How to stop TMJ ear ringing? That persistent ringing in your ear can be a real buzzkill, especially when it’s linked to your jaw. TMJ, or temporomandibular joint disorder, can cause all sorts of annoying symptoms, and ear ringing is one of them. But don’t worry, you’re not alone! There are plenty of things you can do to find relief and get back to enjoying your favorite tunes.
From simple self-care practices to medical interventions, we’ll explore the ins and outs of managing TMJ ear ringing. We’ll dive into the causes, discuss effective treatments, and provide practical tips to help you regain control over your hearing. So, buckle up, it’s time to quiet that ear ringing and reclaim your peace of mind.
Understanding TMJ and Ear Ringing
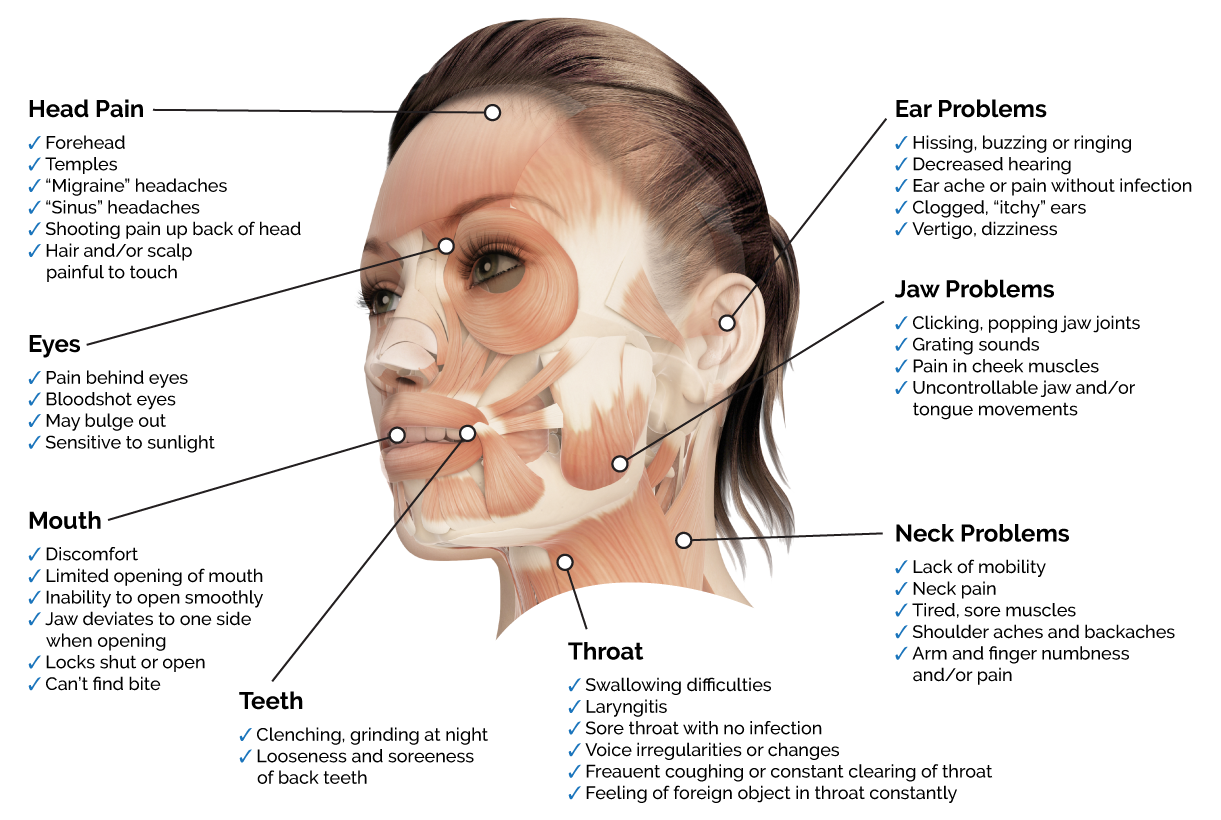
Tinnitus, often described as ringing in the ears, can be a frustrating and debilitating condition. While many factors can contribute to tinnitus, one often overlooked cause is temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ). The temporomandibular joint, located just in front of the ear, connects the jawbone to the skull. When this joint becomes dysfunctional, it can lead to a variety of symptoms, including ear ringing.
The Connection Between TMJ and Ear Ringing
The connection between TMJ disorder and ear ringing is complex and involves several mechanisms. The temporomandibular joint is closely connected to the auditory system, and problems in the joint can disrupt the normal functioning of the ear. For instance, inflammation or misalignment in the TMJ can affect the tiny muscles and bones in the middle ear, which are responsible for transmitting sound waves to the inner ear.
This disruption can result in the perception of ringing, buzzing, or other sounds in the ear.
Types of TMJ Disorders and Their Impact on Ear Ringing
TMJ disorders encompass a range of conditions that affect the temporomandibular joint. The most common types include:
- Myofascial pain: This involves pain and tenderness in the muscles surrounding the jaw. Muscle spasms and tightness can put pressure on the auditory system, leading to ear ringing.
- Internal derangement: This refers to problems within the joint itself, such as a displaced disc or joint damage. These issues can affect the proper functioning of the ear, leading to tinnitus.
- Arthritis: Inflammation and degeneration of the joint can occur due to osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. This can cause pain, stiffness, and clicking in the jaw, as well as ear ringing.
Examples of TMJ Dysfunction Leading to Tinnitus
- Muscle spasms: A person with TMJ disorder might experience muscle spasms in the jaw, which can put pressure on the auditory system and cause ear ringing.
- Disc displacement: A displaced disc in the TMJ can affect the proper functioning of the middle ear, leading to sound distortions and tinnitus.
- Joint inflammation: Inflammation in the TMJ can cause swelling and pressure on the surrounding tissues, including the auditory system, resulting in ear ringing.
Identifying the Causes of TMJ Ear Ringing
Understanding the root causes of TMJ ear ringing is crucial for effective treatment. It’s a complex condition often stemming from a combination of factors. While ear ringing itself might not be directly caused by TMJ, the jaw joint’s dysfunction can trigger or exacerbate the symptoms.
Muscle Tension
Muscle tension, especially in the jaw muscles, is a common culprit behind TMJ ear ringing. The temporomandibular joint, located just in front of the ears, is surrounded by muscles that control chewing, jaw movement, and facial expressions. When these muscles become tight or strained, they can put pressure on the joint and surrounding tissues, leading to ear ringing.
Jaw Misalignment
A misaligned jaw, known as malocclusion, can also contribute to TMJ ear ringing. This occurs when the upper and lower teeth don’t properly align, causing uneven pressure on the jaw joint. The misalignment can strain the muscles, leading to pain, clicking, and potentially ear ringing.
Arthritis
Arthritis, specifically osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, can affect the TMJ, causing inflammation and pain. The cartilage that cushions the joint can wear down, leading to bone-on-bone friction. This inflammation can affect the surrounding nerves, potentially causing ear ringing.
Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety play a significant role in TMJ disorders, including ear ringing. When we’re stressed, our bodies tend to tense up, including the jaw muscles. This constant tension can lead to TMJ dysfunction, contributing to ear ringing.
Dental Problems
Dental issues, such as misaligned teeth, missing teeth, or poorly fitted dentures, can also contribute to TMJ ear ringing. These problems can affect the bite and jaw alignment, causing strain on the joint and surrounding muscles.
Bruxism
Bruxism, the involuntary grinding or clenching of teeth, is a common cause of TMJ disorders and can lead to ear ringing. This habit puts excessive pressure on the jaw joint, causing muscle fatigue, pain, and potentially ear ringing.
Self-Care Measures for TMJ Ear Ringing: How To Stop Tmj Ear Ringing
Taking proactive steps to manage TMJ ear ringing can significantly improve your quality of life. While it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment, incorporating self-care practices can complement your overall approach to relief.
Applying Heat or Cold
Applying heat or cold can help alleviate pain and inflammation associated with TMJ ear ringing. Heat therapy, using a warm compress or heating pad, can relax tight muscles and improve blood flow. Cold therapy, using an ice pack wrapped in a towel, can reduce inflammation and numb the area. You can alternate between heat and cold applications for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
Relaxation Techniques
Stress can exacerbate TMJ symptoms, including ear ringing. Incorporating relaxation techniques into your daily routine can help reduce stress levels and promote muscle relaxation. Some effective techniques include:
- Deep breathing exercises: Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose, hold your breath for a few seconds, and exhale slowly through your mouth. Repeat this several times.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Tense and release different muscle groups in your body, starting with your toes and working your way up to your head. This helps to identify and release tension.
- Meditation: Find a quiet space, close your eyes, and focus on your breath or a calming mantra. This can help to clear your mind and reduce stress.
Jaw Muscle Stretching
Regularly stretching your jaw muscles can help alleviate tension and improve mobility. Here is a simple stretching routine you can practice:
- Chin Tucks: Gently tuck your chin towards your chest, hold for 5 seconds, and then relax. Repeat 10 times.
- Side Stretches: Slowly tilt your head to the side, bringing your ear towards your shoulder. Hold for 5 seconds, and then repeat on the other side. Repeat 10 times on each side.
- Tongue Stretches: Extend your tongue out as far as you can, hold for 5 seconds, and then retract it. Repeat 10 times.
- Jaw Opening and Closing: Open your mouth slowly and widely, hold for 5 seconds, and then close it slowly. Repeat 10 times.
Improving Posture and Reducing Stress
Maintaining good posture and reducing stress are essential for managing TMJ ear ringing.
- Posture: Sit and stand tall, keeping your shoulders relaxed and your head level. Avoid slouching or hunching over, as this can strain your neck and jaw muscles.
- Stress Reduction: Identify and address stress triggers in your life. Practice relaxation techniques, engage in hobbies you enjoy, and prioritize sleep.
Medical Treatments for TMJ Ear Ringing
When self-care measures fail to alleviate TMJ ear ringing, medical interventions may be necessary. A healthcare professional can diagnose TMJ disorder and recommend appropriate treatment options. These treatments aim to reduce pain, improve jaw function, and manage the underlying causes of ear ringing.
Medications, How to stop tmj ear ringing
Medications play a crucial role in managing TMJ symptoms, including ear ringing. Pain relievers, muscle relaxants, and anti-inflammatory drugs can help reduce pain and inflammation. In some cases, antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed to address psychological factors that contribute to TMJ symptoms.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy focuses on strengthening jaw muscles, improving range of motion, and reducing pain. Therapists may use techniques such as heat therapy, cold therapy, ultrasound, and massage to alleviate pain and improve jaw function. They may also recommend exercises to strengthen the muscles involved in jaw movement.
Dental Interventions
Dental interventions are often necessary to correct misalignment or problems with the teeth and jaw. These interventions may include:
- Occlusal adjustment: This involves adjusting the bite to improve the alignment of the teeth and reduce stress on the jaw muscles.
- Mouthguards: Custom-made mouthguards can help protect teeth and reduce clenching and grinding, which can exacerbate TMJ symptoms.
- Splints: Splints are devices worn in the mouth to reposition the jaw and reduce pressure on the TMJ joint.
- Crown and bridgework: Replacing missing teeth or repairing damaged teeth can improve the alignment of the jaw and reduce TMJ symptoms.
- Orthodontic treatment: Braces or other orthodontic devices may be used to correct misalignment of the teeth and jaw.
Effectiveness of Medical Interventions
The effectiveness of medical interventions for TMJ ear ringing varies depending on the individual and the severity of their condition. Some people experience significant improvement in their symptoms with conservative treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, and dental interventions. Others may require more invasive procedures, such as surgery, to address the underlying cause of their TMJ disorder. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your individual needs.
Lifestyle Modifications for TMJ Ear Ringing
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing TMJ ear ringing by addressing underlying factors that contribute to the condition. By adopting these changes, individuals can alleviate symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary changes can significantly impact TMJ ear ringing. Certain foods can exacerbate jaw clenching and grinding, leading to increased pain and discomfort.
- Eat softer foods: Opt for foods that require less chewing, such as soups, stews, mashed potatoes, and soft fruits. This reduces stress on the jaw muscles and temporomandibular joint.
- Avoid chewing gum: Chewing gum puts excessive pressure on the jaw muscles, which can worsen TMJ symptoms. It’s best to avoid chewing gum or choose sugar-free options.
- Limit caffeine and alcohol consumption: These substances can dehydrate the body, leading to muscle tension and increased jaw clenching. Moderation is key.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress is a significant trigger for TMJ ear ringing. It can lead to muscle tension, jaw clenching, and grinding, exacerbating symptoms.
- Practice relaxation techniques: Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation.
- Engage in activities you enjoy: Hobbies and activities that bring you joy can help take your mind off stressors and reduce tension.
- Seek professional help: If stress is a significant factor in your TMJ ear ringing, consider talking to a therapist or counselor. They can provide coping mechanisms and strategies to manage stress effectively.
Regular Exercise and Healthy Diet
Regular exercise and a balanced diet can improve overall health and contribute to managing TMJ ear ringing.
- Engage in moderate-intensity exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling can help strengthen muscles and improve circulation, reducing muscle tension and pain.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight puts extra strain on the jaw muscles and temporomandibular joint, exacerbating TMJ symptoms.
- Consume a balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides essential nutrients for muscle health and overall well-being.
Remember, managing TMJ ear ringing is a journey, not a race. Be patient with yourself, try different approaches, and don’t be afraid to seek professional help. By understanding the connection between TMJ and ear ringing, you can take proactive steps to manage your symptoms and find lasting relief. So, go ahead, crank up the music and enjoy the sweet sounds of silence – your ears will thank you!
FAQ Summary
Is TMJ ear ringing always a sign of a serious problem?
Not necessarily. TMJ ear ringing can be caused by a variety of factors, some more serious than others. It’s always best to consult with a doctor to rule out any underlying conditions.
Can I treat TMJ ear ringing at home?
Yes, many self-care measures can help reduce TMJ ear ringing. These include applying heat or cold, practicing relaxation techniques, and avoiding jaw-clenching activities.
How long does it take for TMJ ear ringing to go away?
The duration of TMJ ear ringing can vary depending on the cause and severity. Some people experience relief quickly, while others may need more time and treatment.