How wide is a wheel chair – How wide is a wheelchair? It’s a question that might seem simple, but it’s actually a complex topic with a lot of factors to consider. From regulations and standards to individual needs and accessibility, the width of a wheelchair plays a huge role in how easily someone can move around. We’re diving deep into the world of wheelchair width, exploring the different types, the reasons behind their variations, and the impact it has on everyone’s lives.
Wheelchairs are more than just a means of transportation. They’re a symbol of independence, a lifeline for many, and a reminder of the importance of accessibility. Whether you’re a wheelchair user yourself or just curious about the topic, understanding the ins and outs of wheelchair width is crucial to creating a more inclusive and accessible world for everyone.
Wheelchair Width Standards and Regulations
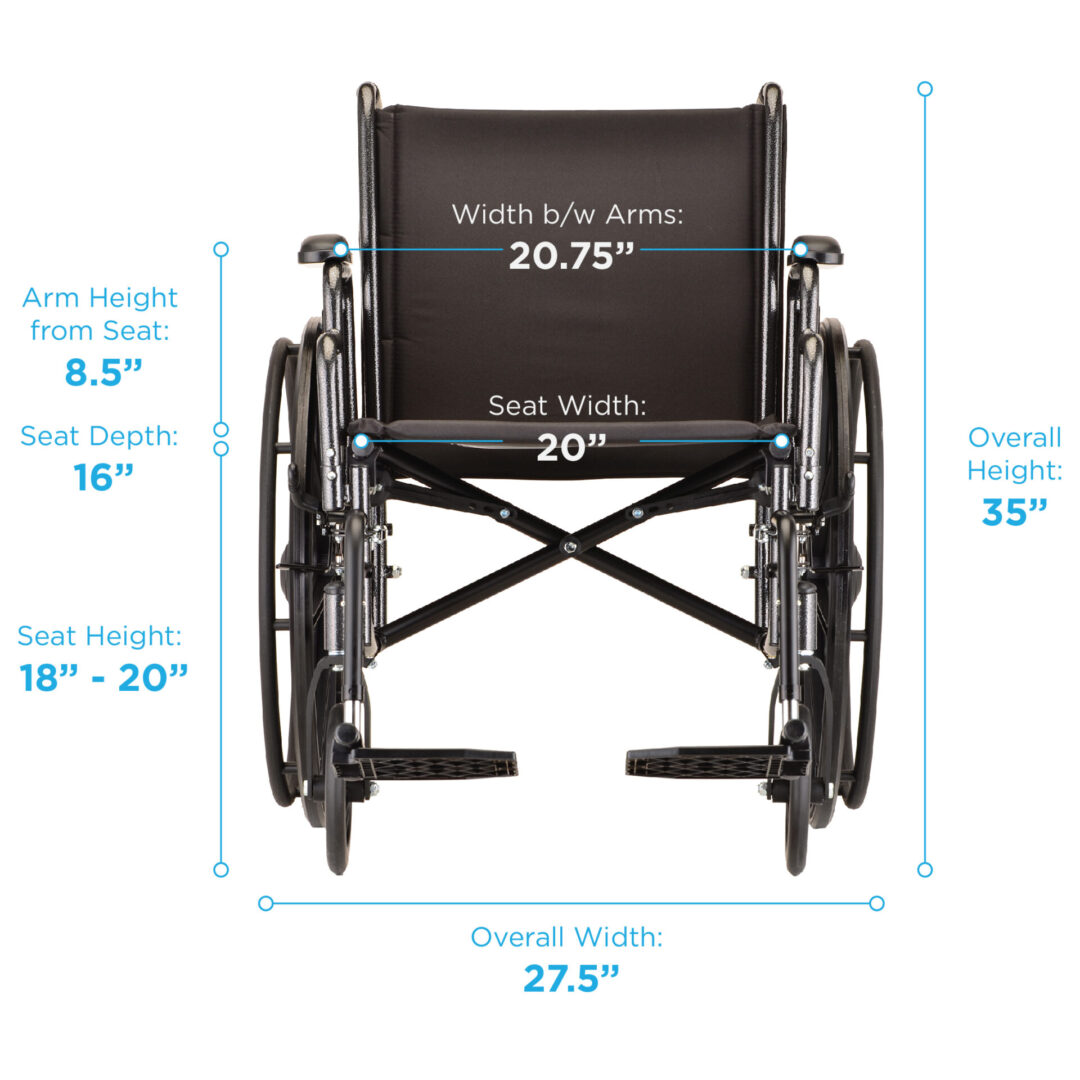
The width of a wheelchair is a crucial factor for its usability and accessibility in public spaces. It directly impacts the ease of movement, maneuverability, and safety of the user. To ensure the seamless integration of wheelchair users into society, international regulations and accessibility guidelines establish standard wheelchair widths, creating a framework for safe and convenient access.
International Standards for Wheelchair Width
Adhering to international standards for wheelchair width is essential for ensuring the safe and convenient use of wheelchairs in public spaces. These standards are developed based on ergonomic principles, considering the needs of wheelchair users and the accessibility of public spaces. The most commonly recognized standard for wheelchair width is 24 inches (61 centimeters). This standard provides ample space for the user to comfortably maneuver and allows for safe passage through doorways, hallways, and other public spaces.
- ISO 7176-1:2008: This international standard defines the minimum dimensions for wheelchairs, including a minimum width of 61 centimeters. This standard is widely adopted globally, ensuring consistency in wheelchair design and accessibility.
- ANSI/RESNA WC19:2019: This standard, developed by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the Rehabilitation Engineering and Assistive Technology Society of North America (RESNA), also sets a minimum width of 24 inches (61 centimeters) for wheelchairs. This standard is widely used in the United States and Canada.
- BS 7001:2008: This British Standard specifies minimum widths for wheelchairs, including a minimum width of 61 centimeters. This standard is used in the United Kingdom and other European countries.
Significance of Wheelchair Width Standards
Compliance with these standards ensures that wheelchair users can access public spaces safely and conveniently. For example, doorways, hallways, and other public spaces are designed with these standard widths in mind, allowing wheelchair users to move freely and independently.
- Safe Passage: Standard wheelchair widths allow for safe passage through doorways, hallways, and other public spaces, reducing the risk of collisions or obstructions.
- Maneuverability: Standard wheelchair widths provide ample space for users to maneuver comfortably, turning, and navigating tight spaces with ease.
- Accessibility: Public spaces designed to accommodate standard wheelchair widths ensure that wheelchair users can access facilities and services without difficulty.
Wheelchair Width Regulations in Specific Countries
Different countries have specific regulations regarding wheelchair width, often building upon international standards and adapting them to local contexts.
- United States: The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requires that all public spaces, including buildings, transportation systems, and public accommodations, be accessible to people with disabilities. This includes specific requirements for wheelchair width, such as doorways, hallways, and restrooms.
- Canada: The Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act (AODA) mandates accessibility standards for public spaces, including requirements for wheelchair width. These standards are similar to those Artikeld in the ADA.
- United Kingdom: The Equality Act 2010 requires that public spaces and services be accessible to people with disabilities. This includes requirements for wheelchair width in public buildings, transportation, and other areas.
- Australia: The Disability Discrimination Act 1992 (DDA) prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities, including ensuring access to public spaces. This act includes specific requirements for wheelchair width in public buildings and transportation.
Wheelchair Types and Their Width Variations: How Wide Is A Wheel Chair
The world of wheelchairs is diverse, encompassing a range of designs tailored to specific needs and functionalities. Each type of wheelchair has its unique width, often influenced by the intended use and the user’s physical characteristics. This section delves into the diverse world of wheelchairs, exploring the variations in width across different types.
Manual Wheelchairs
Manual wheelchairs, propelled by the user’s own strength, are often designed with a focus on maneuverability and lightweight construction. The typical width of a manual wheelchair ranges from 24 to 26 inches, allowing for comfortable and efficient movement through doorways and tight spaces. A narrower width is generally preferred for indoor use, while wider models offer greater stability and support for individuals with larger frames or specific needs.
Power Wheelchairs
Power wheelchairs provide greater independence and mobility for individuals with limited physical strength or endurance. They are typically wider than manual wheelchairs, ranging from 26 to 30 inches. This increased width is attributed to the incorporation of electric motors, batteries, and other components. The broader base provides enhanced stability and maneuverability, especially when navigating uneven terrain or inclines.
Sports Wheelchairs
Sports wheelchairs are specifically designed for competitive athletic activities, such as basketball, tennis, and racing. Their width varies significantly based on the sport and the athlete’s needs. For instance, racing wheelchairs often have a narrow width for aerodynamic advantage, while basketball wheelchairs might be wider to provide a stable platform for maneuvering and pivoting. The choice of width is crucial for optimizing performance and maximizing the athlete’s capabilities.
Specialized Wheelchairs
Specialized wheelchairs are designed to address unique needs and challenges faced by individuals with specific conditions. Examples include:
- Tilt-in-space wheelchairs: These wheelchairs allow the user to recline to a near-horizontal position, promoting comfort and reducing pressure points. They often have a wider base to ensure stability during tilting.
- Stand-up wheelchairs: These wheelchairs allow the user to transition from a seated to a standing position, improving circulation and promoting social interaction. Their width may vary depending on the user’s needs and the specific design features.
- Bariatric wheelchairs: Designed for individuals with larger body sizes, bariatric wheelchairs typically have wider seats and bases to accommodate greater weight and ensure stability.
The width of a wheelchair is a critical factor in determining its maneuverability, stability, and overall functionality.
Factors Influencing Wheelchair Width Selection
Choosing the right wheelchair width is a crucial step in ensuring a comfortable, safe, and independent life for wheelchair users. It involves carefully considering several factors that impact the user’s experience and overall well-being. This section delves into the key considerations that influence wheelchair width selection, emphasizing the importance of a personalized approach to meet individual needs.
User’s Body Size and Shape
The user’s body size and shape are fundamental factors in determining the appropriate wheelchair width. A wheelchair that is too narrow can restrict movement and cause discomfort, while one that is too wide can hinder maneuverability and make it difficult to navigate through doorways and tight spaces.
It’s essential to measure the user’s hips, shoulders, and thighs to ensure adequate space for comfortable seating and movement.
For instance, individuals with wider hips or larger builds may require a wider wheelchair to accommodate their body size comfortably. Conversely, individuals with smaller frames may find a narrower wheelchair more manageable.
Mobility Needs and Activity Level
The user’s mobility needs and activity level are crucial considerations when selecting a wheelchair width. Individuals who are highly active and require frequent maneuvering in tight spaces may benefit from a narrower wheelchair.
A narrower wheelchair can be easier to push and maneuver in crowded areas or through narrow doorways.
Conversely, individuals who are less mobile or primarily use their wheelchair for indoor use may find a wider wheelchair more comfortable and supportive.
Accessibility in Different Environments
Accessibility in different environments is a significant factor in determining the appropriate wheelchair width.
Wheelchair users need to be able to navigate comfortably and safely through doorways, hallways, and other spaces.
A wheelchair that is too wide may not fit through standard doorways or be able to maneuver in tight spaces, such as public restrooms or elevators. Conversely, a wheelchair that is too narrow may not provide sufficient support or stability, particularly for individuals with balance issues or limited mobility.
For instance, a wheelchair user who frequently travels by public transportation may need a wheelchair that meets the accessibility standards of buses, trains, and other public vehicles.
Impact of Wheelchair Width on Accessibility

The width of a wheelchair significantly impacts a user’s ability to navigate various environments, influencing their independence and participation in daily life. While a wider wheelchair can provide increased stability and comfort, it can also create accessibility challenges, restricting movement in tight spaces.
Accessibility Challenges in Various Settings
The width of a wheelchair can pose significant challenges in various settings, impacting a user’s ability to move freely and independently.
- Doorways: Narrow doorways, particularly in older buildings, can present a major obstacle for wheelchair users. A wider wheelchair may not fit through the doorway, requiring the user to maneuver awkwardly or seek alternative routes.
- Hallways: Similarly, narrow hallways can create a difficult experience for wheelchair users, particularly in crowded areas or when navigating around corners. A wider wheelchair might make it impossible to pass another person or object, forcing the user to backtrack or find an alternative route.
- Public Transportation: Public transportation, such as buses and trains, often has limited space for wheelchair users. A wider wheelchair might not fit into designated areas, requiring the user to wait for a different mode of transportation or seek assistance from staff.
Challenges Faced by Wheelchair Users with Limited Space
Wheelchair users with wider chairs often face a range of challenges when navigating tight spaces, including:
- Difficulty in Maneuvering: Wider wheelchairs can be challenging to maneuver in tight spaces, requiring more effort and skill from the user. This can be particularly difficult in crowded areas or when navigating around obstacles.
- Increased Risk of Collisions: The wider profile of a wheelchair can increase the risk of collisions with other people or objects, especially in narrow spaces.
- Limited Access to Facilities: Wider wheelchairs may not fit into certain facilities, such as restrooms or elevators, restricting access to essential services.
- Social Isolation: The challenges associated with navigating tight spaces can lead to social isolation, as wheelchair users may avoid certain environments or activities due to accessibility concerns.
Design Solutions Addressing Accessibility Concerns
To address the accessibility challenges posed by wheelchair width, several design solutions have been implemented:
- Wider Doorways: Building codes and regulations are increasingly requiring wider doorways to accommodate wheelchair users.
- Accessible Routes: Many public spaces now have designated accessible routes with wider hallways and ramps to ensure wheelchair users can move freely.
- Accessible Public Transportation: Public transportation systems are being modified to include wider aisles, designated wheelchair spaces, and accessible boarding ramps.
- Universal Design: Universal design principles aim to create environments that are accessible to everyone, regardless of their abilities. This includes features such as wider doorways, ramps, and accessible restrooms.
Wheelchair Width and Personalization

A wheelchair’s width is not just a matter of fitting through doorways; it’s a critical factor in a user’s comfort, independence, and overall well-being. Personalization in wheelchair width allows users to achieve optimal comfort and functionality, enhancing their quality of life.
Adjustable Features for Wheelchair Width Personalization, How wide is a wheel chair
Customizing a wheelchair’s width involves adjusting various components to achieve the desired fit and maneuverability.
- Adjustable Seat Width: Many wheelchairs feature adjustable seat widths, allowing users to fine-tune the fit to their body size and shape. This is crucial for comfort and stability, preventing pressure points and discomfort during prolonged use.
- Adjustable Armrests: Armrest adjustments are vital for achieving a comfortable seating position and providing proper support. Adjustable width and height ensure optimal positioning and prevent discomfort or pressure on the arms.
- Adjustable Footrests: Footrest adjustments are essential for maintaining proper leg positioning and preventing discomfort. Adjustable width and height allow for optimal foot placement, reducing fatigue and improving circulation.
Role of Specialized Manufacturers
Specialized wheelchair manufacturers play a pivotal role in providing custom-made wheelchairs that cater to individual needs and preferences. These manufacturers work closely with users, therapists, and other healthcare professionals to understand specific requirements and create wheelchairs that are tailored to individual body dimensions, mobility challenges, and lifestyle.
“Custom-made wheelchairs are designed to address specific needs and challenges, offering unparalleled comfort, functionality, and independence.”
So, the next time you see someone in a wheelchair, take a moment to think about the width of their chair and the challenges they might face. It’s not just about the size, it’s about the freedom, independence, and quality of life that a properly sized wheelchair can provide. By understanding the complexities of wheelchair width, we can all contribute to creating a more accessible and inclusive society.
FAQ Resource
What are the different types of wheelchairs?
There are many types of wheelchairs, including manual, power, sports, and specialized wheelchairs. Each type has its own unique features and width variations.
What are the common width standards for wheelchairs?
Wheelchairs typically range in width from 24 to 26 inches, but there are exceptions based on the type of wheelchair and individual needs.
How do I choose the right wheelchair width for me?
It’s important to consider your body size, mobility needs, and the environments you’ll be using the wheelchair in. Consult with a healthcare professional or wheelchair specialist for personalized recommendations.
What are some challenges faced by wheelchair users with limited space?
Wider wheelchairs can make it difficult to navigate through doorways, hallways, and public transportation. This can limit mobility and independence.
How can I make my home more wheelchair-friendly?
Consider widening doorways, removing obstacles, and installing ramps to make your home more accessible for wheelchair users.