Repairs
For complex head gasket repairs, it’s crucial to seek professional help from a qualified mechanic. Experienced mechanics have the knowledge, tools, and expertise to diagnose and repair head gasket issues effectively, minimizing the risk of complications and ensuring a proper repair.
Outcome Summary: How Long Does It Take To Repair Head Gasket
Repairing a head gasket can be a bit of a headache, but understanding the factors involved can help you plan ahead. Remember, regular maintenance is key to preventing these issues, and when it comes to a complex repair like this, it’s always best to seek professional help.
So, keep your engine running smoothly, and you’ll be cruising down the road in no time!
FAQ Corner
What are the signs of a blown head gasket?
Common signs include white smoke from the exhaust, coolant leaking, engine overheating, and a loss of engine power.
Is it possible to drive with a blown head gasket?
It’s not recommended to drive with a blown head gasket as it can lead to further damage to the engine.
How much does a head gasket repair cost?
The cost varies depending on the vehicle, the severity of the damage, and the labor rates in your area. Expect it to be a substantial repair.
Can I do a head gasket repair myself?
While some DIYers attempt it, it’s a complex repair that requires specialized tools and experience. It’s best to leave it to a professional mechanic.