Which wheel bearing is bad turning right? This question can be a source of frustration for any driver, especially when the sound of grinding or roaring fills the cabin. Identifying the culprit can be a puzzle, but understanding the relationship between turning direction and bearing location can lead you to the answer. When a wheel bearing fails, it often creates a noticeable noise, vibration, and handling issues, but the direction of the turn can be a clue to the location of the problem.
The symptoms of a bad wheel bearing can vary depending on the severity of the damage and the location of the bearing. However, a common symptom of a bad wheel bearing when turning right is a loud grinding or roaring noise that increases with speed. This noise is often accompanied by a vibration in the steering wheel or the entire vehicle.
If you notice these symptoms, it is important to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic as soon as possible.
Symptoms of a Bad Wheel Bearing: Which Wheel Bearing Is Bad Turning Right
A bad wheel bearing can cause a variety of symptoms, especially when turning right. The symptoms can be subtle at first, but they will worsen over time if the problem is not addressed. It’s important to understand the different symptoms and how they manifest to diagnose a bad wheel bearing effectively.
Noise During Turning
A common symptom of a bad wheel bearing is noise, particularly when turning. The noise can vary depending on the severity of the damage and the specific bearing involved.
- Grinding noise: This is often a sign of severe damage to the bearing, where the metal components are grinding against each other. This sound is usually louder and more pronounced when turning right.
- Roaring noise: This sound is typically associated with a bearing that is starting to fail. It can be a low-pitched hum or a high-pitched whine, and it will increase in volume as the bearing deteriorates. This sound is often more noticeable when turning right.
- Clicking noise: This sound is often a sign of a bearing that is loose or damaged. It can be a series of clicks or a continuous clicking sound, and it is usually more noticeable when turning right.
Vibration During Turning
Another common symptom of a bad wheel bearing is vibration, especially when turning right. This vibration is often felt in the steering wheel and can be accompanied by a shaking sensation in the vehicle. The vibration is caused by the damaged bearing, which is no longer able to properly support the weight of the vehicle.
Handling Issues
A bad wheel bearing can also cause handling issues, such as a wandering steering wheel, difficulty turning, or a feeling of looseness in the steering. These symptoms are caused by the damaged bearing, which is no longer able to properly support the weight of the vehicle and provide a stable platform for the wheel to rotate.
Differences in Symptoms When Turning Left
While symptoms of a bad wheel bearing are often more pronounced when turning right, they can also be present when turning left. However, the severity of the symptoms may be less noticeable, especially in the early stages of bearing failure. This is because the weight of the vehicle is typically distributed differently when turning left compared to turning right, potentially reducing the strain on the affected bearing.
For instance, a grinding noise might be faint when turning left but become loud and obvious when turning right. Similarly, vibration may be less noticeable when turning left but become more pronounced when turning right.
Identifying the Affected Wheel Bearing
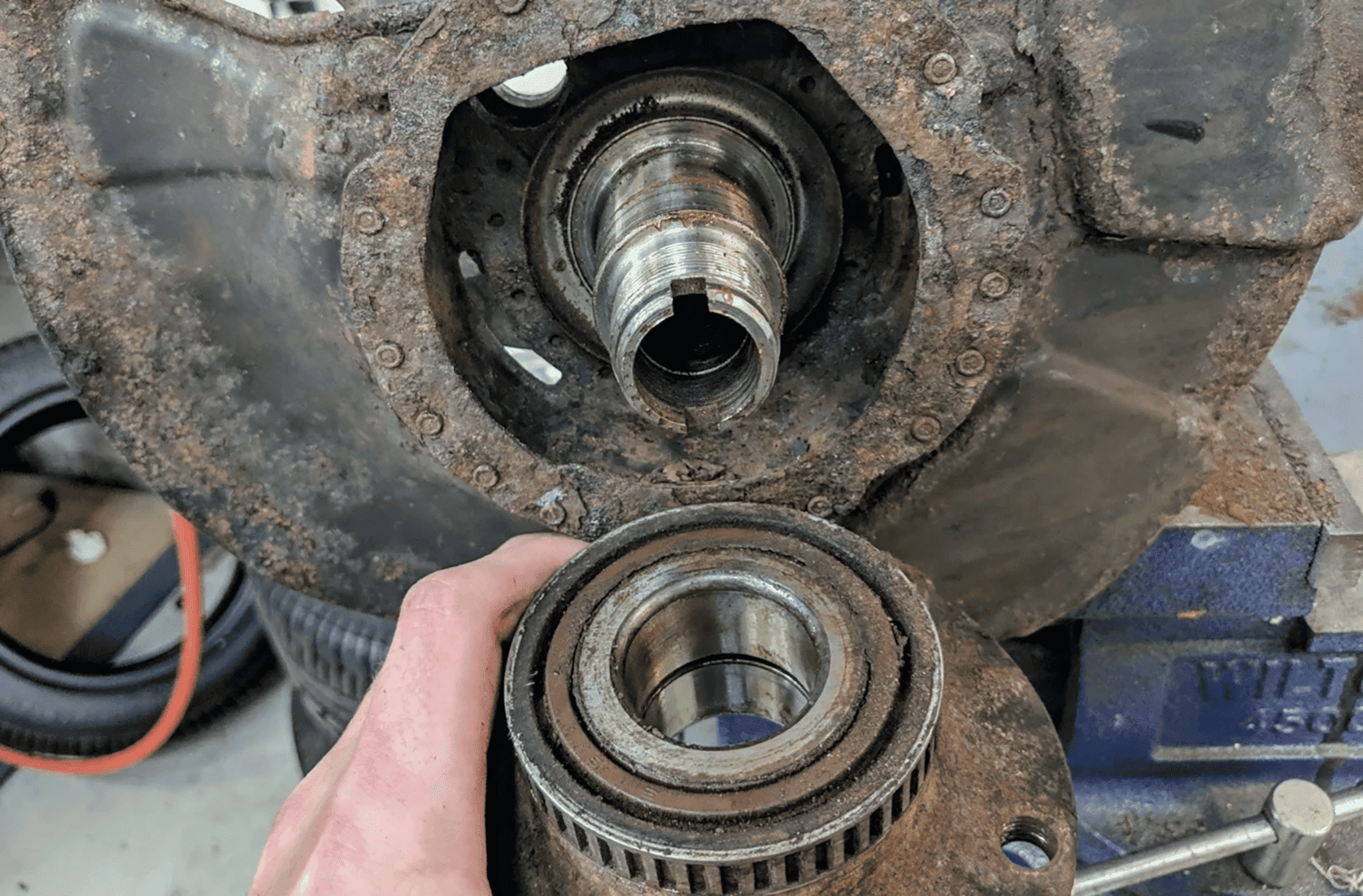
The direction of the turn and the location of the bad wheel bearing are directly related. When a wheel bearing fails, it will often make a noise that is most pronounced when turning in a specific direction. This is because the bearing is under more stress when the wheel is turned, and the noise is amplified as a result.To identify the affected wheel bearing, you will need to pay close attention to the sound and vibration.
The noise will often be a grinding, rumbling, or growling sound, and it will be more pronounced when turning in the direction of the bad bearing. You may also feel a vibration in the steering wheel or the vehicle itself.
Identifying the Affected Wheel Bearing Using Sound and Vibration
The sound and vibration can help pinpoint the affected wheel bearing. Here’s how:
- Front Left Wheel Bearing: If the noise is loudest when turning right, the front left wheel bearing is likely the culprit. This is because the front left wheel bearing is under more stress when turning right. The vibration will also be most noticeable in the steering wheel.
- Front Right Wheel Bearing: If the noise is loudest when turning left, the front right wheel bearing is likely the culprit. This is because the front right wheel bearing is under more stress when turning left. The vibration will also be most noticeable in the steering wheel.
- Rear Left Wheel Bearing: If the noise is loudest when turning right, the rear left wheel bearing is likely the culprit. This is because the rear left wheel bearing is under more stress when turning right. The vibration will also be most noticeable in the vehicle’s rear.
- Rear Right Wheel Bearing: If the noise is loudest when turning left, the rear right wheel bearing is likely the culprit. This is because the rear right wheel bearing is under more stress when turning left. The vibration will also be most noticeable in the vehicle’s rear.
Visual Inspection of the Wheel Bearing
In addition to sound and vibration, a visual inspection of the wheel bearing can help determine if it is faulty. Look for signs of damage, such as:
- Excessive play or movement in the wheel.
- Grease or oil leaks.
- Rust or corrosion on the bearing.
- Damage to the bearing race or balls.
Table of Symptoms for Each Wheel Position
The following table summarizes the symptoms of a bad wheel bearing in each wheel position:
| Wheel Position | Sound | Vibration | Other Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Front Left | Loudest when turning right | Most noticeable in steering wheel | Excessive play or movement in the front left wheel, grease or oil leaks, rust or corrosion on the bearing, damage to the bearing race or balls. |
| Front Right | Loudest when turning left | Most noticeable in steering wheel | Excessive play or movement in the front right wheel, grease or oil leaks, rust or corrosion on the bearing, damage to the bearing race or balls. |
| Rear Left | Loudest when turning right | Most noticeable in vehicle’s rear | Excessive play or movement in the rear left wheel, grease or oil leaks, rust or corrosion on the bearing, damage to the bearing race or balls. |
| Rear Right | Loudest when turning left | Most noticeable in vehicle’s rear | Excessive play or movement in the rear right wheel, grease or oil leaks, rust or corrosion on the bearing, damage to the bearing race or balls. |
Causes of Wheel Bearing Failure
Wheel bearings are essential components of a vehicle’s suspension system, supporting the weight of the vehicle and allowing the wheels to rotate smoothly. However, these bearings can fail prematurely due to a combination of factors, including road conditions, driving habits, and vehicle maintenance. Understanding these causes can help drivers prevent premature wheel bearing failure and ensure a smoother and safer driving experience.
Effects of Road Conditions on Wheel Bearing Longevity
The condition of the roads a vehicle is driven on significantly impacts the lifespan of its wheel bearings. Rough roads, characterized by potholes, bumps, and uneven surfaces, subject wheel bearings to constant shock and vibration, leading to increased wear and tear. This accelerated wear can result in premature bearing failure. Conversely, driving on smooth roads minimizes the impact on wheel bearings, extending their lifespan.
Effects of Driving Habits on Wheel Bearing Longevity, Which wheel bearing is bad turning right
Driving habits can also contribute to wheel bearing failure. Aggressive driving, involving sudden acceleration, braking, and cornering, puts significant stress on wheel bearings. This stress can lead to premature bearing wear and eventual failure. Similarly, driving at high speeds on rough roads can exacerbate the impact on wheel bearings, further accelerating wear and tear.
Effects of Improper Lubrication on Wheel Bearing Longevity
Wheel bearings require proper lubrication to minimize friction and wear. Insufficient lubrication can lead to increased friction, resulting in heat buildup and premature bearing failure. Conversely, excessive lubrication can attract dirt and debris, leading to contamination and increased wear.
Effects of Overloading on Wheel Bearing Longevity
Exceeding a vehicle’s weight capacity puts additional stress on its suspension system, including wheel bearings. Overloading can lead to premature bearing wear and eventual failure. It is crucial to ensure that the vehicle is not overloaded to prevent unnecessary stress on wheel bearings.
Wheel Bearing Inspection and Diagnosis
A thorough inspection is crucial to accurately diagnose a bad wheel bearing. While some signs are noticeable during driving, a visual inspection and other tests can confirm the issue and pinpoint the affected bearing.
Visual Inspection
A visual inspection can reveal signs of damage or wear on the wheel bearing. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Jack up the vehicle and secure it with jack stands. Remove the wheel.
- Inspect the hub assembly for any signs of damage, including cracks, dents, or excessive rust. These can indicate a damaged bearing.
- Check the wheel bearing seal for any signs of leakage. A damaged seal can allow contaminants to enter the bearing, causing premature wear.
- Examine the bearing raceway for any signs of wear or pitting. This can indicate a worn-out bearing.
- Look for any loose or missing components within the hub assembly. This could point to a damaged or missing bearing component.
Using a Stethoscope
A stethoscope can be a valuable tool for diagnosing a bad wheel bearing. It amplifies the sounds coming from the bearing, allowing for a more accurate assessment:
- Position the stethoscope against the hub assembly, near the suspected bearing.
- Listen for any unusual noises, such as grinding, clicking, or roaring. These sounds can indicate a damaged or worn-out bearing.
- Compare the sounds from the suspected bearing to the other bearings on the vehicle. This can help you isolate the problem bearing.
Thorough Inspection by a Qualified Mechanic
While a visual inspection and stethoscope test can provide initial clues, a thorough inspection by a qualified mechanic is essential for a definitive diagnosis:
- A mechanic can use specialized tools to inspect the bearing more thoroughly, such as a bearing raceway gauge and a bearing tester.
- They can also assess the overall condition of the hub assembly and other suspension components, ensuring that the problem is isolated to the bearing and not related to other issues.
- A mechanic can provide professional advice on the best course of action, whether it’s replacing the bearing or addressing other related issues.
Wheel Bearing Replacement Process

Replacing a bad wheel bearing is a relatively straightforward process, but it requires some mechanical aptitude and the right tools. This process involves removing the wheel, hub, and bearing assembly, followed by installing the new bearing and reassembling the components.
Tools and Equipment Required
Before starting the replacement process, ensure you have the necessary tools and equipment. This will make the job much easier and safer.
- Jack and jack stands
- Lug wrench
- Torque wrench
- Wheel bearing puller
- Hammer
- Socket set
- Wrench set
- Penetrating fluid (optional)
- Grease
- Clean rags
- Safety glasses
- Work gloves
Steps Involved in Replacing a Wheel Bearing
The steps involved in replacing a wheel bearing can vary slightly depending on the vehicle make and model. However, the general process remains similar.
- Safety First: Always prioritize safety by parking the vehicle on a level surface, engaging the parking brake, and using jack stands to support the vehicle securely after lifting it with the jack.
- Remove the Wheel: Loosen the lug nuts while the vehicle is still on the ground. Then, jack up the vehicle and remove the wheel.
- Remove the Brake Caliper: Depending on the vehicle, you might need to remove the brake caliper and hang it from the suspension using a wire or a hook. This is usually done to avoid damaging the brake lines.
- Remove the Rotor: Remove the rotor or drum brake assembly, depending on your vehicle’s brake system.
- Remove the Hub Assembly: The hub assembly is attached to the wheel bearing. Use a wheel bearing puller to remove the hub assembly from the spindle.
- Remove the Old Bearing: Once the hub assembly is removed, you can usually separate the bearing from the hub. Some bearings are pressed into the hub, requiring a bearing race remover to extract them.
- Install the New Bearing: Before installing the new bearing, clean the spindle and hub assembly thoroughly. Pack the new bearing with grease, ensuring it is evenly distributed. Some bearings come pre-packed with grease. Install the new bearing using a bearing race installer or by pressing it into the hub using a press.
- Reassemble the Components: Reassemble the hub assembly, rotor or drum brake assembly, and brake caliper in reverse order. Make sure to tighten the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s specified torque.
- Test Drive: After completing the replacement, test drive the vehicle to ensure the new bearing is functioning correctly and that there are no unusual noises or vibrations.
Importance of Using Genuine OEM or High-Quality Replacement Parts
Using genuine OEM or high-quality replacement parts is crucial for several reasons:
- Performance and Durability: OEM or high-quality aftermarket parts are designed and manufactured to meet the specific requirements of your vehicle, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
- Safety: Wheel bearings are critical safety components, and using substandard parts can compromise safety, leading to potential failures and accidents.
- Warranty: Using OEM parts often ensures warranty coverage for the replaced component, giving you peace of mind and protection against defects.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s service manual for specific instructions and torque specifications for your vehicle.
Preventive Maintenance

Proactive wheel bearing maintenance is crucial for preventing premature failure and ensuring a smooth, safe driving experience. Regular inspection and lubrication are key to extending the lifespan of your wheel bearings.
Wheel Bearing Inspection and Lubrication Schedule
A consistent schedule for inspecting and lubricating your wheel bearings is essential for early detection of potential issues and preventing premature wear. The frequency of these tasks depends on various factors, including driving conditions, vehicle age, and the type of grease used.
- New Vehicles: For vehicles under 5 years old, a visual inspection of the wheel bearings should be performed every 12,000 miles or annually, whichever comes first. Lubrication is typically not required during this period unless signs of wear or contamination are observed.
- Older Vehicles: Vehicles over 5 years old require more frequent inspections, ideally every 6,000 miles or semi-annually. Lubrication should be performed at least every 12,000 miles or annually.
- Severe Driving Conditions: If you frequently drive on rough roads, haul heavy loads, or drive in extreme weather conditions, increase the inspection frequency to every 3,000 miles and lubricate every 6,000 miles.
Benefits of High-Quality Grease and Proper Application
Using high-quality grease is essential for protecting your wheel bearings from wear and tear. The right grease provides a protective barrier, reduces friction, and prevents corrosion.
- High-Quality Grease: Choose a grease specifically designed for wheel bearings and that meets the manufacturer’s specifications. Look for greases with high-temperature resistance, excellent water resistance, and good load-carrying capacity. Common types include lithium-based greases, synthetic greases, and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) greases.
- Proper Application: Applying grease correctly is just as important as using the right type. Ensure the bearing races and rollers are thoroughly coated with grease, but avoid over-greasing. Excess grease can create heat and increase friction, leading to premature bearing failure.
Tips for Minimizing Wheel Bearing Failure
By adopting good driving habits and maintaining your vehicle properly, you can significantly reduce the risk of wheel bearing failure.
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Excessive acceleration, braking, and cornering put additional stress on wheel bearings. Driving smoothly and avoiding abrupt maneuvers can help prolong bearing life.
- Maintain Proper Tire Inflation: Underinflated tires increase the load on wheel bearings, leading to faster wear. Ensure your tires are inflated to the manufacturer’s recommended pressure.
- Regular Vehicle Maintenance: Routine maintenance, such as oil changes, brake inspections, and suspension checks, helps identify potential issues before they escalate. This includes checking for signs of wear or damage in the wheel bearings.
- Address Uneven Tire Wear: Uneven tire wear can be a sign of a worn wheel bearing or other suspension issues. If you notice uneven wear, address the underlying problem promptly.
Navigating the world of wheel bearings can be daunting, but understanding the telltale signs of a bad bearing, especially when turning right, can help you identify the issue early on. By recognizing the symptoms, pinpointing the affected wheel, and understanding the potential causes, you can take the necessary steps to ensure a safe and smooth ride. Remember, timely maintenance and a qualified mechanic are your allies in preventing wheel bearing failures and ensuring a safe and enjoyable driving experience.
Detailed FAQs
Can a bad wheel bearing cause a car to pull to one side?
Yes, a bad wheel bearing can cause a car to pull to one side, especially if the bearing is significantly damaged. This is because a bad bearing can cause the wheel to wobble or lose its alignment.
How long can I drive with a bad wheel bearing?
It’s not recommended to drive with a bad wheel bearing for an extended period. Ignoring the problem can lead to further damage, potentially causing a complete bearing failure and putting you at risk of a dangerous accident.
Can I replace a wheel bearing myself?
While some DIY enthusiasts might attempt it, replacing a wheel bearing is a complex procedure that requires specialized tools and experience. It’s best to have a qualified mechanic perform this repair to ensure proper installation and prevent further damage.