Can you make a front wheel drive car awd – Can you make a front-wheel drive car AWD? It’s a question that sparks curiosity and raises eyebrows. While it might seem like an impossible feat, the world of automotive engineering is full of surprises. The answer lies in understanding the intricate workings of both front-wheel drive (FWD) and all-wheel drive (AWD) systems, and the challenges and possibilities that come with converting one to the other.
Imagine transforming a humble FWD car into a capable AWD vehicle, ready to tackle any terrain with newfound confidence. The journey is fraught with technical complexities, but the potential rewards are enticing.
This exploration delves into the realm of automotive modification, exploring the technical feasibility, methods, and considerations involved in converting a FWD car to AWD. We’ll examine the advantages and disadvantages, the complexities of the conversion process, and the impact on performance, fuel economy, and handling. It’s a fascinating exploration into the world of automotive engineering, where creativity and innovation often collide with practical limitations.
Understanding Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is a type of drivetrain system in which the engine’s power is delivered to the front wheels, which are responsible for both propelling and steering the vehicle. This system is widely used in passenger cars due to its simplicity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Basic Principles of Front-Wheel Drive
FWD systems utilize a single driveshaft that connects the engine to a transaxle located at the front of the vehicle. The transaxle combines the functions of a transmission and a differential, allowing power to be distributed to the front wheels while also permitting them to rotate at different speeds during turns. The transaxle sends power through axles to the front wheels, enabling them to propel the vehicle forward.
Advantages of Front-Wheel Drive
- Fuel Efficiency: FWD vehicles generally offer better fuel efficiency compared to rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles. This is primarily due to the reduced weight and complexity of the drivetrain, as well as the absence of a driveshaft running to the rear wheels. The absence of a heavy driveshaft and the reduced mechanical losses in the system contribute to improved fuel economy.
- Improved Traction in Wet Conditions: FWD vehicles often exhibit better traction on wet surfaces. The weight of the engine and transmission over the front wheels provides greater grip, enhancing traction and stability during acceleration and braking. The weight distribution, with more weight on the front wheels, allows for better control on slippery roads.
- Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness: FWD systems are simpler to design and manufacture compared to RWD or all-wheel drive (AWD) systems. This translates into lower production costs, making FWD vehicles more affordable for consumers. The simpler design requires fewer parts and less complex assembly, leading to cost savings.
- Increased Interior Space: The absence of a driveshaft running to the rear wheels allows for a more spacious interior, particularly in the rear passenger area. This is a significant advantage for family cars and other vehicles that prioritize passenger comfort.
Disadvantages of Front-Wheel Drive
- Torque Steer: A common issue in FWD vehicles is torque steer, a phenomenon where the steering wheel pulls to one side during hard acceleration. This occurs due to the uneven distribution of power to the front wheels, which can cause the wheels to rotate at different speeds. The uneven power distribution can lead to a tugging sensation on the steering wheel, especially during acceleration.
- Limited Handling Performance: In general, FWD vehicles tend to have less precise handling than RWD vehicles, especially during cornering at high speeds. The front wheels are responsible for both steering and propulsion, which can limit their ability to effectively steer the vehicle. The combination of steering and driving forces on the front wheels can lead to understeer, where the vehicle fails to turn as sharply as intended.
- Potential for Wheel Spin: FWD vehicles can be prone to wheel spin, especially on slippery surfaces. The front wheels are responsible for both steering and propulsion, which can make it challenging to maintain traction when accelerating or braking on low-grip surfaces. The weight distribution in FWD vehicles can lead to wheel spin if the engine’s power exceeds the available grip.
Examples of Popular FWD Vehicles
- Honda Civic: The Honda Civic is a popular compact car known for its fuel efficiency, reliability, and spacious interior. It has been a top-selling car in the US for decades and is a prime example of a successful FWD vehicle.
- Toyota Corolla: The Toyota Corolla is another best-selling compact car known for its reliability and affordability. It is a popular choice for commuters and families looking for a practical and efficient vehicle.
- Ford Focus: The Ford Focus is a compact car that has been praised for its handling and performance. It offers a sporty driving experience while still maintaining a comfortable ride.
- Chevrolet Cruze: The Chevrolet Cruze is a mid-size sedan that provides a balance of affordability, fuel efficiency, and comfort. It is a popular choice for families and individuals seeking a practical and reliable vehicle.
All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Systems
All-wheel drive (AWD) systems are designed to deliver power to all four wheels of a vehicle, providing enhanced traction and stability compared to front-wheel drive (FWD) systems. AWD systems are becoming increasingly popular, especially in regions with challenging weather conditions and for vehicles intended for off-road use.
Types of AWD Systems
AWD systems can be categorized into different types based on how they distribute power to the wheels and when they engage.
- Part-time AWD: Part-time AWD systems engage the rear wheels only when needed, typically when the front wheels lose traction. This type of system is often found in trucks and SUVs, and it can improve traction on slippery surfaces like snow or mud. It’s important to note that part-time AWD systems are not intended for continuous use on dry pavement, as they can cause wear and tear on the drivetrain.
- Full-time AWD: Full-time AWD systems constantly send power to all four wheels, regardless of the road conditions. This provides continuous traction and stability, making it suitable for driving in a variety of conditions. Full-time AWD systems typically use a center differential to distribute power between the front and rear axles, ensuring that each wheel receives the appropriate amount of torque.
- On-demand AWD: On-demand AWD systems engage the rear wheels only when necessary, typically when the front wheels slip or lose traction. These systems use sensors to monitor wheel speed and torque, and they can engage the rear wheels in a fraction of a second. On-demand AWD systems offer a balance between fuel efficiency and performance, as they only engage the rear wheels when needed.
They are often found in passenger cars and SUVs.
Benefits of AWD
AWD systems offer several benefits over FWD systems, including:
- Improved Traction: AWD systems provide enhanced traction by distributing power to all four wheels, making it easier to accelerate and maintain control on slippery surfaces like snow, ice, and mud. This can be especially beneficial in challenging weather conditions.
- Enhanced Stability: AWD systems improve stability by distributing power to all four wheels, which helps to maintain control during cornering and braking. This can be crucial in situations where the vehicle is at risk of skidding or losing traction.
- Off-Road Capability: AWD systems can significantly improve a vehicle’s off-road capability by providing increased traction and torque to all four wheels. This allows vehicles to navigate challenging terrain with greater ease, such as rocky trails, mud, and sand.
Examples of Vehicles with AWD Configurations
- Part-time AWD: The Jeep Wrangler and Toyota Tacoma are popular examples of vehicles that utilize part-time AWD systems. These systems are designed to provide enhanced traction when needed, but they are not intended for continuous use on dry pavement.
- Full-time AWD: The Subaru Outback and Audi Quattro are examples of vehicles that utilize full-time AWD systems. These systems provide continuous traction and stability, making them suitable for driving in a variety of conditions.
- On-demand AWD: The Honda CR-V and Toyota RAV4 are examples of vehicles that utilize on-demand AWD systems. These systems engage the rear wheels only when necessary, offering a balance between fuel efficiency and performance.
Can You Make a Front-Wheel Drive Car AWD?

Converting a front-wheel drive (FWD) car to all-wheel drive (AWD) is a complex undertaking, requiring significant modifications and expertise. While technically possible, it presents various challenges and limitations.
Technical Feasibility of Converting FWD to AWD
Converting a FWD car to AWD involves a substantial overhaul of the vehicle’s drivetrain. This transformation necessitates the addition of a rear differential, driveshaft, and rear axles, along with modifications to the transmission, suspension, and possibly the engine. The feasibility of such a conversion hinges on several factors, including:
- Vehicle Model and Year: Newer models often have more readily available parts and compatible systems, making the conversion easier. Older models may require extensive custom fabrication.
- Space and Access: The car’s design and layout play a crucial role. Sufficient space for the additional components and accessibility for installation are critical.
- Cost and Complexity: The conversion can be a costly and labor-intensive process, involving specialized tools and skilled technicians.
Challenges and Limitations of FWD to AWD Conversion, Can you make a front wheel drive car awd
Several challenges and limitations arise when converting a FWD car to AWD:
- Space Constraints: FWD cars are typically designed with limited space in the rear, which can hinder the installation of the rear differential, driveshaft, and axles.
- Suspension Modifications: Rear suspension systems need adjustments to accommodate the added weight and torque from the rear axle.
- Transmission Compatibility: The transmission may require modifications or replacement to handle the power distribution to both axles.
- Engine Power: The engine might need modifications to accommodate the increased load from driving all four wheels.
- Control Systems: Integrating the AWD system with the car’s existing electronic control systems can be complex and may require custom programming.
- Weight and Performance: The added weight of the AWD components can negatively impact fuel efficiency and acceleration.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Converting FWD to AWD
Converting a FWD car to AWD can offer several potential benefits, but it also comes with drawbacks:
Benefits
- Improved Traction and Handling: AWD systems enhance traction, particularly on slippery surfaces like snow or ice, leading to improved handling and stability.
- Enhanced Off-Road Capability: AWD provides increased traction and ground clearance, making the car more capable in off-road conditions.
- Increased Safety: Enhanced traction and handling contribute to improved safety, especially in challenging road conditions.
Drawbacks
- Increased Cost: The conversion process can be significantly expensive, involving labor, parts, and potential modifications to existing systems.
- Reduced Fuel Efficiency: The added weight and power requirements of AWD systems can lead to a decrease in fuel efficiency.
- Increased Complexity: The AWD system adds complexity to the vehicle, requiring specialized maintenance and potential issues with electronic controls.
Conversion Methods
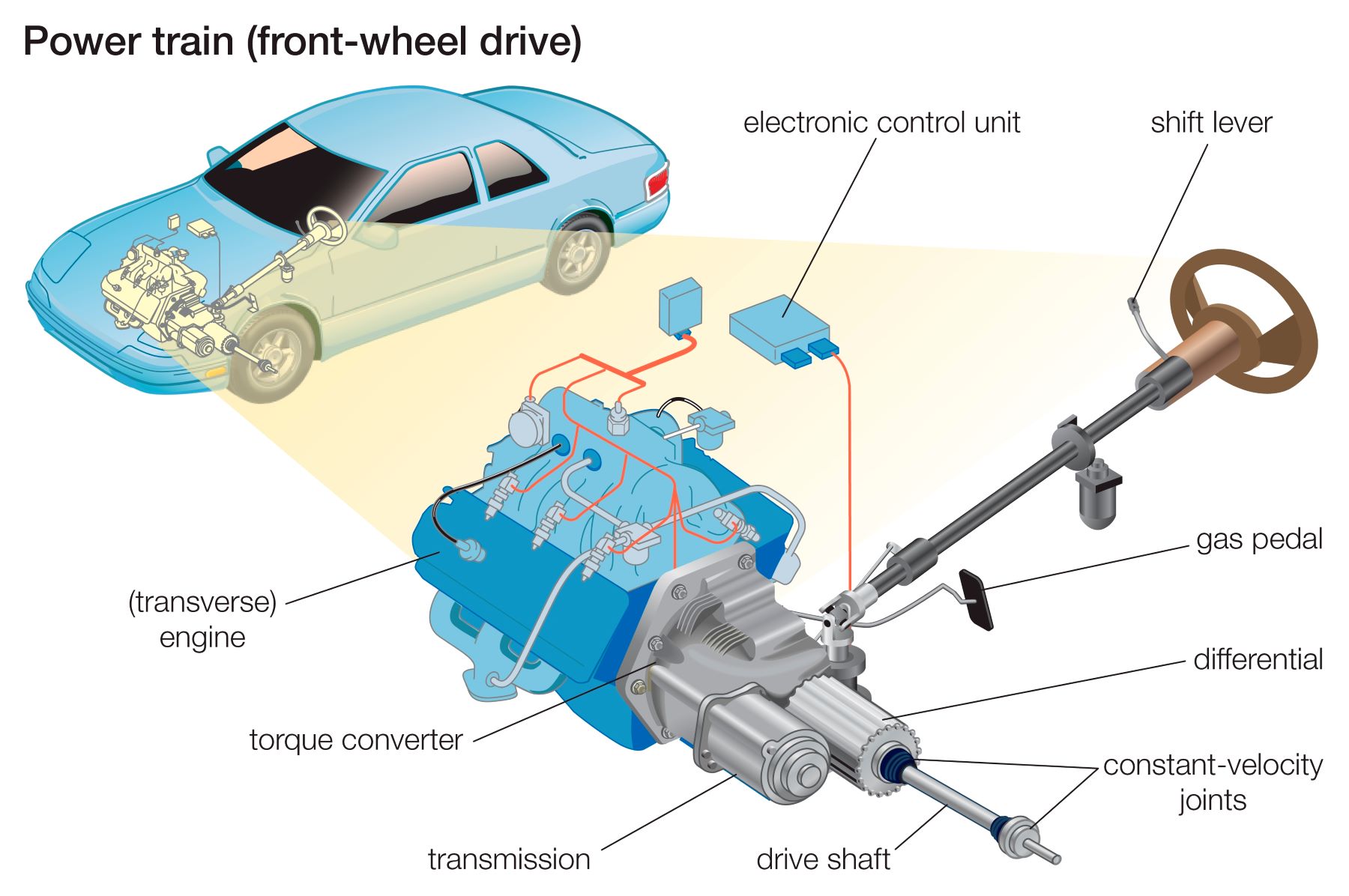
Converting a front-wheel drive (FWD) car to all-wheel drive (AWD) is a complex and challenging process that requires significant modifications to the vehicle’s drivetrain. While it’s not a straightforward task, there are various methods that can be employed to achieve this conversion. These methods differ in their complexity, cost, and effectiveness, and the choice depends on factors such as the specific vehicle, desired performance, and budget.
Methods for Converting a FWD Car to AWD
The conversion process involves adding a rear differential, driveshaft, and axles to transmit power to the rear wheels. This can be accomplished using several approaches, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Complete Drivetrain Swap: This method involves replacing the entire front-wheel drive system with an all-wheel drive system from a compatible donor vehicle. This approach offers the most comprehensive solution, as it utilizes a complete AWD drivetrain designed to work together seamlessly. However, finding a compatible donor vehicle with a suitable drivetrain can be challenging, and the process requires extensive modifications and potentially significant fabrication work.
- Modular AWD Kit: Specialized aftermarket kits are available that provide the necessary components for converting a FWD car to AWD. These kits typically include a rear differential, driveshaft, axles, and mounting hardware. The installation process involves integrating these components with the existing drivetrain, requiring modifications to the vehicle’s chassis and suspension. While modular kits offer a more convenient option, they may not always be compatible with all FWD vehicles, and the installation process can still be complex.
- Custom Fabrication: For those seeking a highly customized approach, a custom AWD conversion can be created using a combination of salvaged components, aftermarket parts, and custom fabrication. This method allows for greater flexibility in terms of component selection and system design. However, it requires significant expertise in mechanical engineering and fabrication, and the cost can be substantial.
Technical Details and Components
Regardless of the conversion method, the following components are essential for transforming a FWD car to AWD:
- Rear Differential: The rear differential is responsible for distributing power to the rear wheels. It is typically chosen based on the vehicle’s weight, power output, and intended use. The differential may need to be modified or adapted to fit the vehicle’s chassis.
- Driveshaft: The driveshaft connects the transmission to the rear differential, transferring power from the front to the rear axles. The length and design of the driveshaft will depend on the specific vehicle and the rear differential location.
- Axles: The axles connect the rear differential to the rear wheels, transmitting power to the wheels for propulsion. The axles must be compatible with the rear differential and the vehicle’s wheel hubs.
- Transfer Case: In some AWD systems, a transfer case is used to split power between the front and rear axles. The transfer case can also include a low-range gear for increased torque and off-road capability. The transfer case is typically mounted between the transmission and the driveshaft.
Costs and Complexities
The cost and complexity of converting a FWD car to AWD vary significantly depending on the method chosen and the specific vehicle.
- Complete Drivetrain Swap: This method is generally the most expensive, as it involves acquiring a complete AWD drivetrain and performing extensive modifications. The cost can range from several thousand dollars to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on the donor vehicle and the complexity of the conversion.
- Modular AWD Kit: Modular kits are typically more affordable than a complete drivetrain swap, but the cost can still be significant. The cost of a kit can range from a few thousand dollars to several thousand dollars, depending on the specific kit and the vehicle. The installation cost can also be substantial, as it involves significant labor and potential modifications.
- Custom Fabrication: Custom fabrication is the most complex and potentially the most expensive method. The cost can vary widely depending on the materials, labor, and the level of customization. This method requires extensive expertise and specialized equipment, and the cost can easily exceed tens of thousands of dollars.
Practical Considerations: Can You Make A Front Wheel Drive Car Awd

Converting a front-wheel drive (FWD) car to all-wheel drive (AWD) can offer significant advantages in terms of traction and handling, but it also comes with a number of practical considerations. These modifications can impact the vehicle’s performance, fuel economy, and handling, and may also raise legal and safety concerns.
Impact on Performance, Fuel Economy, and Handling
Converting a FWD car to AWD can significantly affect the vehicle’s performance, fuel economy, and handling. These effects are not always straightforward and can vary depending on the specific conversion method and the original vehicle.
- Performance: Converting a FWD car to AWD typically results in improved acceleration, especially in low-traction conditions. This is because the additional power delivered to the rear wheels provides greater grip, allowing the car to accelerate more effectively. However, the added weight and complexity of the AWD system can slightly reduce overall performance in terms of top speed and acceleration on dry surfaces.
- Fuel Economy: AWD systems generally require more power to operate than FWD systems, leading to a decrease in fuel economy. The added weight of the drivetrain components also contributes to this reduction. The magnitude of the decrease in fuel economy depends on factors such as the efficiency of the AWD system, the vehicle’s weight, and driving conditions.
- Handling: AWD systems can improve handling, particularly in slippery conditions, by providing greater stability and control. However, the added weight and complexity of the AWD system can also affect handling characteristics, potentially making the car feel heavier or less responsive in some situations. The specific impact on handling will depend on the design of the AWD system and the overall suspension setup.
Legal and Regulatory Aspects
Converting a FWD car to AWD can raise legal and regulatory concerns. It’s important to be aware of these issues before undertaking such a conversion.
- Emissions and Safety Standards: The conversion may affect the vehicle’s emissions and safety compliance. Modifying the drivetrain could potentially impact the vehicle’s emissions output, which might not meet current standards. Additionally, the conversion may need to meet certain safety standards related to braking, stability control, and other systems. It is essential to research and comply with all applicable regulations in your region.
- Vehicle Registration and Insurance: The converted vehicle may need to be inspected and re-registered after the conversion. Insurance companies may also have specific requirements for modified vehicles, and insurance premiums could potentially increase due to the conversion. It is crucial to contact your local authorities and insurance provider to understand the necessary procedures and potential implications.
Safety Concerns
Converting a FWD car to AWD can introduce potential safety concerns. These concerns are primarily related to the increased complexity of the drivetrain and the potential for improper installation.
- Improper Installation: An improperly installed AWD system can lead to a range of safety issues, including drivetrain failures, loss of control, and increased risk of accidents. It is essential to have the conversion performed by qualified professionals who have experience with AWD systems and can ensure proper installation and integration.
- System Malfunction: AWD systems are more complex than FWD systems and can be susceptible to malfunctions. These malfunctions can lead to loss of traction, power, or control, potentially increasing the risk of accidents. Regular maintenance and inspections of the AWD system are essential to minimize the risk of malfunctions.
The quest to transform a front-wheel drive car into an all-wheel drive marvel is a testament to human ingenuity. While the technical hurdles are significant, the allure of enhanced traction, stability, and off-road capability is undeniable. The journey of converting a FWD car to AWD is not for the faint of heart, demanding a deep understanding of automotive mechanics, meticulous planning, and a willingness to embrace both the challenges and the potential rewards.
As we delve deeper into the complexities of this conversion, we uncover the intricate dance between engineering, practicality, and the pursuit of enhanced performance.
FAQs
What are the most common types of AWD systems?
AWD systems come in various configurations, including part-time, full-time, and on-demand. Part-time AWD engages the rear wheels only when needed, typically in slippery conditions. Full-time AWD continuously sends power to all four wheels, providing constant traction. On-demand AWD engages the rear wheels electronically when wheel slip is detected.
Is it legal to convert a FWD car to AWD?
The legality of converting a FWD car to AWD varies by region. It’s essential to check local laws and regulations before attempting any modifications. Some jurisdictions may require inspections or certifications after a significant drivetrain alteration.
What are the potential safety concerns associated with converting a FWD car to AWD?
Converting a FWD car to AWD can introduce new safety considerations. Improperly installed components can lead to instability, handling issues, or even mechanical failures. It’s crucial to ensure that all components are properly installed and that the vehicle undergoes thorough testing after the conversion.