How many wheels do tricycles have? The answer, of course, is three, but that simple fact opens a door to a fascinating world of transportation, design, and cultural significance. From the humble children’s toy to specialized adult vehicles, tricycles have played a vital role in human history, evolving alongside our needs and ingenuity.
This exploration delves into the anatomy, types, and uses of tricycles, revealing the unique advantages of their three-wheeled design and showcasing the diverse ways they’ve impacted societies around the globe.
Introduction to Tricycles

A tricycle is a three-wheeled vehicle, typically powered by human effort, and used for transportation, recreation, or as a toy. The basic design consists of two wheels at the rear and one wheel at the front, providing stability and ease of maneuverability. Tricycles have a rich history, dating back centuries. They were initially used for practical purposes, such as hauling goods and transporting people.
Historical Examples of Tricycles
Tricycles have been around for a long time, with evidence suggesting their existence in ancient civilizations. For instance, in the 18th century, a French inventor named Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot built a steam-powered tricycle that is considered one of the first self-propelled vehicles. In the 19th century, tricycles gained popularity as a mode of transportation, particularly in Europe and the United States.
The development of the bicycle led to the decline of tricycles as a primary mode of transport, but they remained popular as toys for children and as recreational vehicles.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Using Tricycles
Tricycles offer several advantages, making them suitable for various purposes. They are generally considered more stable than bicycles, making them easier to balance and control, especially for young children or individuals with balance issues. They are also easier to maneuver in tight spaces and on uneven terrain, making them suitable for use in urban environments or off-road adventures.However, tricycles also have some drawbacks.
They are typically heavier and less efficient than bicycles, making them less suitable for long distances or high-speed travel. They also have a lower turning radius than bicycles, making them less agile in tight spaces.
The Anatomy of a Tricycle
A tricycle, like any other vehicle, comprises various components that work together to enable its functionality. Understanding the anatomy of a tricycle is crucial for comprehending its mechanics and appreciating its design. This section delves into the key parts of a tricycle, exploring their roles and how they contribute to the overall structure and operation.
The Frame
The frame serves as the backbone of the tricycle, providing structural support and holding all other components in place. It is typically made of durable materials such as steel or aluminum, depending on the type and intended use of the tricycle. The frame’s design determines the overall shape and size of the tricycle, influencing its stability, maneuverability, and weight distribution.
The Wheels
Tricycles typically have three wheels, as their name suggests, each serving a specific purpose. The front wheel is responsible for steering and direction control, while the two rear wheels provide stability and support the weight of the rider and the tricycle itself. The size and type of wheels can vary significantly depending on the intended use of the tricycle. For instance, tricycles designed for children often have smaller, lighter wheels, while adult tricycles might have larger wheels for greater stability and smoother riding on different terrains.
The Handlebars
The handlebars are connected to the front wheel and allow the rider to steer the tricycle. They are typically made of metal or plastic and can come in various shapes and sizes. The handlebars are often equipped with grips for a comfortable hold and may include additional controls, such as brakes or gears.
The Seat
The seat provides a comfortable and supportive position for the rider. It is usually padded and adjustable to accommodate riders of different heights and preferences. The seat height can be adjusted to ensure proper leg positioning and comfortable pedaling.
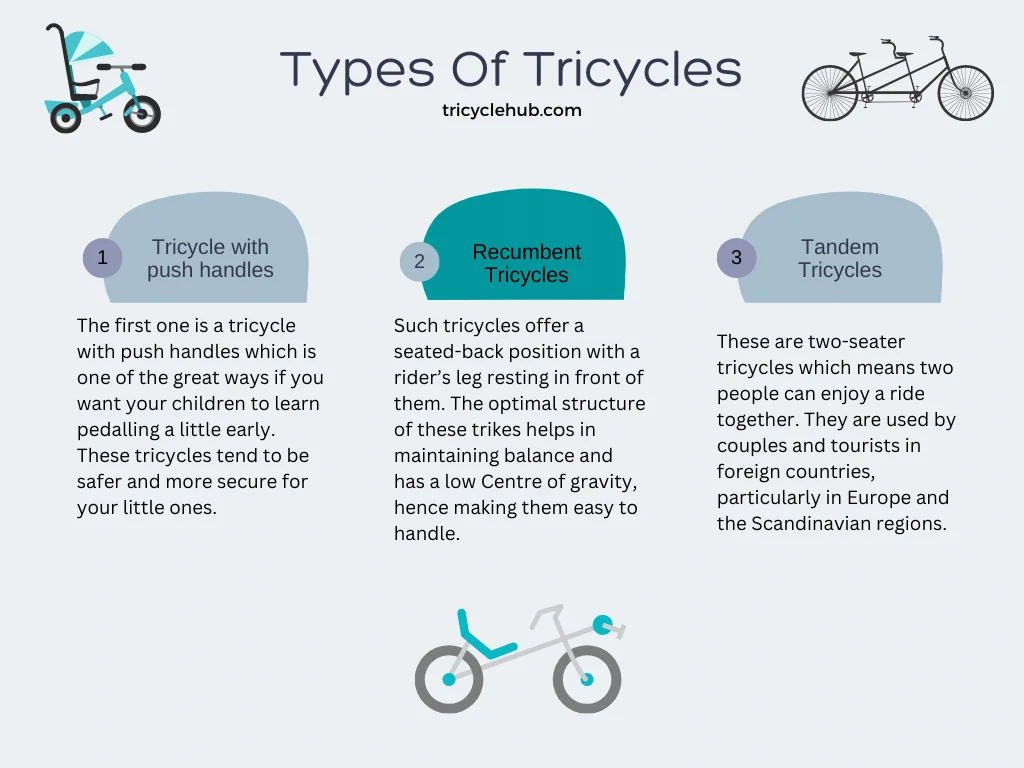
Types of Tricycles
Tricycles are a versatile form of transportation, available in various designs catering to diverse needs and purposes. From children’s toys to adult transportation and cargo hauling, tricycles offer a unique blend of stability and maneuverability.
Classification of Tricycles
Tricycles can be broadly categorized based on their intended use, each type offering specific features and benefits.
- Children’s Tricycles: Designed for young children, these tricycles are typically smaller and lighter, with features like training wheels and adjustable seats. They are primarily used for recreational purposes, promoting balance and coordination in children.
- Adult Tricycles: These tricycles are designed for adult riders and come in various configurations, including recumbent, upright, and folding models. They offer a comfortable and stable riding experience, making them suitable for recreational cycling, commuting, and fitness purposes.
- Cargo Tricycles: These tricycles are built for hauling goods and come in various sizes and designs. They feature robust frames, large cargo compartments, and often have electric assist systems for easier transportation. Cargo tricycles are commonly used for deliveries, transporting goods, and carrying heavy loads.
Features and Comparisons, How many wheels do tricycles have
Different types of tricycles offer unique features that cater to their intended use.
- Children’s Tricycles: They typically have low seats, handlebars designed for smaller hands, and training wheels to provide stability. Many also feature a basket or storage compartment for toys or snacks.
- Adult Tricycles: Adult tricycles offer various features, including adjustable seats, handlebars, and gears. Some models have suspension systems for a smoother ride, while others include electric assist systems for added power. Recumbent tricycles provide a more comfortable riding position, while upright models offer a more traditional feel.
- Cargo Tricycles: Cargo tricycles are characterized by their robust frames, large cargo compartments, and often include features like electric assist systems, brakes, and lights. They are designed for hauling heavy loads and may feature specialized attachments for specific applications.
Examples of Tricycles
The following table provides examples of tricycles in each category, highlighting their intended use, features, and materials:
| Type | Example | Intended Use | Features | Materials |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children’s Tricycle | Radio Flyer Classic Tricycle | Recreational use for young children | Adjustable seat, training wheels, basket | Steel, plastic |
| Adult Tricycle | Sun Bicycles Easy Rider Tricycle | Recreational cycling, commuting | Adjustable seat, handlebars, gears, suspension | Aluminum, steel |
| Cargo Tricycle | Yuba Mundo Electric Cargo Tricycle | Deliveries, transporting goods | Electric assist system, large cargo compartment, robust frame | Aluminum, steel |
The Importance of Three Wheels
The three-wheeled design of a tricycle is not merely a quirky quirk of engineering; it serves a crucial purpose. The addition of a third wheel fundamentally alters the dynamics of a vehicle, offering distinct advantages over its two-wheeled counterparts.
Stability and Maneuverability
The presence of three wheels significantly enhances a vehicle’s stability, particularly at low speeds. This is because the three-point contact with the ground provides a wider base of support, making it more resistant to tipping over. In contrast, a two-wheeled vehicle relies on a smaller base and is more susceptible to losing balance, especially when turning or encountering uneven terrain.
This stability is paramount for young children learning to ride, ensuring a safe and enjoyable experience.
“The larger the base of support, the greater the stability.”
The three-wheeled design also influences maneuverability. While a tricycle might not be as nimble as a bicycle when navigating tight corners, its wider turning radius offers greater control and safety, particularly for beginners. The extra wheel provides a more predictable turning experience, allowing for smoother transitions and reducing the risk of sudden instability.
Tricycles in Different Cultures: How Many Wheels Do Tricycles Have

Tricycles are a ubiquitous form of transportation and recreation across the globe, with their unique designs and applications reflecting the diverse needs and cultural contexts of different societies. From bustling city streets to rural villages, tricycles have carved out a niche in various cultures, showcasing their adaptability and versatility.
Tricycles in Asia
Tricycles have a long history in Asia, with their use dating back centuries. In many Asian countries, tricycles are a common sight, serving as a primary mode of transportation for both people and goods.
- Bajaj Auto-rickshaws in India, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka are iconic three-wheeled vehicles used for public transportation. These auto-rickshaws are a vital part of urban life, providing affordable and accessible transportation to millions of people.
- Tuk-tuks in Thailand, Cambodia, and Laos are similar to auto-rickshaws but often feature distinctive decorations and colourful designs. They are a popular mode of transportation for tourists and locals alike, offering a unique and exhilarating ride through the streets.
- Becak in Indonesia are traditional human-powered tricycles used for passenger transport. These tricycles are a common sight in many Indonesian cities, particularly in areas where motorised vehicles are limited.
In addition to transportation, tricycles are also used for various other purposes in Asia. For instance, in Vietnam, xe om, or motorcycle taxis, are widely used, with many opting for three-wheeled versions for greater stability and carrying capacity. Tricycles are also commonly used in agriculture and construction, providing a cost-effective and versatile solution for transporting goods and materials.
Tricycles in Africa
In Africa, tricycles are an essential part of transportation, particularly in rural areas where road infrastructure is limited.
- Velomobiles are human-powered tricycles that are gaining popularity in Africa, offering a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to motorised vehicles. These tricycles are often used for transporting goods, passengers, and even livestock.
- Tricycles modified for cargo transport are commonly used in many African countries, particularly in West Africa, for transporting goods to markets and other destinations. These tricycles are often fitted with large cargo boxes or platforms to maximise their carrying capacity.
Beyond transportation, tricycles also play a significant role in recreational activities in Africa. In many communities, tricycles are used for cycling, racing, and other forms of entertainment.
Tricycles in Europe
In Europe, tricycles are often associated with leisure and recreation.
- Adult tricycles are popular among older adults and individuals with mobility challenges, providing a safe and comfortable way to enjoy cycling.
- Cargo tricycles are gaining popularity in European cities, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to cars for transporting goods. These tricycles are often used by businesses and individuals for deliveries, errands, and other purposes.
- Recumbent tricycles are a popular choice for recreational cycling, offering a comfortable and aerodynamic riding experience. These tricycles are often used for long-distance cycling and touring.
While tricycles are not as prevalent as in other parts of the world, they have found a niche in Europe, catering to specific needs and preferences.
Tricycles in North America
In North America, tricycles are primarily used for recreational purposes.
- Children’s tricycles are a popular toy, helping children develop their balance and coordination skills.
- Adult tricycles are becoming increasingly popular as a form of exercise and recreation, particularly among older adults and individuals with mobility challenges.
- Cargo tricycles are gaining popularity in North American cities, offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to cars for transporting goods.
Tricycles are also used for various other purposes in North America, such as in parades, festivals, and community events.
Tricycles, with their simple yet ingenious design, demonstrate the power of adaptation and innovation. They have served as both practical transportation and playful companions, adapting to different needs and cultures throughout history. As we continue to explore new ways to move and interact with our environment, the tricycle stands as a reminder of the enduring value of simple, yet effective solutions.
FAQ
Are tricycles only for children?
No, while tricycles are popular for children, they are also used by adults for various purposes, including transportation, cargo hauling, and recreation.
Why are tricycles more stable than bicycles?
The extra wheel provides a wider base, increasing stability and making it easier to balance. This makes tricycles ideal for young children and individuals who find bicycles challenging.
What are some examples of tricycles used in different cultures?
From the traditional “trishaw” in Southeast Asia used for transportation to the “velomobile” in Europe designed for speed and efficiency, tricycles have found unique applications in various cultures.