What is BP 6-120 mean in wheels? This cryptic code isn’t some secret message from a car enthusiast’s club, but a crucial piece of information that determines the fit and function of your wheels. It’s all about bolt pattern, and getting it right can mean the difference between a smooth ride and a bumpy, potentially dangerous one. Understanding BP 6-120 is key to ensuring your wheels are properly matched to your vehicle, ensuring a safe and comfortable driving experience.
Think of it like this: Imagine trying to fit a square peg into a round hole. That’s essentially what happens if you use wheels with the wrong bolt pattern. The wheels won’t mount securely, potentially leading to wobbly wheels, premature wear and tear, or even catastrophic failure. That’s why understanding BP 6-120 is so important, and we’re about to break it down for you.
Understanding BP 6-120 in Wheel Terminology: What Is Bp 6-120 Mean In Wheels

When you see “BP 6-120” on a wheel, it’s a crucial piece of information that helps ensure the wheel is compatible with your vehicle. This designation refers to the wheel’s bolt pattern, a critical factor in wheel fitment.
Understanding the Components of BP 6-120
The term “BP 6-120” breaks down into three key components:
- BP: Stands for “Bolt Pattern,” indicating the arrangement of the lug holes on the wheel where the lug nuts are tightened to secure the wheel to the vehicle’s hub.
- 6: Represents the number of lug holes on the wheel. This means the wheel has six evenly spaced lug holes.
- 120: Refers to the bolt circle diameter (BCD) in millimeters. This is the diameter of the imaginary circle that passes through the center of each lug hole. A 120mm BCD means the distance between the centers of two adjacent lug holes is 120 millimeters.
The Importance of Bolt Pattern for Wheel Compatibility
The bolt pattern is a critical factor for wheel compatibility. To ensure a safe and proper fit, the wheel’s bolt pattern must match the bolt pattern of the vehicle’s hub. If the bolt patterns don’t match, the wheel won’t mount securely, potentially leading to wheel failure and serious safety hazards.
The wheel’s bolt pattern must match the vehicle’s hub bolt pattern for safe and proper fitment.
Wheel Size and Dimensions
“BP 6-120” is a bolt pattern designation, but it’s only part of the story when it comes to wheel size. Understanding the relationship between bolt pattern and other wheel dimensions like diameter, width, and offset is crucial for choosing the right wheels for your vehicle.
Wheel Diameter and Width
Wheel diameter and width are two fundamental dimensions that directly influence the overall size of a wheel. Wheel diameter, measured in inches, refers to the distance across the wheel from one rim edge to the other, including the tire. Wheel width, also measured in inches, refers to the distance between the inner and outer edges of the wheel rim.
- Wheel Diameter: A larger diameter wheel typically provides a larger tire, offering advantages in terms of ride comfort, off-road capability, and visual appeal. However, larger wheels can also impact acceleration and fuel efficiency.
- Wheel Width: A wider wheel rim allows for a wider tire, enhancing grip and stability, especially during cornering. Wider tires also provide a larger contact patch, improving traction and handling. However, wider tires can negatively impact steering responsiveness and increase rolling resistance.
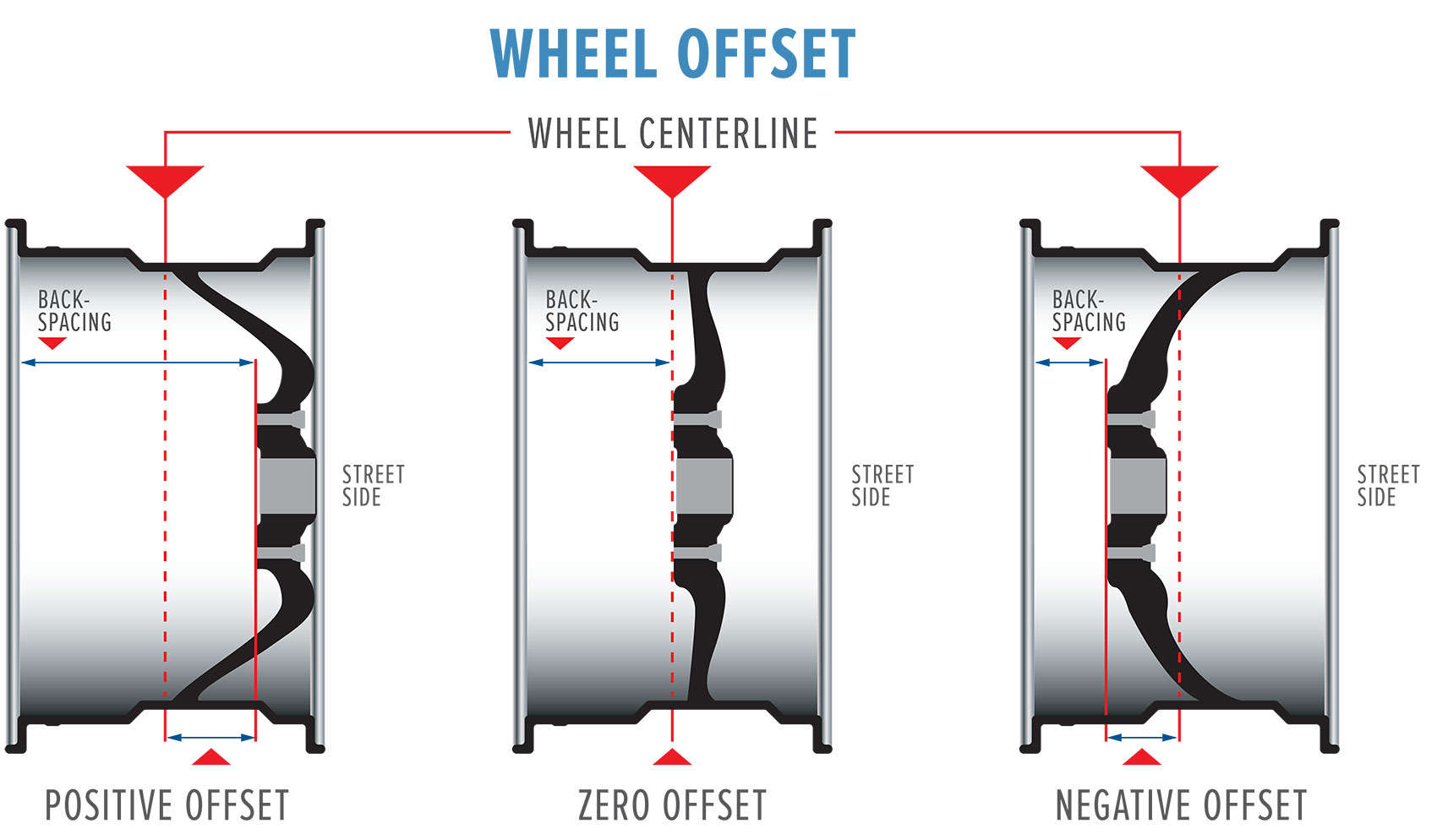
Offset
Offset, measured in millimeters, refers to the distance between the wheel’s mounting surface and the center of the wheel rim. It influences how far the wheel sits in or out from the vehicle’s body.
- Positive Offset: A positive offset means the mounting surface is further out from the center of the wheel, resulting in the wheel being pushed inward towards the vehicle.
- Negative Offset: A negative offset means the mounting surface is closer to the center of the wheel, resulting in the wheel being pushed outward away from the vehicle.
Bolt Pattern and PCD
The term “BP 6-120” refers to a specific bolt pattern used in wheels, indicating the arrangement of lug holes. Understanding the bolt pattern is crucial for ensuring proper wheel fitment and safety.
Bolt Pattern Explained
The bolt pattern, also known as the “PCD” (Pitch Circle Diameter), defines the circle on which the lug holes are located. It’s represented by two numbers: the number of lug holes and the diameter of the circle. In the case of “BP 6-120,” it means the wheel has six lug holes spaced evenly on a circle with a diameter of 120mm.
Importance of Matching Bolt Pattern
Matching the bolt pattern is essential for safe and secure wheel installation. The lug bolts or studs need to align perfectly with the lug holes on the wheel and the hub of the vehicle. If the bolt pattern doesn’t match, the wheel won’t sit properly on the hub, leading to potential safety risks.
Implications of Incompatible Bolt Pattern
Using an incompatible bolt pattern can have serious consequences:
- Wheel Wobble: The wheel might not sit flush on the hub, causing vibration and instability while driving.
- Loose Wheel: The lug nuts might not tighten properly, increasing the risk of the wheel detaching from the vehicle while driving.
- Hub Damage: Misaligned lug holes can damage the hub, requiring costly repairs.
- Uneven Wear: Improper wheel alignment can lead to uneven tire wear, reducing tire life and handling performance.
Wheel Applications and Compatibility
Wheels with a BP 6-120 bolt pattern are quite common in the automotive world, particularly for specific vehicle types. Understanding the applications and compatibility of these wheels is crucial for ensuring a safe and proper fit for your vehicle.
Vehicles Utilizing BP 6-120 Wheels
Wheels with a BP 6-120 bolt pattern are commonly found on a variety of vehicles, including:
- Ford Vehicles: Ford has widely adopted the BP 6-120 pattern for many of its vehicles, including popular models like the Mustang, Focus, Fiesta, and Escape. This pattern is often found on both standard and performance-oriented models.
- Lincoln Vehicles: Lincoln, the luxury brand owned by Ford, also uses the BP 6-120 bolt pattern on many of its vehicles, including the MKZ, MKX, and Navigator.
- Other Manufacturers: While Ford and Lincoln are the most prominent users of the BP 6-120 bolt pattern, some other manufacturers, such as Mazda and Volvo, have also incorporated this pattern on specific models.
Suitability for Driving Conditions and Terrains, What is bp 6-120 mean in wheels
The BP 6-120 bolt pattern is generally suitable for a wide range of driving conditions and terrains. The size and spacing of the bolts provide adequate strength and stability for everyday driving, as well as for light off-road adventures. However, it’s important to consider the overall wheel and tire combination when assessing suitability for specific terrains:
- On-Road Performance: Wheels with a BP 6-120 pattern are generally well-suited for on-road driving, providing a good balance between performance and comfort.
- Light Off-Road: While not ideal for extreme off-roading, wheels with a BP 6-120 pattern can handle light off-road conditions, such as gravel roads and unpaved trails, especially when paired with tires designed for such terrains.
- Extreme Off-Road: For extreme off-roading, a different bolt pattern with a larger diameter and higher bolt count might be more suitable for increased strength and durability.
Comparison with Other Bolt Patterns
The BP 6-120 bolt pattern is not the only one used in the automotive industry. Other common bolt patterns include:
- BP 5×114.3 (4.5 inches): This pattern is widely used by Japanese and Korean manufacturers, including Toyota, Honda, Nissan, and Hyundai. It offers a similar level of strength and stability to the BP 6-120 pattern.
- BP 5×120 (4.72 inches): This pattern is popular among European manufacturers, including BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Audi. It provides a larger contact area for the bolts, enhancing strength and stability.
The BP 6-120 bolt pattern stands out for its versatility and compatibility with a range of vehicle types. While it may not be suitable for extreme off-roading, it provides a good balance of performance and strength for everyday driving and light off-road adventures.
Wheel Maintenance and Safety

Keeping your wheels in top condition is crucial for safe driving. Regular inspections and maintenance are essential for ensuring your wheels remain strong and reliable, capable of handling the stresses of driving.
Inspecting and Maintaining Wheels with BP 6-120
Regularly inspecting your wheels can help you identify potential issues before they become serious. Here’s a quick guide to ensure your wheels are in good condition:
- Visual Inspection: Check for any visible damage, such as cracks, dents, or scratches. These can compromise the structural integrity of the wheel. Also, look for signs of corrosion or rust.
- Tire Pressure: Ensure your tire pressure is within the recommended range for your vehicle. Underinflated tires can lead to premature wear and tear on the wheels, while overinflated tires can make the ride harsher and increase the risk of a blowout.
- Wheel Nuts: Regularly check the tightness of your wheel nuts. Loose nuts can cause the wheel to detach, leading to a serious accident.
- Bearing Inspection: Listen for any unusual noises coming from your wheels, such as grinding or clicking. These sounds could indicate a problem with the wheel bearings.
Proper Torque Settings for Wheel Nuts
Using the correct torque setting for your wheel nuts is critical for safety. Under-torqued nuts can loosen over time, leading to wheel detachment, while over-torqued nuts can damage the wheel or studs.
The recommended torque setting for your wheel nuts can be found in your vehicle’s owner’s manual or on a sticker located on the driver’s side doorjamb.
- Torque Wrench: Use a torque wrench to tighten the wheel nuts to the specified torque setting. Torque wrenches provide a precise and controlled tightening force, ensuring the nuts are properly secured.
- Lubrication: Applying a small amount of anti-seize lubricant to the threads of the wheel studs can prevent them from seizing and make it easier to remove the nuts in the future.
- Cross-Pattern Tightening: Tighten the wheel nuts in a cross-pattern to ensure even pressure distribution across the wheel. This helps to prevent the wheel from warping or becoming misaligned.
Risks Associated with Damaged or Worn-Out Wheels
Driving with damaged or worn-out wheels can be extremely dangerous. Here are some of the potential risks:
- Wheel Detachment: A damaged or cracked wheel can detach from the vehicle, leading to a catastrophic accident.
- Tire Blowout: A damaged wheel can cause a tire blowout, which can result in loss of control of the vehicle.
- Uneven Tire Wear: A damaged wheel can cause uneven tire wear, reducing tire life and compromising vehicle handling.
- Suspension Damage: A damaged wheel can put stress on the suspension components, leading to premature wear and tear or even failure.
So, the next time you’re looking at wheels, don’t just focus on the size and style. Pay attention to the BP 6-120 designation, which tells you everything you need to know about the bolt pattern. It’s the key to ensuring your wheels are a perfect fit for your vehicle, giving you a safe, comfortable, and enjoyable ride. Remember, the right wheels can make all the difference in your driving experience.
FAQ Overview
What does the “6” in BP 6-120 represent?
The “6” refers to the number of lug studs or bolts on the wheel.
What are the implications of using wheels with a different bolt pattern?
Using wheels with an incompatible bolt pattern can lead to improper wheel mounting, potential wheel failure, and safety hazards.
How can I determine the correct bolt pattern for my vehicle?
You can find the bolt pattern information on your vehicle’s owner’s manual, the vehicle’s VIN sticker, or by checking online resources.
Can I use wheel spacers to accommodate a different bolt pattern?
While wheel spacers can sometimes be used to adapt a different bolt pattern, it’s generally not recommended due to potential safety risks and increased stress on the wheel and hub.