How to test a ABS wheel sensor, a crucial component of your vehicle’s braking system, is a skill every car owner should possess. Understanding the function of these sensors and how to diagnose their health can help prevent dangerous driving situations and ensure your safety on the road. ABS wheel sensors, also known as speed sensors, are responsible for detecting the speed of each wheel and transmitting this information to the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) control module.
This information is vital for the ABS to properly activate and prevent wheel lock-up during emergency braking, allowing you to maintain steering control and avoid skidding.
The effectiveness of your ABS system hinges on the accurate operation of these sensors. Over time, they can be susceptible to wear and tear, damage from road debris, or electrical malfunctions. When a sensor malfunctions, it can lead to a range of issues, including an illuminated ABS warning light on your dashboard, a decrease in braking performance, or even a complete failure of the ABS system.
Understanding ABS Wheel Sensors
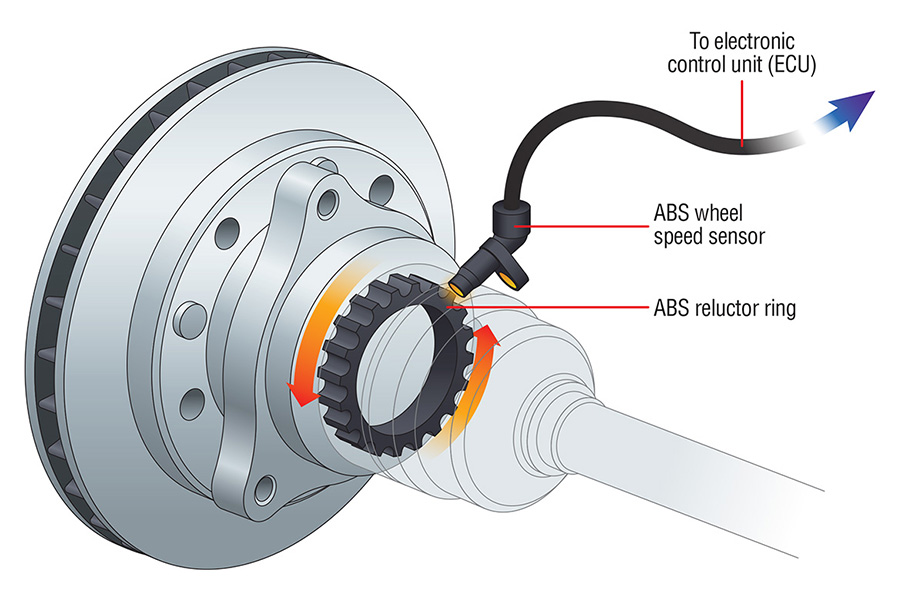
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) is a safety feature in vehicles that prevents wheel lock-up during braking, enhancing vehicle control and stability. A crucial component of this system is the ABS wheel sensor, which plays a vital role in detecting wheel speed and transmitting this information to the ABS control unit.
Types of ABS Wheel Sensors
ABS wheel sensors are classified into different types based on their working principles and construction.
- Passive Sensors: These sensors rely on a magnetic field generated by a permanent magnet within the sensor. As the wheel rotates, the teeth on the wheel’s tone ring interrupt the magnetic field, generating a signal that is transmitted to the ABS control unit. This signal frequency is proportional to the wheel’s rotational speed.
- Active Sensors: These sensors employ an electromagnetic coil that generates a magnetic field. When the wheel rotates, the tone ring’s teeth interrupt the magnetic field, inducing a voltage in the coil. This voltage is then processed by the ABS control unit to determine the wheel speed.
- Hall Effect Sensors: These sensors utilize the Hall effect principle, where a magnetic field interacts with a semiconductor material to generate a voltage. As the wheel rotates, the tone ring’s teeth pass by the sensor, altering the magnetic field and producing a voltage change. This voltage change is then interpreted by the ABS control unit to measure wheel speed.
How an ABS Wheel Sensor Works
ABS wheel sensors are strategically positioned near the wheel hub, typically mounted on the suspension or brake caliper. The sensor’s core component is the tone ring, a toothed wheel attached to the wheel hub.
- As the wheel rotates, the tone ring’s teeth pass by the sensor, generating a signal that is proportional to the wheel’s speed. This signal is then transmitted to the ABS control unit.
- The ABS control unit analyzes the signal from each wheel sensor to determine the speed of each wheel. This information is then used to monitor wheel slip during braking.
- If the ABS control unit detects wheel lock-up, it rapidly modulates brake pressure to individual wheels, preventing them from locking and maintaining vehicle control.
Components of an ABS Wheel Sensor
- Sensor Housing: This is the protective outer shell that encloses the sensor’s internal components.
- Sensor Element: This is the core component that detects the wheel’s rotation. It can be a magnet, coil, or Hall effect sensor, depending on the sensor type.
- Tone Ring: This toothed wheel is attached to the wheel hub and rotates with the wheel. The teeth interrupt the sensor’s magnetic field, generating a signal.
- Wiring Harness: This connects the sensor to the ABS control unit, transmitting the signal from the sensor to the control unit.
The signal generated by an ABS wheel sensor is a series of pulses, with the frequency of these pulses directly proportional to the wheel’s speed. The ABS control unit interprets these pulses to determine the wheel’s rotational speed.
Common Signs of a Faulty ABS Wheel Sensor: How To Test A Abs Wheel Sensor

A malfunctioning ABS wheel sensor can lead to a variety of issues, ranging from annoying warning lights to potentially dangerous driving conditions. Recognizing the common symptoms of a faulty sensor is crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s safety and preventing costly repairs.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty ABS Wheel Sensor
A faulty ABS wheel sensor can manifest in various ways, depending on the specific sensor that is malfunctioning. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
- ABS Warning Light: The most obvious sign of a faulty ABS wheel sensor is the illumination of the ABS warning light on your dashboard. This light indicates that the ABS system has detected a problem with one or more sensors.
- Braking Issues: A faulty ABS sensor can lead to issues with your braking system. You might experience a delay in braking response, a spongy brake pedal, or even a complete loss of braking power in extreme cases.
- ABS System Deactivation: If the ABS system detects a fault, it might deactivate itself as a safety precaution. This means that your vehicle will not have the benefits of ABS, which could increase the risk of skidding during emergency braking.
- Wheel Speed Sensor Malfunction: In some cases, the faulty sensor might cause the vehicle’s speed gauge to fluctuate or become inaccurate. This is because the speed gauge relies on information from the wheel speed sensors.
- Vehicle Stability Control Issues: If your vehicle is equipped with vehicle stability control (ESC), a faulty ABS sensor can disrupt its operation. This can lead to a loss of stability, especially during cornering or sudden maneuvers.
Potential Causes of ABS Wheel Sensor Symptoms, How to test a abs wheel sensor
The symptoms you experience can vary depending on the specific sensor that is malfunctioning.
| Symptom | Potential Causes |
|---|---|
| ABS Warning Light | Faulty ABS wheel sensor, damaged wiring, or a problem with the ABS control module. |
| Braking Issues | Faulty ABS wheel sensor, damaged wiring, or a problem with the ABS control module. |
| ABS System Deactivation | Faulty ABS wheel sensor, damaged wiring, or a problem with the ABS control module. |
| Wheel Speed Sensor Malfunction | Faulty ABS wheel sensor, damaged wiring, or a problem with the ABS control module. |
| Vehicle Stability Control Issues | Faulty ABS wheel sensor, damaged wiring, or a problem with the ABS control module. |
Examples of Dangerous Driving Conditions
A faulty ABS wheel sensor can create dangerous driving conditions, especially in emergency situations. For example:
- Loss of Braking Power: If the ABS system fails due to a faulty sensor, you might lose braking power during an emergency stop. This could lead to a collision if you are unable to stop in time.
- Skidding: Without ABS, your vehicle is more likely to skid during emergency braking. This can make it difficult to control the vehicle, especially on slippery surfaces.
- Loss of Vehicle Stability: A faulty ABS sensor can disrupt the operation of vehicle stability control, which can lead to a loss of control during cornering or sudden maneuvers. This can result in a rollover or other serious accidents.
Testing the ABS Wheel Sensor
Testing an ABS wheel sensor involves verifying its ability to generate a signal proportional to the wheel’s speed. This signal is essential for the ABS system to function correctly. A multimeter is a handy tool for this task, allowing you to measure the sensor’s output voltage.
Testing the ABS Wheel Sensor with a Multimeter
To test an ABS wheel sensor using a multimeter, you’ll need to understand its basic operation and the expected readings. The sensor generates a voltage that fluctuates with the wheel’s rotation. This voltage is sent to the ABS control module, which interprets it to determine the wheel’s speed.
- Safety Precautions: Before working with any automotive electrical system, it’s crucial to disconnect the battery to prevent electrical shocks. Additionally, avoid working on a hot engine or exhaust system, as this can cause burns.
- Locating the ABS Wheel Sensor: The ABS wheel sensor is typically located near the wheel hub, often mounted on the suspension arm or brake caliper. It might be covered by a protective boot or shield.
- Connecting the Multimeter: Set the multimeter to the AC voltage range. Connect the red probe to the sensor’s signal wire and the black probe to a good ground connection on the vehicle’s chassis.
- Expected Readings: With the wheel stationary, the multimeter should read a low voltage (typically less than 0.5 volts). When the wheel is rotated, the voltage should fluctuate, increasing and decreasing with the wheel’s speed. The voltage amplitude will vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model, but it should be a consistent pattern.
- Interpreting the Results: If the multimeter reads a constant voltage or no voltage at all, it indicates a faulty sensor. Similarly, if the voltage fluctuations are erratic or inconsistent, the sensor may be malfunctioning.
Advanced Testing Methods
While basic testing can pinpoint a faulty ABS wheel sensor, advanced methods offer a more comprehensive diagnosis, particularly when dealing with intermittent issues or complex system malfunctions. These methods utilize specialized tools and procedures, providing deeper insights into the sensor’s functionality and the overall ABS system.
Using a Digital Multimeter
A digital multimeter (DMM) is a versatile tool for testing ABS wheel sensors. It can measure voltage, resistance, and continuity, providing valuable information about the sensor’s electrical characteristics.To test an ABS wheel sensor using a DMM, follow these steps:
- Disconnect the sensor connector from the ABS control module.
- Set the DMM to resistance mode (Ohms).
- Touch the DMM probes to the sensor’s terminals.
- The resistance reading should fall within the manufacturer’s specified range for the particular sensor model.
- If the resistance reading is outside the specified range, the sensor is likely faulty.
Utilizing an Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a specialized instrument that displays electrical signals over time. It can be used to analyze the waveform generated by an ABS wheel sensor, providing insights into its functionality and identifying potential problems.To test an ABS wheel sensor using an oscilloscope, follow these steps:
- Connect the oscilloscope probes to the sensor’s terminals.
- Rotate the wheel while observing the oscilloscope display.
- A healthy sensor will produce a square wave pattern that changes frequency with the wheel’s rotation.
- Any deviations from the expected waveform, such as a distorted or irregular pattern, indicate a faulty sensor.
Employing an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner is a diagnostic tool that communicates with the vehicle’s onboard computer system. It can retrieve error codes that indicate potential problems with the ABS system, including faulty wheel sensors.To diagnose ABS sensor issues using an OBD-II scanner, follow these steps:
- Connect the OBD-II scanner to the vehicle’s diagnostic port.
- Select the ABS system from the scanner’s menu.
- Retrieve any error codes related to ABS wheel sensors.
- Refer to the scanner’s database or a repair manual to interpret the error codes and identify the faulty sensor.
Interpreting Error Codes
OBD-II error codes related to ABS wheel sensors typically start with “C” and may include a specific number that identifies the faulty sensor or a related problem. For example, a code like “C1234” might indicate a fault with the right rear ABS wheel sensor.To understand the meaning of a specific error code, refer to a repair manual, an online database, or the scanner’s own database.
These resources provide detailed descriptions of each error code and potential solutions.
Example:An OBD-II error code “C1234” might indicate a fault with the right rear ABS wheel sensor. This could be due to a damaged sensor, a wiring issue, or a problem with the ABS control module.
Troubleshooting and Repair

Once you’ve identified a faulty ABS wheel sensor, it’s time to tackle the repair. This process involves removing the old sensor, installing a new one, and ensuring proper functionality.
Identifying and Replacing a Faulty ABS Wheel Sensor
The process of identifying and replacing a faulty ABS wheel sensor involves a series of steps that ensure the correct sensor is targeted and the replacement is done effectively.
- Locate the faulty sensor: Using a digital multimeter or a scan tool, you can pinpoint the specific sensor that’s malfunctioning. The multimeter can be used to check the sensor’s resistance, while a scan tool can display error codes that indicate the sensor location.
- Prepare for removal: Before removing the sensor, it’s crucial to disconnect the vehicle’s battery to prevent any electrical hazards. You’ll also need to remove the wheel that corresponds to the faulty sensor.
- Remove the sensor: The sensor is typically secured with a bolt or clip. Carefully remove the sensor from its mounting position, taking care not to damage the surrounding components.
- Install the new sensor: Once the old sensor is removed, install the new sensor in its place, ensuring it’s properly aligned and secured.
- Reconnect the battery: After installing the new sensor, reconnect the vehicle’s battery.
- Test the system: After reconnecting the battery, test the ABS system to ensure the new sensor is working correctly. You can do this by driving the vehicle and checking for any warning lights on the dashboard.
Common Causes of ABS Wheel Sensor Failure
Several factors can contribute to ABS wheel sensor failure. Understanding these causes can help you take preventative measures to extend the life of your sensors.
- Physical damage: The sensor can be damaged due to road debris, impacts, or even excessive brake wear.
- Corrosion: Over time, the sensor can corrode, particularly if exposed to moisture or road salt.
- Wiring issues: Damaged or loose wiring can disrupt the sensor’s signal.
- Electrical interference: Electromagnetic interference from other components in the vehicle can affect the sensor’s performance.
- Heat damage: Excessive heat from the brake system can damage the sensor’s internal components.
Preventing Future Sensor Issues
By taking proactive steps, you can minimize the risk of future ABS wheel sensor failures.
- Regular maintenance: Regularly inspect the sensor for signs of damage, corrosion, or loose wiring.
- Proper brake maintenance: Ensure your brakes are properly maintained to prevent excessive wear and tear on the sensors.
- Avoid driving through deep water: Excessive water exposure can lead to corrosion and damage.
- Use high-quality parts: When replacing a sensor, choose high-quality parts to ensure long-term reliability.
Tools and Materials Needed for Sensor Replacement
To successfully replace an ABS wheel sensor, you’ll need a few essential tools and materials.
- Jack and jack stands: To lift the vehicle and provide safe access to the sensor.
- Lug wrench: To remove the wheel.
- Torque wrench: To tighten the sensor bolt to the correct specification.
- Digital multimeter or scan tool: To diagnose the faulty sensor and test the system after replacement.
- New ABS wheel sensor: The replacement sensor should be compatible with your vehicle model.
- Socket wrench: To remove and install the sensor bolt.
- Protective gloves: To protect your hands from dirt and potential hazards.
Mastering the art of testing an ABS wheel sensor empowers you to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By understanding the basic procedures, using the right tools, and interpreting the results, you can ensure the optimal performance of your vehicle’s braking system. This knowledge will allow you to diagnose potential issues early on, preventing costly repairs and ensuring your safety on the road.
Query Resolution
What are the common causes of ABS wheel sensor failure?
ABS wheel sensor failure can be caused by various factors, including physical damage from road debris, corrosion, wiring issues, and even the wear and tear of the sensor itself.
Can I replace an ABS wheel sensor myself?
While replacing an ABS wheel sensor is a relatively straightforward procedure, it’s recommended to consult a professional mechanic, especially if you’re not comfortable working with automotive electrical systems.
How often should I test my ABS wheel sensors?
It’s advisable to test your ABS wheel sensors as part of your regular vehicle maintenance routine, ideally every 12 months or whenever you notice any unusual braking behavior.