How to change wheel speed sensor – How to change a wheel speed sensor: It might sound daunting, but it’s a task within reach for anyone with a little mechanical know-how and the right tools. Wheel speed sensors are critical components in your car’s braking and stability systems, and a faulty sensor can lead to erratic braking, ABS malfunctions, and even a loss of traction control.
This guide will walk you through the process, from identifying the sensor to testing the new one, ensuring you get back on the road safely and confidently.
Understanding the function of a wheel speed sensor is the first step. These sensors, often found near the wheel hub, monitor the rotation speed of each wheel. This data is relayed to the vehicle’s electronic control unit (ECU), which uses it to calculate important parameters like vehicle speed, wheel slip, and braking force distribution. When a sensor malfunctions, the ECU receives inaccurate information, potentially leading to a cascade of problems.
Understanding Wheel Speed Sensors: How To Change Wheel Speed Sensor
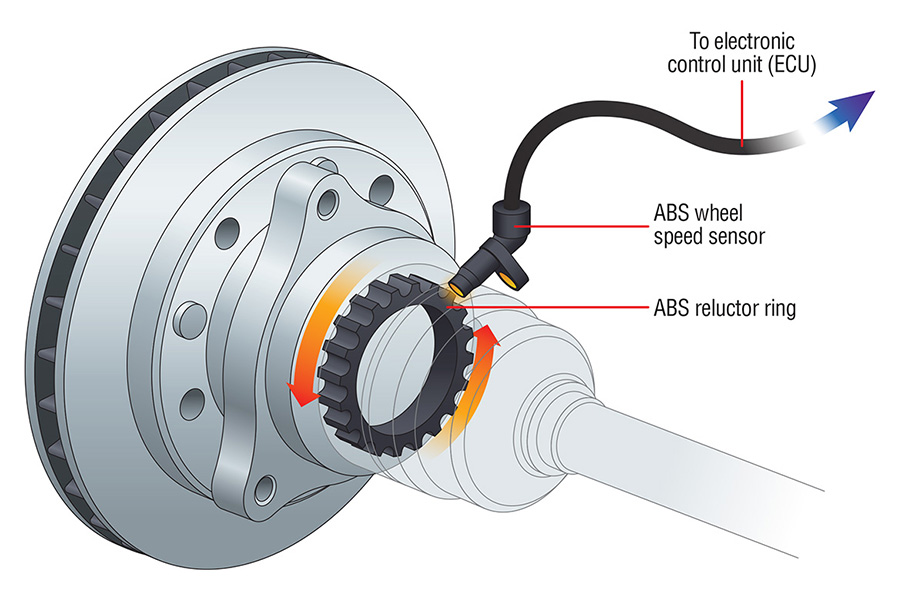
Wheel speed sensors are vital components in a vehicle’s braking and stability systems. They play a crucial role in providing information about the rotational speed of each wheel, which is used to activate the anti-lock braking system (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and traction control (TC) systems.
Types of Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors are designed to detect the rotation of the wheel and send a signal to the vehicle’s computer. They come in different types, each with its own unique operating principle.
- Magnetic Sensors: These sensors are commonly used in modern vehicles. They work by detecting the magnetic field generated by a toothed wheel or a magnetic ring attached to the wheel hub. As the wheel rotates, the teeth or magnetic poles pass by the sensor, generating a series of electrical pulses that correspond to the wheel’s speed.
- Hall Effect Sensors: Hall effect sensors use a magnetic field to generate a voltage that is proportional to the speed of the wheel. These sensors are typically mounted near the wheel hub and are used to measure the speed of the wheel by detecting the magnetic field created by a rotating magnet attached to the wheel.
- Optical Sensors: These sensors use light to detect the rotation of the wheel. They typically consist of a light source, a photodetector, and a rotating disc with slots or holes. As the disc rotates, the light passes through the slots or holes, generating a series of pulses that correspond to the wheel’s speed.
Causes of Wheel Speed Sensor Failure
Wheel speed sensors are relatively reliable components, but they can fail over time due to various factors.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the sensor’s internal components can wear out, leading to inaccurate readings or complete failure. This is particularly common in vehicles that are frequently driven in harsh conditions, such as off-road or in areas with extreme temperatures.
- Damage: Wheel speed sensors can be damaged by road debris, impacts, or corrosion. This can cause the sensor to malfunction or become disconnected from the wiring harness.
- Wiring Problems: Faulty wiring or loose connections can also lead to wheel speed sensor failure. This can prevent the sensor from sending a signal to the vehicle’s computer or cause the signal to be distorted.
- Toothed Wheel or Magnetic Ring Damage: The toothed wheel or magnetic ring attached to the wheel hub can become damaged or worn out, leading to inaccurate readings from the sensor.
Identifying the Location of the Wheel Speed Sensor

Knowing where to find the wheel speed sensor is crucial for replacing it. The sensor’s location varies depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
Typical Wheel Speed Sensor Locations
The wheel speed sensor is usually located near the wheel hub, within easy reach of the mechanic. To locate the sensor, you can follow these steps:
- Locate the Wheel Hub: The wheel hub is the central part of the wheel where the wheel attaches to the axle. It is typically located at the center of the wheel, near the brake disc or drum.
- Identify the Sensor’s Placement: The wheel speed sensor is usually mounted on the suspension arm or brake caliper, close to the wheel hub. Look for a small, cylindrical sensor with a wire attached to it.
- Trace the Wire: Follow the wire from the sensor to its connection point, which is usually located near the vehicle’s ABS control module.
Visual Examples of Wheel Speed Sensor Locations
Here are some examples of where wheel speed sensors are typically located on various vehicle models:
- Front Wheel Drive Vehicles: In front-wheel drive vehicles, the wheel speed sensors are usually located near the front wheel hubs, often on the suspension arm or brake caliper.
- Rear Wheel Drive Vehicles: In rear-wheel drive vehicles, the wheel speed sensors are usually located near the rear wheel hubs, often on the suspension arm or brake caliper.
- All Wheel Drive Vehicles: In all-wheel drive vehicles, the wheel speed sensors are usually located near all four wheel hubs, often on the suspension arm or brake caliper.
Wheel Speed Sensor Locations for Common Vehicle Makes and Models, How to change wheel speed sensor
The following table provides a general overview of the wheel speed sensor locations for some common vehicle makes and models. However, it’s important to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a reliable online resource for specific instructions:
| Vehicle Make and Model | Wheel Speed Sensor Location |
|---|---|
| Honda Civic (2006-2011) | Front and Rear Wheel Hubs |
| Toyota Camry (2007-2011) | Front and Rear Wheel Hubs |
| Ford Focus (2008-2011) | Front and Rear Wheel Hubs |
| Chevrolet Silverado (2007-2013) | Front and Rear Wheel Hubs |
Tools and Materials Needed for Replacement
Before you begin replacing a wheel speed sensor, you’ll need to gather the necessary tools and materials. Having everything ready will make the process smoother and more efficient. The tools and materials required will vary slightly depending on the specific make and model of your vehicle. However, the following list includes the essentials for most replacement jobs.
Essential Tools and Materials
- Jack and Jack Stands: These are crucial for lifting the vehicle safely and securely. Ensure the jack stands are rated for the weight of your vehicle and are placed on a firm, level surface.
- Lug Wrench: This tool is used to loosen and tighten the lug nuts that hold the wheel in place.
- Torque Wrench: A torque wrench is essential for tightening the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specified torque. This ensures the wheel is securely fastened and prevents damage to the wheel or hub.
- Socket Set: You’ll need a socket set that includes sockets of various sizes, including the size that fits the wheel speed sensor bolt.
- Ratchet Wrench: A ratchet wrench is used to turn the sockets, providing leverage for loosening and tightening bolts.
- Flathead Screwdriver: A flathead screwdriver may be needed to pry off any clips or trim pieces that obstruct access to the wheel speed sensor.
- New Wheel Speed Sensor: This is the replacement part you’ll install. Ensure you purchase a sensor specifically designed for your vehicle’s make, model, and year.
- Penetrating Fluid (Optional): If the sensor bolt is rusted or stuck, penetrating fluid can help loosen it.
- Gloves: Wearing gloves can protect your hands from dirt, grease, and potential cuts.
- Safety Glasses: Safety glasses are essential to protect your eyes from debris or flying objects.
Safety Precautions
- Always use a jack and jack stands to lift the vehicle safely. Never rely on the jack alone for support.
- Ensure the vehicle is parked on a level surface and engage the parking brake. This will prevent the vehicle from rolling while you’re working on it.
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris or flying objects.
- Use caution when working around the brake system. Avoid contaminating the brake pads or rotors with grease or oil.
- Before driving the vehicle after replacing the sensor, check the brake system for proper operation. This includes testing the brakes and ensuring the wheels are rotating freely.
The Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement Process
Now that you have gathered the necessary tools and materials and identified the location of the wheel speed sensor, you’re ready to begin the replacement process. This process is relatively straightforward, but it’s crucial to follow the steps carefully to ensure a smooth and successful replacement.
Disconnecting the Wheel Speed Sensor
Before you can remove the sensor, you need to disconnect it from the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Locate the sensor’s connector, typically a small black or grey plug with a few wires.
- Carefully disconnect the connector by pressing the release tab or lever on the connector.
- You can use a small flat-head screwdriver to help pry the connector apart if necessary.
Removing the Wheel Speed Sensor
Once the connector is disconnected, you can remove the sensor from its mounting location.
- Depending on your vehicle, the sensor might be held in place by a clip, bolt, or a combination of both.
- Use a wrench or socket to loosen and remove any bolts securing the sensor.
- If the sensor is held by a clip, carefully pry it loose using a small flat-head screwdriver or a similar tool.
Installing the New Wheel Speed Sensor
With the old sensor removed, you can now install the new one.
- Align the new sensor with its mounting location on the vehicle.
- If the sensor is held by bolts, thread them back into place and tighten them securely.
- If the sensor uses a clip, snap it back into place, ensuring it’s securely fastened.
Connecting the Wheel Speed Sensor
The final step is to reconnect the sensor to the vehicle’s electrical system.
- Align the connector on the new sensor with the connector on the vehicle’s wiring harness.
- Press the connector together firmly until you hear a click, ensuring a secure connection.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While replacing a wheel speed sensor is usually a straightforward process, you might encounter some common issues.
- Difficulty Removing the Sensor: If the sensor is stuck or difficult to remove, try applying some penetrating oil to loosen it.
- Damaged Wiring: Inspect the wiring harness for any damage or wear. If you find any damage, repair it before installing the new sensor.
- Loose Connection: Ensure that both the sensor and the connector are securely fastened to avoid any loose connections.
Testing the New Wheel Speed Sensor
After successfully replacing the wheel speed sensor, it’s crucial to verify its functionality to ensure a smooth and safe driving experience. Testing the new sensor ensures it’s working correctly and transmitting accurate data to the vehicle’s computer.
Methods for Testing a Wheel Speed Sensor
Testing a wheel speed sensor involves assessing its ability to generate a signal proportional to the wheel’s rotation speed. Here are the common methods used for testing:
- Using a Digital Multimeter: This method involves connecting a digital multimeter to the sensor’s wires to measure the voltage output. The sensor should generate a fluctuating voltage as the wheel rotates.
- Using a Diagnostic Scanner: A diagnostic scanner can read data from the sensor and display it on the screen. This allows you to check the sensor’s signal strength and frequency, ensuring it’s within the acceptable range.
- Using an Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope provides a visual representation of the sensor’s signal waveform. This method offers a detailed analysis of the signal’s frequency, amplitude, and shape, helping identify any irregularities.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting the test results requires understanding the expected behavior of a wheel speed sensor. Here’s a guide to help you identify potential problems:
- No Output: If the sensor doesn’t generate any output, it indicates a faulty sensor, a broken wire, or a problem with the sensor’s power supply.
- Constant Voltage: A constant voltage output suggests the sensor is not detecting wheel rotation, indicating a malfunctioning sensor or a broken wire.
- Intermittent Output: An intermittent output indicates a loose connection, a damaged wire, or a failing sensor.
- Signal Strength and Frequency: The signal strength and frequency should be within the specified range for the particular vehicle model. Deviations from this range could indicate a faulty sensor or a problem with the vehicle’s computer.
Additional Considerations and Maintenance

Regular maintenance and inspection of your wheel speed sensors are crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of your vehicle’s safety systems and overall performance. By understanding the importance of sensor maintenance and implementing preventative measures, you can minimize the risk of sensor failure and enjoy a smoother driving experience.
Importance of Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection of your wheel speed sensors are crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of your vehicle’s safety systems and overall performance. By understanding the importance of sensor maintenance and implementing preventative measures, you can minimize the risk of sensor failure and enjoy a smoother driving experience.
- Ensuring Accurate Speed and Distance Readings: Wheel speed sensors play a vital role in providing accurate information about your vehicle’s speed and distance traveled. This data is used by various systems, including the anti-lock braking system (ABS), traction control, and cruise control, to function correctly. Regular inspections ensure that the sensors are providing accurate readings, preventing potential safety hazards.
- Maintaining Optimal Braking Performance: The ABS relies on wheel speed sensor data to distribute braking force effectively to each wheel, preventing wheel lock-up during emergency braking. Faulty sensors can disrupt this process, leading to reduced braking efficiency and an increased risk of accidents.
- Preventing Traction Control System Malfunctions: The traction control system uses wheel speed sensor data to detect wheel slip and adjust engine power or braking force to regain traction. Faulty sensors can compromise the traction control system’s ability to maintain control, increasing the risk of skidding or loss of control, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Ensuring Cruise Control Accuracy: Cruise control relies on accurate wheel speed sensor readings to maintain a constant speed. Faulty sensors can cause the cruise control system to fluctuate or even disengage, potentially leading to unintended acceleration or deceleration.
Preventing Future Sensor Failures
Here are some tips to help prevent future sensor failures:
- Regular Inspections: As part of routine vehicle maintenance, have your wheel speed sensors inspected by a qualified mechanic. This inspection should include checking for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Keep Sensors Clean: Dirt, debris, and road grime can accumulate on the sensor’s tip, affecting its ability to accurately detect wheel rotation. Regularly clean the sensors with a soft brush and compressed air to ensure optimal performance.
- Avoid Excessive Wheel Wear: Worn-out tires and uneven tire wear can put stress on the wheel speed sensors, potentially leading to damage or premature failure. Ensure your tires are properly inflated and rotated regularly to minimize wear and tear.
- Protect Sensors from Damage: Be mindful of potential hazards that could damage the wheel speed sensors, such as sharp objects or road debris. When working on your vehicle’s brakes or suspension, take care not to damage the sensors.
Consequences of Ignoring a Faulty Wheel Speed Sensor
Ignoring a faulty wheel speed sensor can have serious consequences, including:
- Reduced Braking Efficiency: A faulty wheel speed sensor can disrupt the anti-lock braking system (ABS), potentially leading to wheel lock-up during emergency braking. This can significantly reduce braking distance and increase the risk of accidents.
- Loss of Traction Control: A malfunctioning sensor can compromise the traction control system’s ability to maintain control, increasing the risk of skidding or loss of control, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Inaccurate Speed and Distance Readings: Faulty sensors can provide inaccurate information about your vehicle’s speed and distance traveled, affecting the performance of other systems, such as cruise control and navigation.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A faulty wheel speed sensor can affect the engine’s fuel injection system, leading to increased fuel consumption and reduced fuel efficiency.
- Potential Safety Hazards: A malfunctioning wheel speed sensor can significantly compromise your vehicle’s safety systems, increasing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Replacing a wheel speed sensor is a straightforward process that can be tackled with a few essential tools and a little patience. By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you can confidently tackle this repair and restore your vehicle’s braking and stability systems to their optimal performance. Remember, safety is paramount, so always prioritize your well-being and follow proper safety precautions when working on your vehicle.
FAQ
What are the signs of a faulty wheel speed sensor?
Common symptoms include the ABS light illuminating on the dashboard, erratic braking, a loss of traction control, and a speedometer that fluctuates or stops working.
Can I drive with a faulty wheel speed sensor?
While it’s possible to drive with a faulty wheel speed sensor, it’s not recommended. Driving with a malfunctioning sensor can compromise your safety, especially during emergency braking or in slippery conditions.
How long does it take to replace a wheel speed sensor?
The replacement time varies depending on the vehicle and accessibility of the sensor. It typically takes between 30 minutes to an hour for a skilled mechanic.