What is the wheel cylinder – What is a wheel cylinder? It’s a critical component in your vehicle’s braking system, silently working behind the scenes to keep you safe on the road. Imagine pressing the brake pedal – that action triggers a chain reaction, culminating in the wheel cylinder’s crucial role in converting hydraulic pressure into the force needed to stop your car.
This humble component is a hydraulic actuator, housed within each wheel’s brake assembly. Its primary function is to translate the pressure generated by the master cylinder into a mechanical force that pushes the brake shoes or pads against the brake drum or rotor, creating friction and slowing down the vehicle.
Wheel Cylinder Installation and Maintenance
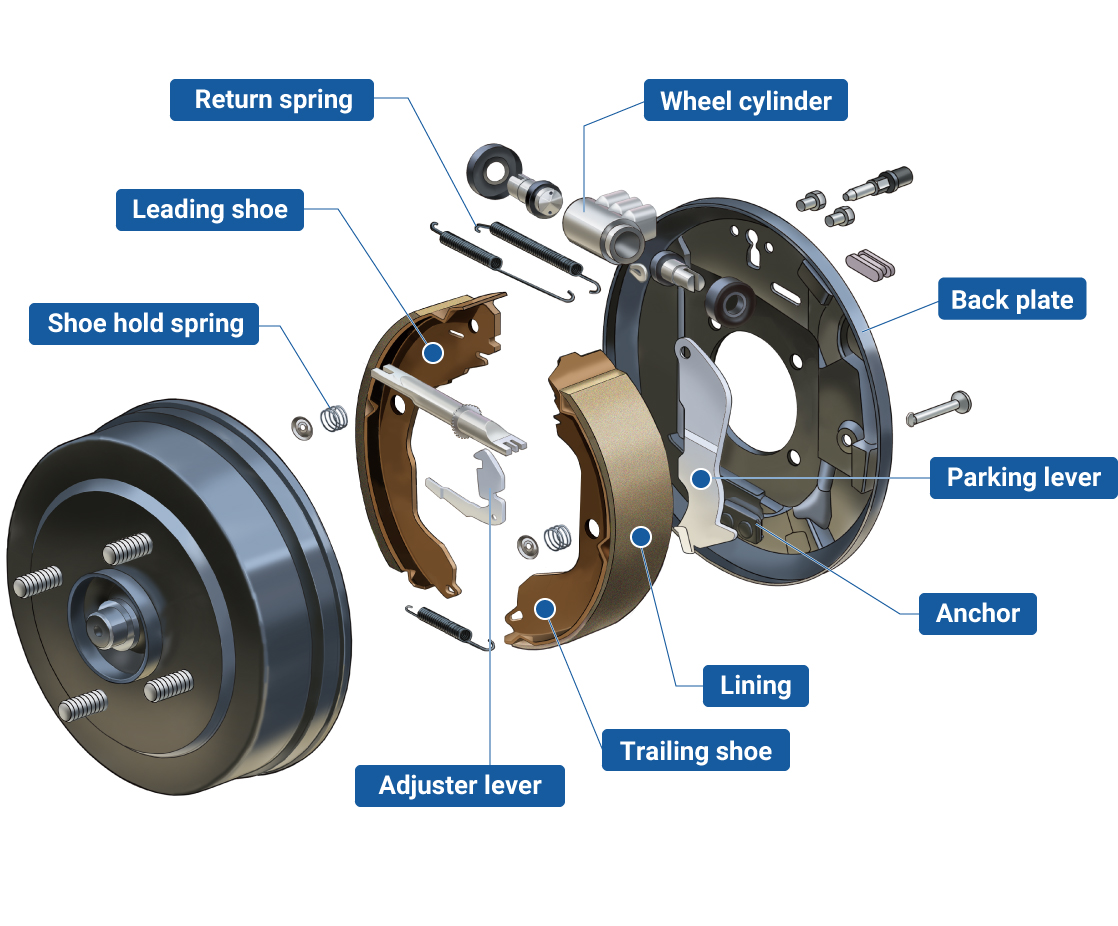
Installing a new wheel cylinder is an important part of maintaining your vehicle’s braking system. This process ensures that the brake fluid can effectively pressurize the brake pads and shoes, providing the necessary stopping power.
Wheel Cylinder Installation
Installing a new wheel cylinder involves replacing the old one with a new one. This process requires removing the old wheel cylinder, cleaning the area, and installing the new one. Here are the steps involved in installing a new wheel cylinder:
- Remove the wheel. Loosen the lug nuts and jack up the vehicle, supporting it with jack stands. Remove the wheel.
- Remove the brake caliper or drum. Depending on your vehicle, you’ll need to remove either the brake caliper or the brake drum.
- Remove the old wheel cylinder. Disconnect the brake lines from the wheel cylinder and remove the mounting bolts holding it in place.
- Clean the area. Use a wire brush to clean the mounting surface and brake line connections.
- Install the new wheel cylinder. Install the new wheel cylinder in the same position as the old one.
- Connect the brake lines. Connect the brake lines to the new wheel cylinder and tighten the fittings.
- Bleed the brakes. After installing the new wheel cylinder, you’ll need to bleed the brakes to remove any air bubbles that may have entered the system.
- Reassemble the brakes. Reinstall the brake caliper or drum, tighten the lug nuts, and lower the vehicle.
Tools and Equipment
You will need a few tools and equipment to install a new wheel cylinder.
- Jack and jack stands. These are necessary to lift the vehicle and support it safely.
- Lug wrench. This is used to loosen and tighten the lug nuts.
- Socket set. This is used to remove the bolts holding the wheel cylinder in place.
- Wrench set. This is used to tighten the brake line fittings.
- Brake bleeding kit. This is used to remove air bubbles from the brake system.
- Cleaning supplies. You’ll need a wire brush and cleaning solvent to clean the mounting surface and brake line connections.
Wheel Cylinder Maintenance
Routine maintenance and inspection of your wheel cylinders are essential for ensuring proper braking function.
- Inspect for leaks. Regularly check for brake fluid leaks around the wheel cylinders.
- Check for damage. Inspect the wheel cylinders for any signs of damage, such as cracks or corrosion.
- Replace worn or damaged cylinders. If you find any leaks or damage, replace the wheel cylinder.
- Maintain proper brake fluid levels. Ensure that the brake fluid level is within the specified range in the reservoir.
Wheel Cylinder Troubleshooting
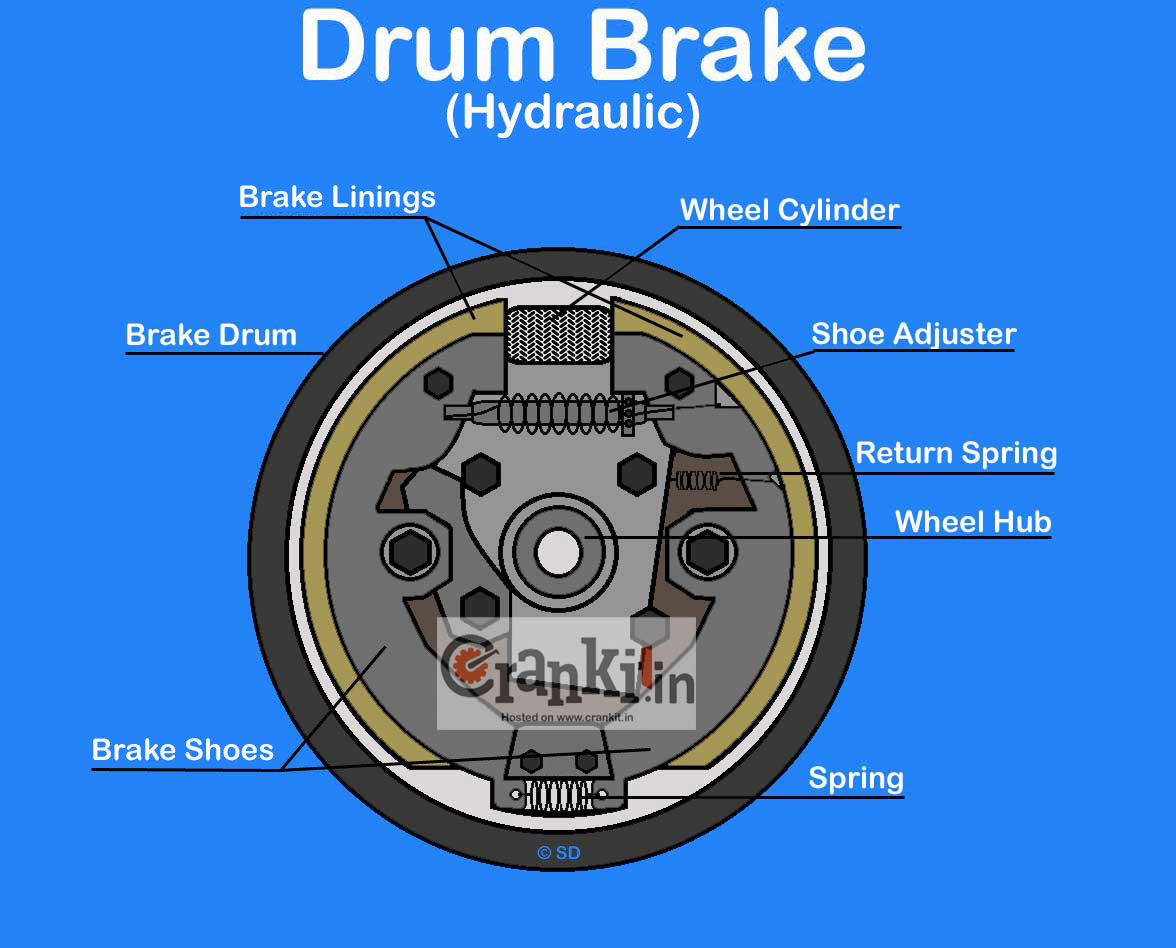
Wheel cylinders are crucial components of your vehicle’s braking system, and problems with them can lead to brake failure. This section will explore common issues, diagnostic techniques, and repair or replacement strategies for wheel cylinders.
Identifying Common Wheel Cylinder Problems
Understanding the potential issues associated with wheel cylinders is essential for effective troubleshooting. Here are some common problems:
- Fluid Leakage: This is the most prevalent issue, often manifested as brake fluid leaks from the cylinder’s boot or around the piston seals. Fluid leaks can lead to reduced brake performance and potentially brake failure.
- Seized Pistons: Wheel cylinder pistons can become seized due to corrosion, rust, or debris accumulation. This prevents proper piston movement, affecting braking efficiency and potentially leading to brake dragging.
- Damaged or Worn Parts: Wear and tear can affect the cylinder’s components, including the piston seals, boot, and internal parts. This can lead to fluid leaks, reduced braking performance, and potential brake failure.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect installation of wheel cylinders can result in misalignment, fluid leaks, and compromised braking effectiveness.
Diagnosing Wheel Cylinder Issues
Accurate diagnosis is key to addressing wheel cylinder problems. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the wheel cylinder for signs of fluid leaks, rust, or corrosion. Look for any damage or wear on the boot or other components.
- Brake Fluid Level Check: A low brake fluid level can indicate a leak in the wheel cylinder or elsewhere in the braking system.
- Brake Pedal Feel: A spongy or soft brake pedal can signal a fluid leak or air in the braking system. A hard brake pedal may indicate a seized piston or other issues.
- Brake System Bleeding: Bleeding the brakes can help identify and isolate the source of a fluid leak. If the fluid level drops after bleeding a particular wheel, it may indicate a problem with the wheel cylinder.
Repairing or Replacing Faulty Wheel Cylinders
Once you’ve diagnosed a problem with a wheel cylinder, you’ll need to repair or replace it. Here’s a guide to common repair and replacement procedures:
- Repairing: In some cases, repairing a wheel cylinder might be possible. This typically involves replacing worn or damaged seals and boots. However, if the cylinder is severely corroded or damaged, replacement is usually the best option.
- Replacing: Replacing a faulty wheel cylinder requires removing the old one and installing a new one. This involves disconnecting the brake lines, removing the cylinder from the brake shoe assembly, and installing the new cylinder. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use proper tools and techniques to ensure a safe and effective installation.
Wheel Cylinder Safety

Your vehicle’s braking system is crucial for your safety and the safety of others on the road. The wheel cylinders play a vital role in this system, ensuring that your brakes function correctly. Maintaining these components is essential for preventing accidents and ensuring a smooth, reliable braking experience.
Importance of Proper Maintenance
Proper wheel cylinder maintenance is critical for vehicle safety. Regular inspections and timely repairs can help prevent potential hazards and ensure the effectiveness of your braking system.
- Reduced Braking Efficiency: Worn or damaged wheel cylinders can lead to brake fluid leaks, causing a gradual reduction in braking power. This can increase stopping distances and make it difficult to stop in emergency situations.
- Uneven Braking: If one or more wheel cylinders malfunction, the brakes on those wheels may not engage properly, leading to uneven braking and potential vehicle instability.
- Brake Fade: Overheated wheel cylinders can experience brake fade, a condition where the brakes lose their effectiveness due to excessive heat. This can be particularly dangerous at high speeds.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: A malfunctioning wheel cylinder can lead to a complete brake failure, increasing the risk of accidents.
Safety Precautions When Handling Wheel Cylinders, What is the wheel cylinder
Wheel cylinders contain brake fluid, which is a hazardous substance. It is essential to follow safety precautions when handling and disposing of these components.
- Wear Protective Gear: Always wear gloves and eye protection when handling wheel cylinders or brake fluid. Brake fluid can irritate the skin and eyes.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Brake fluid is flammable and can release harmful fumes. Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling these fumes.
- Proper Disposal: Dispose of used brake fluid and old wheel cylinders responsibly. Do not pour brake fluid down the drain or into the environment. Check with your local waste management facility for proper disposal guidelines.
- Avoid Contact with Skin and Eyes: If brake fluid comes into contact with your skin, wash the affected area immediately with soap and water. If it gets in your eyes, flush them with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
Safe Disposal
Properly disposing of wheel cylinders is crucial for environmental safety.
- Do not Throw Away in Trash: Wheel cylinders contain hazardous materials that can contaminate the environment. Do not dispose of them in your regular trash.
- Recycle or Dispose at Hazardous Waste Facility: Many communities have recycling or hazardous waste facilities where you can safely dispose of used wheel cylinders. Contact your local waste management agency for information on these options.
Understanding the inner workings of the wheel cylinder is essential for maintaining your vehicle’s safety and performance. Regular inspection and maintenance are crucial to ensure optimal braking function. From its role in hydraulic braking to the various types and their operation, the wheel cylinder plays a vital part in keeping you and your passengers safe on the road.
FAQ Overview: What Is The Wheel Cylinder
What are the signs of a bad wheel cylinder?
Signs of a bad wheel cylinder include brake fluid leaks, a spongy brake pedal, uneven braking, and a grinding noise when braking.
How often should I inspect my wheel cylinders?
It’s recommended to inspect your wheel cylinders during every brake service, typically every 25,000 to 30,000 miles.
Can I replace a wheel cylinder myself?
While possible, replacing a wheel cylinder requires some mechanical expertise. It’s best to consult a professional mechanic for proper installation.
What is the difference between a wheel cylinder and a caliper?
Wheel cylinders are used in drum brake systems, while calipers are used in disc brake systems. Both components serve the same purpose: to convert hydraulic pressure into braking force.