Does front wheel drive have transfer case –
Does front-wheel drive have a transfer case? This question often arises when people think about the power distribution in vehicles. While transfer cases are essential for four-wheel drive systems, they’re not found in front-wheel drive vehicles. Let’s delve into why that is and explore the differences in power distribution between these two drivetrain configurations.
Front-wheel drive systems are designed to send power directly to the front wheels, providing efficient traction and handling, especially in everyday driving conditions. The absence of a transfer case simplifies the drivetrain and contributes to better fuel economy. However, this simplicity comes with trade-offs, particularly in terms of off-road capabilities. We’ll explore these aspects in more detail as we examine the fundamental principles behind front-wheel drive and the role of transfer cases in four-wheel drive systems.
*
The Absence of Transfer Cases in Front-Wheel Drive
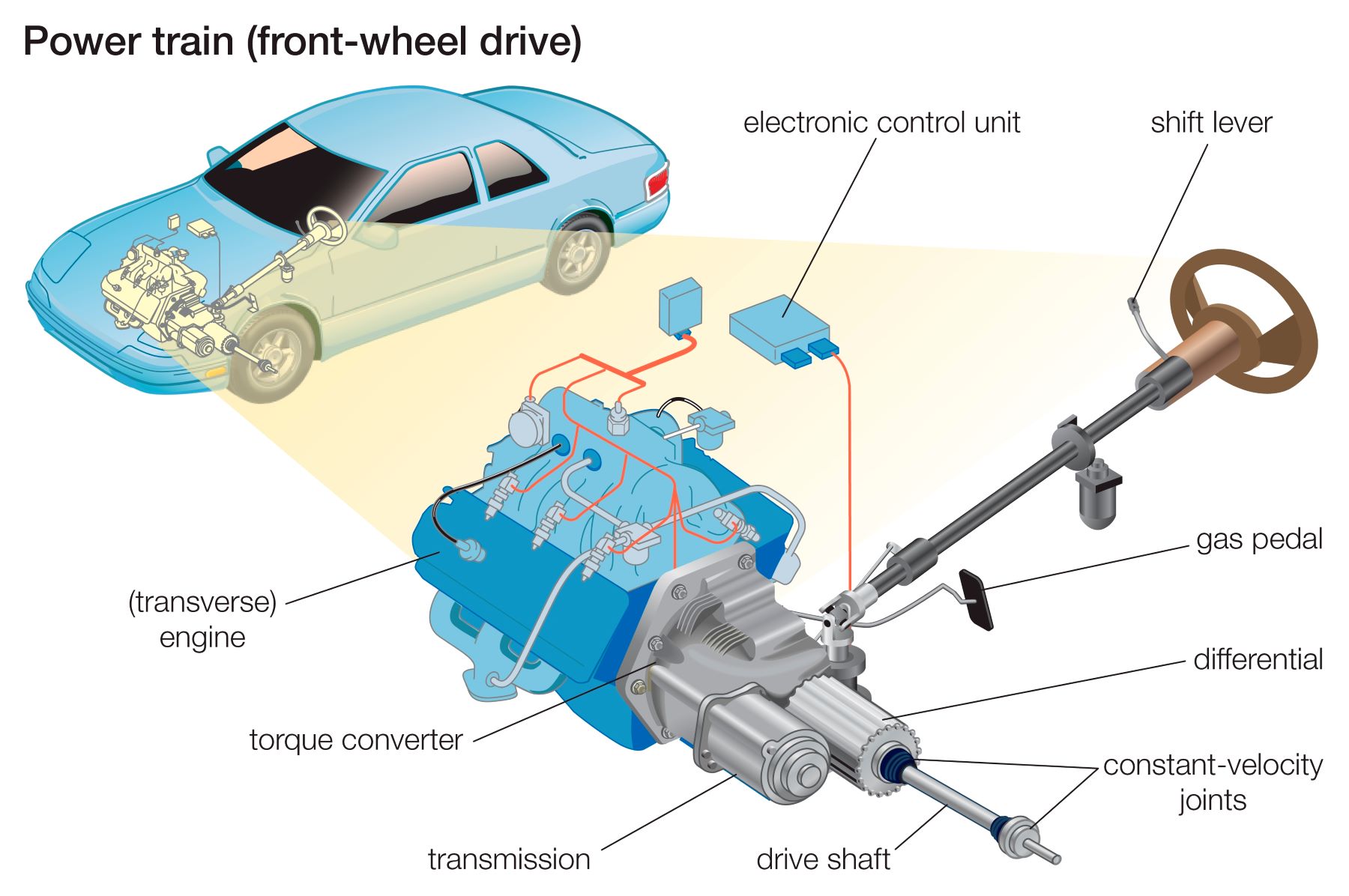
Front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles, unlike their four-wheel drive (4WD) counterparts, do not require a transfer case. This fundamental difference stems from the distinct power distribution mechanisms employed in each system.
Power Distribution in Front-Wheel Drive
Front-wheel drive vehicles utilize a simpler power distribution system. The engine’s power is transmitted directly to the front wheels through a single driveshaft and differential. This configuration eliminates the need for a transfer case, which is crucial in 4WD systems for managing power distribution between the front and rear axles.
The Absence of Transfer Cases and Off-Road Capabilities, Does front wheel drive have transfer case
The absence of a transfer case in FWD vehicles significantly impacts their off-road capabilities. Transfer cases are essential for enabling low-range gearing, which provides increased torque for tackling challenging terrain. This feature allows 4WD vehicles to maintain traction and power even on slippery surfaces, steep inclines, and rough terrain.FWD vehicles, lacking this crucial component, are typically better suited for on-road driving.
Their power delivery is optimized for smooth, paved surfaces, making them efficient and comfortable for daily commutes and highway driving.
Common Misconceptions: Does Front Wheel Drive Have Transfer Case

The absence of a transfer case in front-wheel drive vehicles often leads to confusion and misconceptions. This is especially true for individuals accustomed to the workings of four-wheel drive systems. Let’s delve into some common misconceptions surrounding front-wheel drive and transfer cases.
The Role of the Differential
The differential plays a crucial role in front-wheel drive systems, often mistaken for a transfer case. The differential is a vital component that allows the wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds. This is essential for smooth cornering and maneuvering. In a front-wheel drive vehicle, the differential is located within the transmission, while in rear-wheel drive vehicles, it is typically housed in the rear axle.
It is important to understand that the differential’s primary function is to ensure that both wheels on the same axle can rotate at different speeds, which is necessary for smooth turning. The transfer case, on the other hand, is responsible for distributing power between the front and rear axles.
Examples of Misconceptions
Here are some common examples of how the misconception of front-wheel drive having a transfer case arises:
- The term “all-wheel drive” (AWD) is often used interchangeably with “four-wheel drive” (4WD). While both systems provide power to all four wheels, they operate differently. AWD systems use a differential to distribute power between the front and rear axles, while 4WD systems typically utilize a transfer case. This distinction often leads to the incorrect assumption that front-wheel drive vehicles have transfer cases, as they are associated with AWD systems.
- The presence of a “4-wheel drive” or “AWD” button on some front-wheel drive vehicles can also contribute to this misconception. This button is not actually engaging a transfer case, but rather activating an electronic system that distributes power to the rear wheels when needed. The system is typically engaged automatically in slippery conditions to improve traction.
- Front-wheel drive vehicles equipped with a “limited-slip differential” (LSD) are sometimes mistakenly thought to have a transfer case. LSDs are designed to improve traction by preventing one wheel from spinning excessively when the other wheel loses traction. This function is distinct from the role of a transfer case, which distributes power between axles.
In conclusion, front-wheel drive vehicles do not utilize transfer cases. Their power distribution is handled through a different mechanism, focusing on efficiency and everyday driving performance. Understanding the distinctions between front-wheel drive and four-wheel drive systems, along with the purpose of transfer cases, helps clarify the unique characteristics of each drivetrain configuration. While front-wheel drive excels in fuel efficiency and everyday driving, four-wheel drive offers superior traction and off-road capabilities.
Choosing the right drivetrain ultimately depends on your specific needs and driving preferences.
Expert Answers
What are the benefits of front-wheel drive?
Front-wheel drive offers advantages in terms of fuel efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ease of maintenance. It also provides good traction in most everyday driving conditions.
What are the limitations of front-wheel drive?
Front-wheel drive systems can experience reduced traction in slippery conditions, particularly on uneven surfaces or during aggressive acceleration. They also generally have limited off-road capabilities.
What is a differential, and how does it work in front-wheel drive?
A differential is a vital component in both front-wheel and rear-wheel drive systems. It allows the wheels on the same axle to rotate at different speeds, enabling smooth cornering and preventing tire slippage.
What are some examples of vehicles that use front-wheel drive?
Many popular cars, hatchbacks, and SUVs utilize front-wheel drive, including the Honda Civic, Toyota Corolla, and Subaru Impreza.
-*