How to rotate all wheel drive tires is a crucial maintenance task for owners of AWD vehicles. This process ensures even tire wear, enhances traction, and prolongs the life of your tires. By understanding the differences between AWD and 4WD systems, the various types of AWD setups, and the recommended rotation patterns, you can optimize your vehicle’s performance and safety.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of tire rotation for AWD vehicles, covering the necessary tools, safety precautions, and a step-by-step process for rotating tires correctly. We will also delve into the importance of regular tire maintenance and inspection, ensuring your AWD system remains in optimal condition.
Understanding All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Systems: How To Rotate All Wheel Drive Tires
All-wheel drive (AWD) systems are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles, offering enhanced traction and stability, particularly in challenging road conditions. AWD systems distribute power to all four wheels, providing greater control and grip compared to front-wheel drive (FWD) or rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles.
Differences between AWD and 4WD Systems
AWD and 4WD systems are often used interchangeably, but there are key differences between them.
- AWD systems are designed for everyday driving and typically engage all four wheels automatically when needed, such as during acceleration, braking, or when encountering slippery surfaces. They are typically more fuel-efficient than 4WD systems.
- 4WD systems are designed for off-road driving and often require the driver to manually engage the four-wheel drive mode. They typically have a lower gear ratio for greater torque and traction, making them suitable for rough terrain.
Benefits of AWD for Tire Rotation
AWD systems provide several benefits for tire rotation, including:
- Even Wear: AWD systems distribute power more evenly across all four wheels, resulting in more even tire wear. This is because all four tires are actively involved in propelling the vehicle, unlike FWD or RWD vehicles where the front or rear tires experience greater wear due to the majority of power being sent to them.
- Enhanced Safety: AWD systems improve traction and stability, particularly on slippery surfaces. This enhanced grip reduces the risk of skidding or losing control, promoting safer driving conditions.
- Longer Tire Life: Even wear patterns extend the lifespan of tires, reducing the need for premature replacements and saving costs in the long run.
Types of AWD Systems and Their Tire Rotation Requirements
There are various types of AWD systems, each with its own tire rotation requirements.
- Full-Time AWD: This type of system engages all four wheels constantly, even during normal driving conditions. Full-time AWD systems typically use a center differential to distribute power between the front and rear axles.
- Part-Time AWD: This system only engages all four wheels when needed, such as when the vehicle senses a loss of traction. Part-time AWD systems often have a lever or button to manually engage the four-wheel drive mode.
- Automatic AWD: This system automatically engages all four wheels when necessary, using sensors to detect wheel slip or other factors.
It is important to consult the owner’s manual for specific tire rotation recommendations for your vehicle. The manual will Artikel the recommended tire rotation pattern and frequency for your particular AWD system. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations ensures optimal tire wear and performance.
Tire Rotation Patterns for AWD Vehicles
Tire rotation is an essential maintenance task for all vehicles, including those with all-wheel drive (AWD). Rotating your tires helps ensure even wear and tear, prolonging their lifespan and improving overall vehicle performance. However, AWD systems introduce unique considerations that require specific rotation patterns.
AWD Tire Rotation Patterns
AWD systems distribute power to all four wheels, providing enhanced traction and stability, especially in challenging conditions. However, this power distribution can lead to uneven tire wear, particularly on the front wheels. Therefore, understanding the different tire rotation patterns for AWD vehicles is crucial.
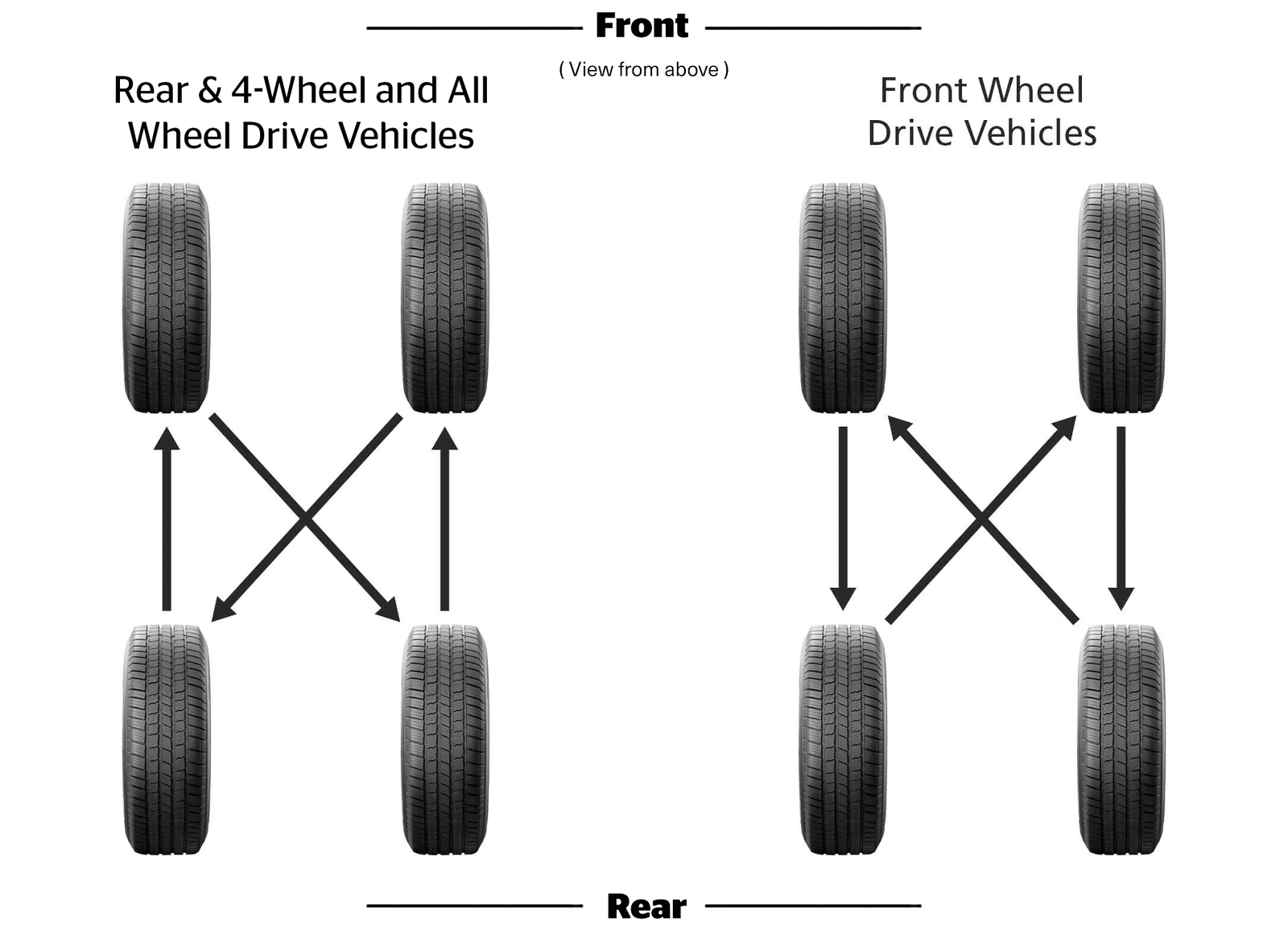
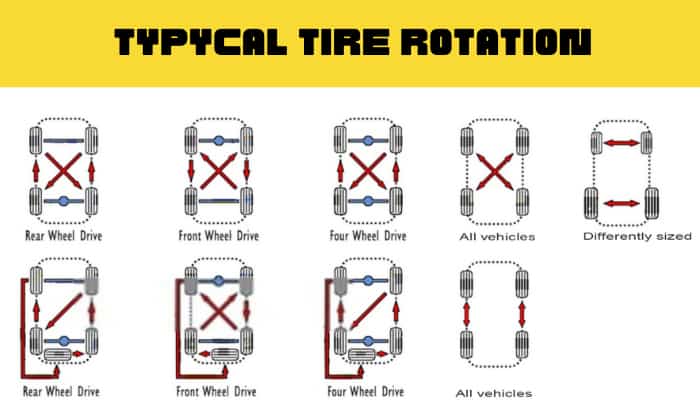
- X-Pattern Rotation: This pattern involves rotating the tires in a diagonal “X” shape. The front right tire moves to the rear left, the front left tire moves to the rear right, the rear right tire moves to the front left, and the rear left tire moves to the front right. This pattern is commonly recommended for AWD vehicles, as it helps distribute wear evenly across all four tires.
- Front-to-Rear Rotation: This pattern involves rotating the front tires to the rear positions and vice versa. While simpler than the X-pattern, it may not be suitable for all AWD vehicles, especially those with a limited-slip differential or torque-vectoring systems. This pattern can lead to uneven wear if the front and rear tires have different tread patterns or wear characteristics.
- Cross Rotation: This pattern involves moving the front tires to the opposite sides of the vehicle and the rear tires to the opposite sides. This pattern is not recommended for AWD vehicles, as it can disrupt the power distribution and lead to uneven wear, especially on the front tires.
Recommended Rotation Pattern for Your AWD Vehicle
The best tire rotation pattern for your AWD vehicle depends on the specific model and its AWD system. Consult your owner’s manual for the recommended rotation pattern. If the manual doesn’t provide specific instructions, consult with a qualified mechanic or tire specialist. They can assess your vehicle and recommend the appropriate rotation pattern.
Pros and Cons of Each Rotation Pattern
- X-Pattern Rotation:
- Pros: Even wear across all four tires, suitable for most AWD vehicles, helps maintain optimal traction and handling.
- Cons: Requires more time and effort to complete, may not be suitable for all AWD vehicles.
- Front-to-Rear Rotation:
- Pros: Simple and quick to perform, suitable for some AWD vehicles.
- Cons: May lead to uneven wear if front and rear tires have different tread patterns, may not be suitable for all AWD vehicles.
- Cross Rotation:
- Pros: Not applicable for AWD vehicles.
- Cons: Can disrupt power distribution, lead to uneven wear, not recommended for AWD vehicles.
Tools and Equipment for Tire Rotation
Performing a tire rotation on an AWD vehicle requires a few essential tools and equipment to ensure a safe and efficient process. This section will cover the tools you need, safety precautions, and a step-by-step guide on safely jacking up your AWD vehicle.
Safety Precautions
Safety is paramount when working with tires and tools. Here are some essential safety precautions to observe:
- Always use a jack stand to support the vehicle once it is lifted. Never rely solely on the jack to hold the vehicle.
- Engage the parking brake and chock the wheels that are not being lifted. This prevents the vehicle from rolling.
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from flying debris.
- Avoid working under the vehicle while it is raised.
- If you are unsure about any part of the process, consult a qualified mechanic.
Jacking Up an AWD Vehicle
To safely jack up an AWD vehicle, follow these steps:
- Choose a level surface: Ensure the vehicle is parked on a level, firm surface.
- Engage the parking brake: Apply the parking brake to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
- Chock the wheels: Place chocks behind the wheels that are not being lifted.
- Locate the jack points: Consult your owner’s manual or refer to the jack points marked on the vehicle’s undercarriage.
- Position the jack: Position the jack securely under the designated jack point.
- Begin lifting: Slowly raise the vehicle until the tire is slightly off the ground.
- Place the jack stand: Once the tire is off the ground, place a jack stand under the vehicle’s frame near the jack point. Lower the vehicle onto the jack stand.
- Repeat for other tires: If you need to lift another tire, repeat the process.
Step-by-Step Tire Rotation Process

Rotating your tires on an all-wheel drive (AWD) vehicle is crucial for even wear and tear, maximizing tire life, and ensuring optimal performance. Following the correct rotation pattern is essential for maintaining the AWD system’s functionality.
Tire Rotation Pattern for AWD Vehicles
The tire rotation pattern for AWD vehicles differs from that of two-wheel drive vehicles. The most common pattern for AWD vehicles is the “X” pattern. This pattern involves moving the front tires to the rear and the rear tires to the front, crossing them over. This ensures that the tires are rotated in a way that balances wear and tear across all four wheels.
- Front-Left Tire: Moves to the Rear-Right position.
- Front-Right Tire: Moves to the Rear-Left position.
- Rear-Left Tire: Moves to the Front-Right position.
- Rear-Right Tire: Moves to the Front-Left position.
This pattern ensures that the tires are rotated in a way that balances wear and tear across all four wheels, promoting even wear and tear, maximizing tire life, and ensuring optimal performance.
Step-by-Step Guide to Rotating Tires on an AWD Vehicle, How to rotate all wheel drive tires
Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide for rotating tires on an AWD vehicle:
- Gather the Necessary Tools and EquipmentBefore you begin, make sure you have the following:
- A jack and jack stands
- A torque wrench
- A lug wrench
- A tire pressure gauge
- A marker or chalk
- Park the Vehicle on a Level SurfaceEnsure the vehicle is parked on a level surface and engage the parking brake.
- Loosen the Lug NutsUsing the lug wrench, loosen the lug nuts on all four wheels. Do not remove them completely at this stage.
- Jack Up the VehiclePlace the jack under the designated jacking point for the front-left tire. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the specific jacking points. Slowly raise the vehicle until the front-left tire is slightly off the ground.
- Remove the Front-Left TireOnce the tire is off the ground, remove the lug nuts completely and carefully remove the front-left tire.
- Mark the TireUse a marker or chalk to mark the front-left tire. This will help you track the tire’s rotation throughout the process.
- Install the Rear-Right TireCarefully place the rear-right tire onto the front-left hub, aligning the tire with the hub’s mounting holes. Tighten the lug nuts by hand until the tire is secure.
- Lower the VehicleLower the vehicle until the front-left tire is back on the ground.
- Tighten the Lug NutsUsing the torque wrench, tighten the lug nuts to the specified torque for your vehicle. This information can be found in your owner’s manual.
- Repeat Steps 4-10 for the Remaining TiresFollow the same steps to rotate the remaining tires, ensuring you follow the correct “X” pattern.
- Check Tire PressureAfter rotating all four tires, check the tire pressure using the tire pressure gauge and adjust as needed.
- Test DriveAfter rotating the tires, take the vehicle for a short test drive to ensure everything is running smoothly.
Maintenance and Inspection
Maintaining the tires on your AWD vehicle is crucial for optimal performance, safety, and longevity. Regular inspections and maintenance ensure your tires are in top condition, providing the necessary grip and traction for a smooth and safe ride.
Tire Wear Patterns
Understanding tire wear patterns can help you identify potential issues with your AWD vehicle. Uneven wear can indicate problems with wheel alignment, suspension components, or even tire pressure.
- Outer Edge Wear: This indicates overinflation, which can lead to a harsh ride and reduced traction.
- Inner Edge Wear: This indicates underinflation, which can lead to a bouncy ride and increased tire wear.
- Center Wear: This indicates overinflation, which can lead to a harsh ride and reduced traction.
- Feathering: This indicates improper wheel alignment, which can cause uneven wear and affect handling.
- Cupping: This indicates worn suspension components, which can cause uneven wear and affect handling.
Tire Pressure
Maintaining the correct tire pressure is essential for optimal AWD performance and safety. Incorrect tire pressure can lead to reduced traction, uneven wear, and compromised handling.
Tire pressure should be checked regularly, ideally when the tires are cold. Refer to the sticker on your driver’s side doorjamb or your owner’s manual for the recommended tire pressure for your vehicle.
Rotating tires on your AWD vehicle is an essential part of proper maintenance. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can ensure even tire wear, enhance traction, and prolong the life of your tires. Remember to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific recommendations and to always prioritize safety when working with tires and tools.
FAQ Compilation
Can I rotate my AWD tires the same way I would for a 2WD vehicle?
No, AWD vehicles have specific rotation patterns to ensure even wear on all four tires. Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual or consult a qualified mechanic for the correct pattern.
How often should I rotate my AWD tires?
The recommended tire rotation interval varies depending on your vehicle and driving habits. However, it is generally recommended to rotate tires every 5,000 to 7,500 miles.
What if my AWD vehicle has different tire sizes?
If your vehicle has different tire sizes (e.g., larger tires on the rear), you should consult your owner’s manual or a mechanic for the appropriate rotation pattern.