Do front wheel drive cars have rear brakes – Do front-wheel drive cars have rear brakes? This question often sparks curiosity among car enthusiasts and those seeking to understand the intricacies of vehicle mechanics. While the front wheels handle the power and acceleration, the rear brakes play a vital role in ensuring stability and control during braking, even in front-wheel drive vehicles.
This article delves into the world of front-wheel drive (FWD) vehicles, exploring the importance of rear brakes in maintaining safe and efficient braking performance. We’ll discuss the fundamental principles of FWD, the role of brakes in general, and the specific design and functionality of rear brakes in FWD cars. By understanding these concepts, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex engineering that goes into modern vehicles and how rear brakes contribute to a smooth and safe driving experience.
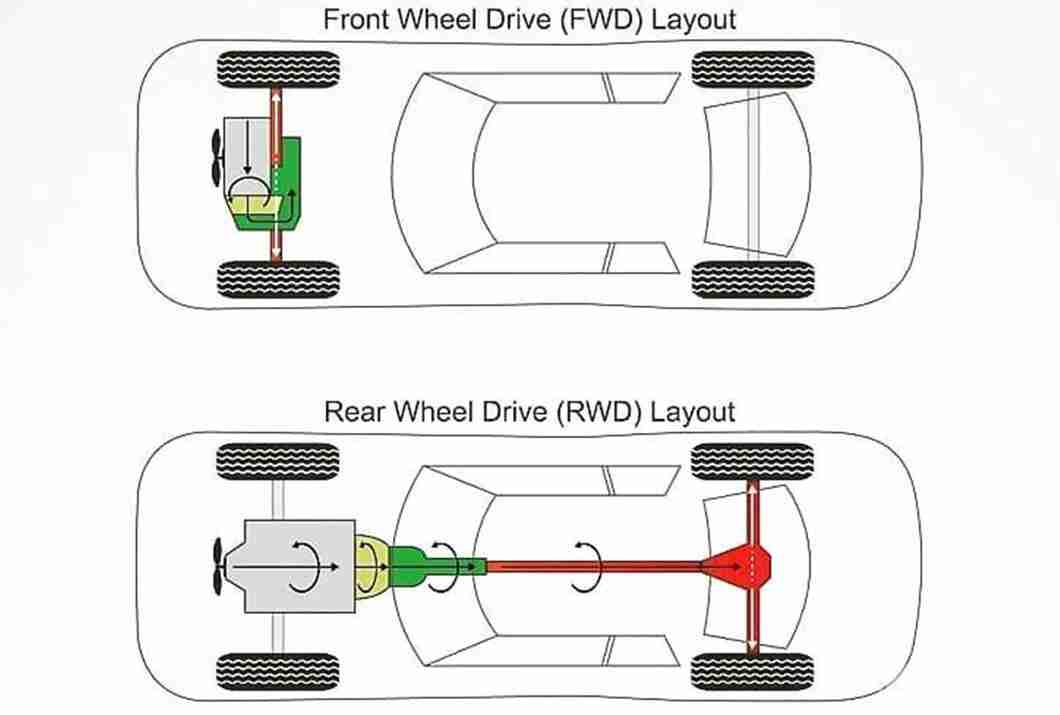
Introduction to Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is a type of drivetrain system in automobiles where the engine’s power is transmitted to the front wheels, which are responsible for both driving and steering the vehicle. This configuration is widely used in modern cars, particularly in smaller and more fuel-efficient models.FWD systems are designed to deliver power efficiently to the front wheels, allowing for better traction on slippery surfaces like snow or ice.
This is because the weight of the engine and transmission is positioned over the drive wheels, providing more grip.
Advantages of Front-Wheel Drive
The advantages of FWD systems are numerous, making them a popular choice for many car manufacturers.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: FWD systems are generally more fuel-efficient than rear-wheel drive (RWD) systems. This is because the front wheels only need to handle the steering and driving forces, while the rear wheels are free to rotate more efficiently.
- Increased Space Efficiency: FWD vehicles typically have a more spacious interior than RWD vehicles because the drivetrain components are located in the front, leaving more room for passengers and cargo.
- Enhanced Traction in Slippery Conditions: FWD vehicles tend to have better traction in slippery conditions, such as snow or ice, due to the weight distribution over the drive wheels.
- Lower Production Costs: FWD systems are generally less expensive to manufacture than RWD systems, making them a more cost-effective option for car manufacturers.
Disadvantages of Front-Wheel Drive
While FWD systems offer numerous advantages, they also have some drawbacks.
- Torque Steer: Torque steer is a phenomenon that can occur in FWD vehicles when the engine produces a lot of torque. This can cause the steering wheel to pull in one direction, especially during acceleration.
- Limited Performance: FWD vehicles generally have a lower performance potential compared to RWD vehicles, especially in terms of handling and acceleration.
- Less Engaging Driving Experience: FWD vehicles can feel less engaging to drive than RWD vehicles, as the driver has less control over the car’s dynamics.
Examples of Popular FWD Vehicles, Do front wheel drive cars have rear brakes
Many popular and widely-used vehicles employ FWD systems, including:
- Honda Civic: A compact car known for its fuel efficiency, reliability, and spacious interior.
- Toyota Corolla: Another popular compact car known for its reliability, affordability, and fuel efficiency.
- Ford Focus: A compact car with a sporty driving experience and a range of engine options.
- Volkswagen Golf: A popular hatchback known for its handling, performance, and interior quality.
- Chevrolet Cruze: A compact car with a comfortable ride and a range of features.
The Role of Brakes in a Vehicle

Brakes are essential safety components in any vehicle, enabling drivers to control the speed and stop the vehicle safely. They work by converting kinetic energy into heat energy, slowing down the wheels and bringing the vehicle to a halt.
Types of Brakes
The braking system in a vehicle comprises different types of brakes. The two most common types are disc brakes and drum brakes.
- Disc Brakes: Disc brakes are commonly found on modern vehicles, particularly on the front wheels. They consist of a disc (rotor) attached to the wheel, a caliper that houses brake pads, and a hydraulic system. When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure forces the brake pads against the disc, creating friction and slowing down the wheel.
- Drum Brakes: Drum brakes are typically used on the rear wheels of older vehicles. They consist of a drum, brake shoes, and a hydraulic system. When the brake pedal is pressed, the hydraulic system forces the brake shoes against the inside of the drum, creating friction and slowing down the wheel.
Brake Balance
Brake balance refers to the distribution of braking force between the front and rear wheels. It is crucial for maintaining vehicle stability during braking. Proper brake balance ensures that the vehicle stops in a straight line without skidding or veering.
A well-balanced braking system ensures that the vehicle stops smoothly and predictably, even under challenging conditions.
Braking Systems in FWD Cars
Front-wheel drive (FWD) cars have a braking system designed to work effectively with the powertrain and the vehicle’s weight distribution. This system ensures safe and controlled stopping, even when the engine is providing power to the front wheels.
Components of a Typical FWD Braking System
The braking system in FWD cars is similar to that in rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, with key components that work together to slow down the car. These components include:
- Brake Calipers: These are clamps that house the brake pads and apply pressure to the brake rotors. In FWD cars, calipers are typically mounted on the front and rear wheels.
- Brake Rotors: These are metal discs that rotate with the wheels. When the brake pads are pressed against the rotors, friction is generated, slowing the wheels down.
- Brake Pads: These are friction materials that are pressed against the rotors by the calipers. The friction created between the pads and rotors generates heat, which is dissipated by the braking system.
- Master Cylinder: This is a hydraulic pump that is activated by the brake pedal. When the brake pedal is pressed, the master cylinder pushes brake fluid through the brake lines to the calipers.
- Brake Lines: These are tubes that carry brake fluid from the master cylinder to the calipers. The brake lines are typically made of steel or rubber.
- Brake Booster: This is a vacuum-powered device that assists the driver in applying brake pressure. It amplifies the force applied to the brake pedal, making it easier to stop the car.
Interaction with the Powertrain
The braking system in FWD cars interacts with the powertrain to ensure efficient braking. The engine’s torque is transmitted to the front wheels, which are also responsible for braking. The braking system must be designed to handle the additional load placed on the front wheels during braking.
In FWD cars, the braking system needs to be designed to handle the combined load of engine power and braking forces, which are both applied to the front wheels.
FWD cars often have larger brake rotors and calipers on the front wheels compared to the rear wheels. This helps to provide more braking force to the front wheels, which are under greater load during braking.
The Need for Rear Brakes in FWD Cars: Do Front Wheel Drive Cars Have Rear Brakes
While front-wheel-drive (FWD) cars send power to the front wheels, they still require rear brakes to maintain stability and control during braking. The rear brakes play a crucial role in balancing the braking forces and preventing the vehicle from skidding.
Rear Brakes and Vehicle Stability
Rear brakes are essential for maintaining stability in FWD cars, even though the engine power is directed to the front wheels. This is because the weight distribution shifts towards the front during braking, increasing the load on the front wheels. This shift in weight can lead to the rear wheels losing traction, causing instability and potential skidding.The rear brakes help to counteract this weight shift by applying braking force to the rear wheels.
This helps to keep the rear wheels firmly planted on the ground, preventing them from locking up and causing the car to skid.
Rear Brakes and Directional Control
Rear brakes also play a critical role in maintaining directional control during braking. When the front brakes are applied, the car’s nose tends to dive down, which can lead to the rear end swinging out. The rear brakes help to counter this effect by applying braking force to the rear wheels, helping to keep the car aligned with the intended direction of travel.
- Preventing Skidding: The rear brakes help to prevent the rear wheels from locking up during hard braking. This is crucial for maintaining control and preventing the vehicle from skidding out of control.
- Maintaining Directional Control: Rear brakes help to keep the car aligned with the intended direction of travel during braking. This is especially important when braking on slippery surfaces, where the rear wheels are more prone to losing traction.
- Optimizing Braking Performance: Rear brakes help to distribute braking forces evenly across all four wheels, maximizing braking efficiency and reducing stopping distances.
In essence, rear brakes in FWD cars act as a stabilizing force, preventing the rear wheels from losing traction and helping the driver maintain control during braking.
Rear Brake Design and Functionality in FWD Cars

While front-wheel drive (FWD) cars are known for their front wheels handling the power delivery and steering, rear brakes play a crucial role in ensuring stability and control during braking. Understanding the design and functionality of rear brakes in FWD cars is essential for appreciating their importance in overall vehicle performance.
Rear Brake Design in FWD Cars
The rear brake design in FWD cars is generally similar to that found in rear-wheel drive (RWD) cars, employing either drum brakes or disc brakes. However, there are some key differences that stem from the unique characteristics of FWD vehicles.
- Drum Brakes: Drum brakes, while less common in modern cars, are still found in some FWD models. They consist of a brake drum, brake shoes, and a wheel cylinder. When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure forces the brake shoes to expand against the drum, creating friction and slowing the wheel.
- Disc Brakes: Disc brakes are more prevalent in FWD cars due to their superior performance and durability. They consist of a brake disc attached to the wheel hub, a brake caliper, and brake pads. When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure forces the brake pads to clamp onto the disc, generating friction and slowing the wheel.
Rear Brake Operation in FWD Cars
The operation of rear brakes in FWD cars is largely similar to that in RWD cars, relying on hydraulic pressure to engage the brakes. However, the braking force distribution between the front and rear wheels is significantly different.
- Braking Force Distribution: In FWD cars, the majority of the braking force is applied to the front wheels, typically around 70-80%. This is because the front wheels are responsible for both steering and braking, and they experience a higher weight transfer during braking. The rear wheels, while still contributing to braking, experience less weight transfer and therefore receive a smaller proportion of the braking force.
Role of ABS in Rear Brake Functionality
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) plays a vital role in optimizing rear brake functionality in FWD cars.
- Preventing Wheel Lock-up: ABS prevents the rear wheels from locking up during hard braking. When the wheels lock up, the car loses traction and becomes difficult to control. ABS monitors wheel speed and applies the brakes in a pulsing manner, preventing the wheels from locking up and maintaining traction.
- Maintaining Stability: By preventing wheel lock-up, ABS helps maintain vehicle stability during braking, particularly in slippery conditions. This is especially important in FWD cars, where the rear wheels can lose traction more easily due to the reduced braking force.
Common Misconceptions About FWD Brakes
Many people have misconceptions about the braking systems in front-wheel-drive (FWD) cars. These misconceptions often stem from a lack of understanding of how FWD vehicles function and the role of rear brakes in their overall stability. This section aims to clarify these misconceptions and highlight the crucial role of rear brakes in FWD cars.
The Effectiveness of Rear Brakes in FWD Cars
A common misconception is that rear brakes are less important in FWD cars because the front wheels are responsible for both acceleration and braking. However, this is not entirely accurate. While the front brakes do handle the majority of the braking force, rear brakes play a critical role in maintaining stability and preventing skidding, especially during emergency braking or cornering.
- Enhanced Stability: Rear brakes help to maintain vehicle stability during braking by counteracting the weight transfer to the front wheels. This transfer occurs as the car slows down, and the front wheels bear more weight, potentially causing them to lock up if only the front brakes are applied.
- Reduced Skidding: Rear brakes also help to prevent the rear wheels from locking up, which can lead to skidding and loss of control. When the rear wheels lock up, the car loses its ability to steer effectively, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Improved Handling: Rear brakes contribute to better handling by helping to balance the braking forces between the front and rear axles. This balanced braking ensures a more controlled and predictable braking experience, especially during cornering or when encountering slippery surfaces.
Rear Brakes Do Not Just “Help”
It is important to note that rear brakes are not simply there to “help” the front brakes. They play a crucial role in maintaining vehicle stability and control, especially during critical braking situations.
Rear brakes are not merely supplementary to front brakes in FWD cars; they are integral to maintaining vehicle stability and control.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
Proper maintenance of the rear brakes in front-wheel drive (FWD) cars is crucial for ensuring safe and reliable braking performance. Neglecting rear brake maintenance can lead to various problems, compromising the vehicle’s stability and potentially causing accidents.
Importance of Regular Rear Brake Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the rear brakes in FWD cars is essential for maintaining optimal braking performance and ensuring the vehicle’s safety. Neglecting rear brake maintenance can lead to various problems, compromising the vehicle’s stability and potentially causing accidents.
- Inspecting brake pads and rotors: Regularly inspecting brake pads and rotors for wear and tear is crucial. Worn-out brake pads can lead to reduced braking effectiveness, while damaged rotors can cause uneven braking and noise.
- Checking brake fluid levels and condition: Brake fluid plays a vital role in transferring pressure from the brake pedal to the calipers, which then squeeze the brake pads against the rotors. Over time, brake fluid can absorb moisture, reducing its effectiveness and leading to brake fade. It is essential to check the brake fluid level regularly and replace it as needed.
- Lubricating brake components: Lubricating brake components such as caliper pins and slider pins helps to prevent them from seizing up, which can lead to uneven braking and premature wear.
- Inspecting brake lines and hoses: Brake lines and hoses can deteriorate over time, leading to leaks and loss of brake fluid. It is important to inspect them regularly for signs of damage or corrosion.
Consequences of Neglecting Rear Brake Maintenance
Neglecting rear brake maintenance can lead to several serious consequences, compromising the vehicle’s safety and potentially causing accidents.
- Reduced braking effectiveness: Worn-out brake pads and rotors can significantly reduce braking effectiveness, increasing the stopping distance and making it harder to control the vehicle.
- Uneven braking: Damaged brake components can lead to uneven braking, making the vehicle difficult to control and potentially causing it to swerve or skid.
- Brake fade: Contaminated brake fluid can lead to brake fade, a condition where the brakes lose their effectiveness under heavy braking.
- Increased risk of accidents: Neglecting rear brake maintenance can significantly increase the risk of accidents, especially in emergency situations where quick and effective braking is crucial.
In conclusion, while front-wheel drive cars primarily utilize their front wheels for power and acceleration, rear brakes are essential for maintaining stability and control during braking. These brakes contribute to balanced braking force distribution, prevent skidding, and ensure a safe and predictable stopping experience. Understanding the importance of rear brakes in FWD vehicles is crucial for drivers and mechanics alike, ensuring proper maintenance and safe operation of these vehicles on the road.
FAQ Guide
Do front-wheel drive cars have better fuel efficiency than rear-wheel drive cars?
Generally, front-wheel drive cars tend to have better fuel efficiency compared to rear-wheel drive cars. This is because FWD systems are typically lighter and simpler, reducing the overall weight and power requirements for the vehicle.
Are rear brakes less important in front-wheel drive cars?
While front brakes handle the majority of braking force in FWD cars, rear brakes are still crucial for stability and control. They help prevent the rear wheels from locking up, which can lead to skidding and loss of control.
Can I replace the rear brakes myself on a front-wheel drive car?
While it’s possible for some individuals with mechanical experience to replace rear brakes themselves, it’s recommended to consult a professional mechanic for proper installation and safety considerations.