What to look at when buying a bike is a crucial question for any aspiring cyclist, whether you’re a seasoned veteran or a first-time buyer. Navigating the vast world of bicycles can be overwhelming, with a myriad of choices and considerations to make. From the type of bike that best suits your needs to the quality of components and proper fit, each aspect plays a significant role in ensuring a satisfying and enjoyable riding experience.
This guide will delve into the essential factors you should consider when making your bike purchase, providing you with the knowledge and insights to make an informed decision. We’ll explore various bike types, frame materials, key components, fit and sizing, budget considerations, riding style, safety features, and additional factors to help you find the perfect bike for your adventures.
Bike Type
Choosing the right bike type is crucial for an enjoyable and efficient riding experience. Different bike types are designed for specific purposes, terrains, and riding styles. Understanding the key features and benefits of each type will help you make an informed decision.
Road Bikes
Road bikes are designed for speed and efficiency on paved surfaces. They feature lightweight frames, narrow tires, and drop handlebars for an aerodynamic riding position.
Key Features
- Lightweight frame: Constructed from aluminum, carbon fiber, or steel, road bike frames are designed to be lightweight and responsive, allowing for faster acceleration and climbing.
- Narrow tires: Thin tires with high pressure provide low rolling resistance, minimizing energy loss and maximizing speed on smooth surfaces.
- Drop handlebars: The distinctive drop handlebars offer multiple hand positions, enabling riders to maintain an aerodynamic posture and reduce wind resistance.
Benefits
- Speed and efficiency: Road bikes are optimized for speed and efficiency on paved roads, making them ideal for long-distance rides, racing, and commuting.
- Aerodynamic design: The lightweight frame, narrow tires, and drop handlebars contribute to an aerodynamic profile, reducing wind resistance and enhancing speed.
- Versatility: Road bikes can be used for various purposes, including racing, recreational riding, and commuting.
Popular Brands and Models
- Specialized: Tarmac, Allez
- Trek: Emonda, Domane
- Giant: TCR, Defy
- Cannondale: SuperSix Evo, CAAD13
Mountain Bikes
Mountain bikes are designed for off-road riding on rugged terrain. They feature sturdy frames, wide tires with knobby treads, and suspension systems to absorb shocks.
Key Features
- Sturdy frame: Mountain bike frames are made from durable materials like aluminum, steel, or carbon fiber, capable of handling rough terrain and impacts.
- Wide tires with knobby treads: These tires provide excellent traction on loose surfaces, allowing for stable riding on uneven trails and climbs.
- Suspension systems: Front suspension forks and rear suspension systems absorb shocks and vibrations, enhancing rider comfort and control.
Benefits
- Off-road capability: Mountain bikes are designed to handle challenging terrain, including trails, rocks, and roots, providing a thrilling and adventurous riding experience.
- Traction and control: Wide tires with knobby treads provide excellent traction, allowing for stable riding on uneven surfaces and steep climbs.
- Comfort and stability: Suspension systems absorb shocks and vibrations, enhancing rider comfort and control, especially on rough terrain.
Popular Brands and Models
- Specialized: Stumpjumper, Epic
- Trek: Fuel EX, Supercaliber
- Giant: Anthem, Trance
- Santa Cruz: Bronson, Nomad
Hybrid Bikes
Hybrid bikes combine features of road bikes and mountain bikes, offering a versatile and comfortable riding experience on both paved and unpaved surfaces.
Key Features
- Upright riding position: Hybrid bikes have a more upright riding position compared to road bikes, providing better visibility and comfort for longer rides.
- Wider tires: Hybrid bikes have wider tires than road bikes, providing better comfort and traction on rougher surfaces.
- Flat handlebars: Flat handlebars provide a comfortable and versatile grip, suitable for both casual and fitness riding.
Benefits
- Versatility: Hybrid bikes can be used on a variety of surfaces, including paved roads, gravel paths, and light trails.
- Comfort: The upright riding position and wider tires provide a comfortable ride, making them suitable for long-distance rides and commuting.
- Ease of use: Hybrid bikes are relatively easy to ride and maintain, making them a good choice for beginners and casual riders.
Popular Brands and Models
- Specialized: Sirrus, Crosstrail
- Trek: FX, Dual Sport
- Giant: Escape, Cypress
- Cannondale: Quick, Synapse
Commuter Bikes
Commuter bikes are designed for daily transportation, offering durability, practicality, and comfort for navigating city streets.
Key Features
- Durable frame: Commuter bikes often feature sturdy frames made from steel or aluminum, capable of withstanding the rigors of daily use.
- Rack and fender mounts: Many commuter bikes have mounts for racks and fenders, allowing riders to carry cargo and protect themselves from the elements.
- Comfortable features: Commuter bikes often include features like upright handlebars, comfortable saddles, and wide tires for a smooth and comfortable ride.
Benefits
- Practicality: Commuter bikes are designed for everyday use, with features that make them practical for transportation, carrying cargo, and navigating city streets.
- Durability: Commuter bikes are built to withstand the wear and tear of daily use, with sturdy frames and components that can handle rough roads and weather conditions.
- Comfort: Commuter bikes prioritize comfort, with features like upright handlebars, comfortable saddles, and wide tires that provide a smooth and enjoyable ride.
Popular Brands and Models
- Specialized: Globe, Roll
- Trek: District, Verve
- Giant: Quick, Cypress
- Cannondale: Quick, Bad Boy
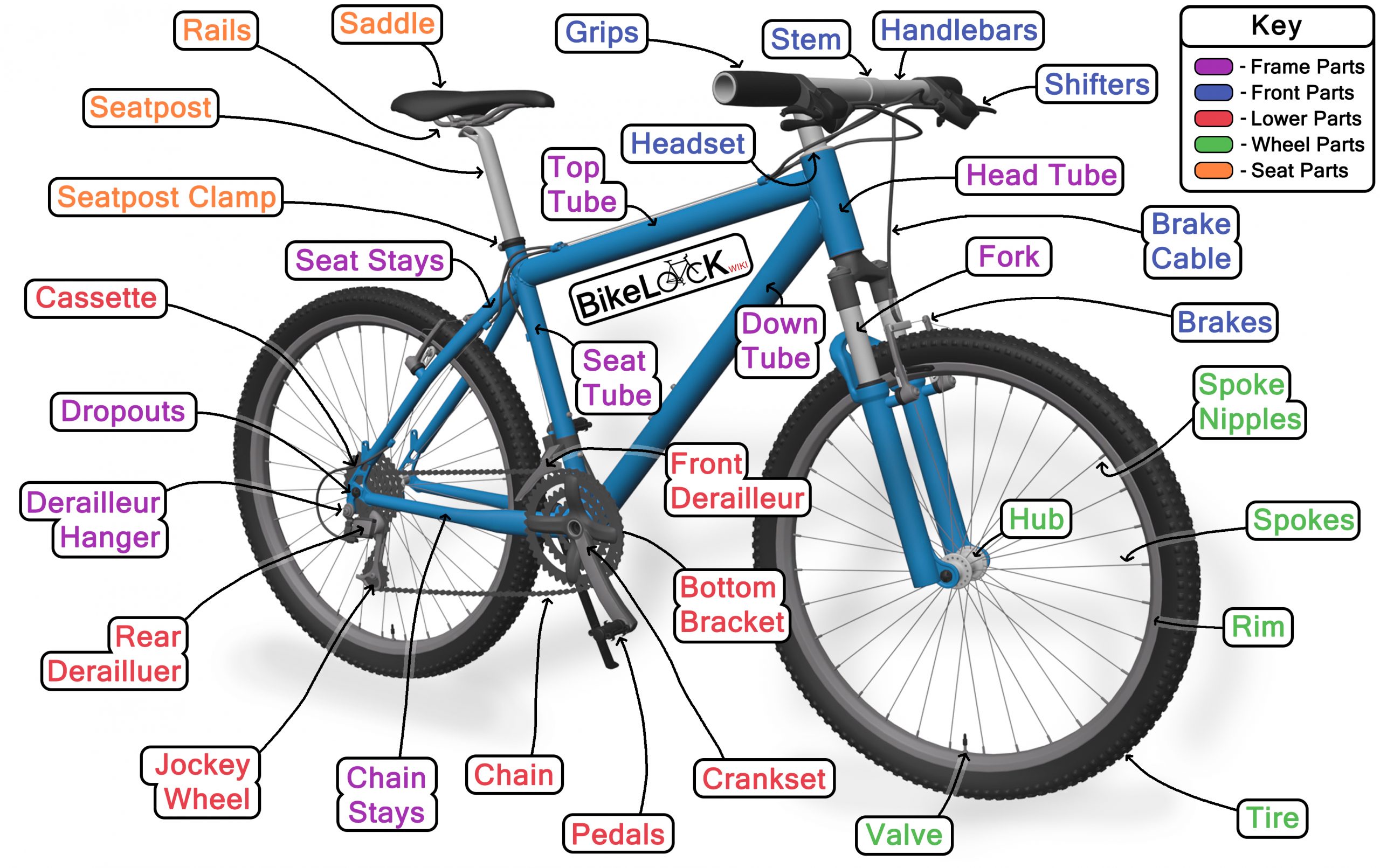
Components
The components of a bike are the parts that make it work. They can be grouped into several categories, each with its own set of options and considerations. Understanding these components will help you choose the right bike for your needs and budget.
Drivetrain, What to look at when buying a bike
The drivetrain is the system that transfers power from your legs to the wheels. It consists of the following components:
- Crankset: The crankset is the set of arms that connect to the pedals. It includes the chainrings, which are the gears that your chain engages with. The number of chainrings on a crankset determines the range of gears available.
- Chain: The chain connects the crankset to the cassette. It is responsible for transferring power from the chainrings to the cassette. Chains come in different widths and lengths, depending on the type of bike and drivetrain.
- Cassette: The cassette is the set of gears on the rear wheel. It allows you to change gears while riding. The number of gears on a cassette determines the range of gears available.
- Derailleurs: Derailleurs are the mechanisms that shift the chain between the gears on the crankset and cassette. They come in two types: front derailleur and rear derailleur.
- Shifters: Shifters are the levers that you use to change gears. They are typically located on the handlebars.
Brakes
Brakes are essential for stopping and slowing down. There are two main types of brakes:
- Rim brakes: Rim brakes use pads that press against the rim of the wheel to create friction and slow the bike down. They are typically found on road bikes and some mountain bikes.
- Disc brakes: Disc brakes use calipers that press pads against a rotor attached to the wheel hub. They provide more stopping power than rim brakes, especially in wet conditions. Disc brakes are becoming increasingly popular on all types of bikes.
Wheels
Wheels are the foundation of the bike. They consist of the following components:
- Rims: Rims are the circular part of the wheel that the tire sits on. They come in different sizes, materials, and widths, depending on the type of bike and riding style.
- Hubs: Hubs are the central part of the wheel that the spokes attach to. They house the bearings that allow the wheel to rotate smoothly.
- Spokes: Spokes are the thin wires that connect the rim to the hub. They provide structural support for the wheel.
- Tires: Tires are the rubber coverings that provide traction and cushion the ride. They come in different sizes, tread patterns, and materials, depending on the type of bike and riding surface.
Handlebars
Handlebars are the part of the bike that you grip to steer and control the bike. They come in different shapes and sizes, depending on the type of bike and riding style.
- Road handlebars: Road handlebars are typically drop handlebars, which have a curved shape that allows for different hand positions. This is beneficial for aerodynamics and comfort on long rides.
- Mountain bike handlebars: Mountain bike handlebars are typically flat handlebars, which provide a more upright riding position. This is beneficial for control and visibility on technical trails.
- City bike handlebars: City bike handlebars are typically upright handlebars, which provide a comfortable riding position for everyday riding.
Fit and Sizing
A proper bike fit is crucial for comfort, performance, and injury prevention. When a bike is correctly sized and adjusted, it allows for a natural and efficient pedaling motion, reduces strain on joints, and enhances overall riding experience.
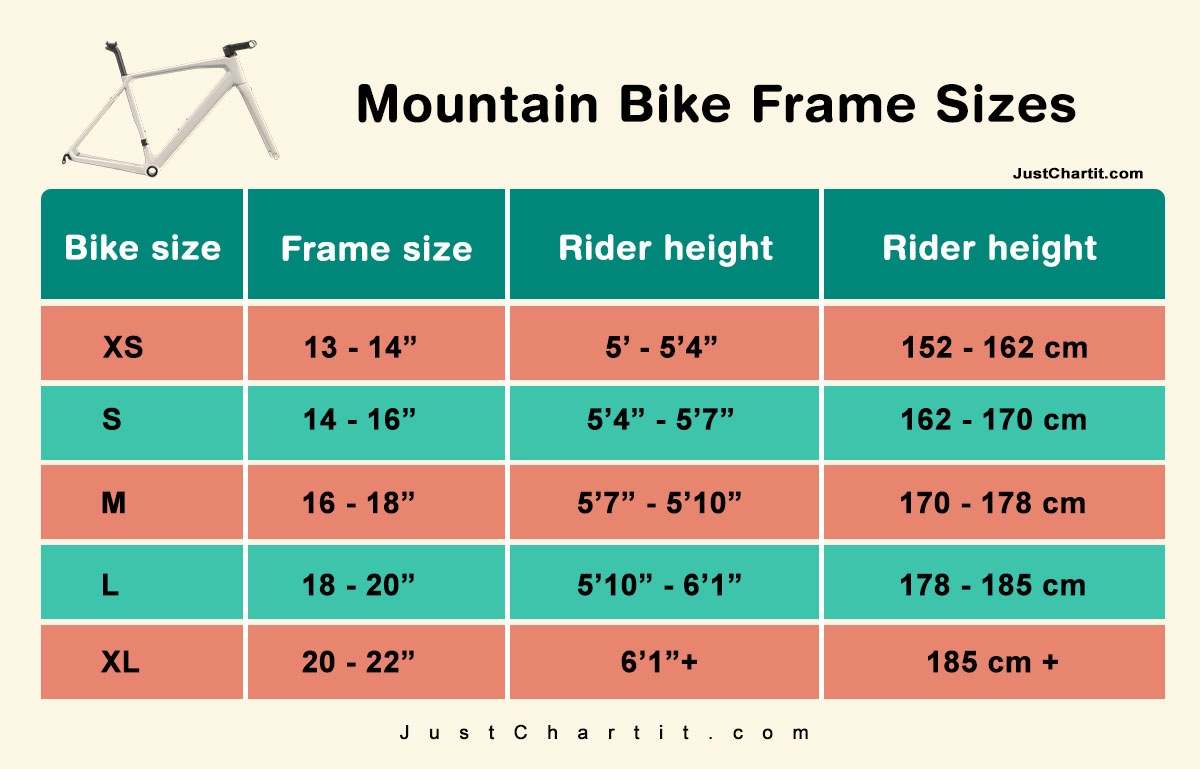
Determining the Correct Bike Size
To determine the correct bike size, you need to consider your height and other measurements. Different bike types have varying sizing systems, so it’s essential to consult with a knowledgeable salesperson or refer to the manufacturer’s size charts.
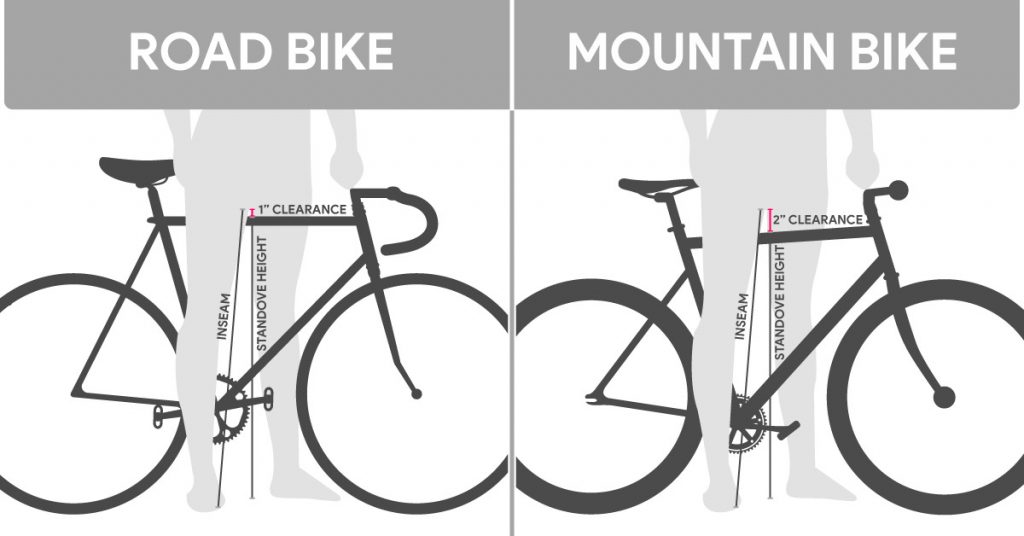
- Standover Height: Measure the distance between the ground and the top tube of the bike frame when the bike is standing upright. Ensure there’s enough clearance between your crotch and the top tube for comfortable mounting and dismounting.
- Reach: This measurement indicates the horizontal distance between the center of the bottom bracket and the center of the head tube. A longer reach typically results in a more aggressive riding position, while a shorter reach offers a more upright and comfortable posture.
- Stack: The stack height refers to the vertical distance between the center of the bottom bracket and the top of the head tube. A higher stack provides a more upright riding position, while a lower stack offers a more aerodynamic and aggressive posture.
Adjusting Bike Components for Comfort and Efficiency
Once you have a bike that’s roughly the right size, you can fine-tune its components to achieve a comfortable and efficient riding position.
- Seat Height: Adjust the seat height so that your leg is almost fully extended when the pedal is at its lowest point. This ensures efficient power transfer and reduces knee strain.
- Handlebar Height and Reach: Adjust the handlebar height and reach to achieve a comfortable and efficient posture. A more upright position is suitable for casual riding, while a more aggressive position is better for performance and speed.
- Stem Length: The stem connects the handlebars to the fork. A shorter stem results in a more compact riding position, while a longer stem provides a more stretched-out position.
Budget
Determining your budget is crucial when buying a bike. The price range for bikes is vast, encompassing entry-level models suitable for casual riders to high-end machines designed for professional athletes and demanding terrain. The cost of a bike is influenced by various factors, including the frame material, components, and brand reputation.
Factors Influencing Bike Cost
The cost of a bike is a reflection of the materials, components, and craftsmanship involved in its construction. Here are some key factors that influence the price of a bike:
- Frame Material: The frame is the backbone of a bike, and the material used significantly impacts its price. Aluminum frames are generally affordable, while carbon fiber frames are lighter and more durable, but come at a higher cost.
- Components: Components like the drivetrain (shifters, derailleurs, and cassette), brakes, wheels, and tires contribute to the overall performance and cost of a bike. Higher-end components are often made from lighter and more durable materials, offering improved performance and longevity.
- Brand Reputation: Established brands often command a premium price due to their reputation for quality, innovation, and performance. However, there are also many reputable brands offering excellent value for money at various price points.
Bike Recommendations Within Price Ranges
Here are some recommendations for bikes offering good value for money within different price ranges:
- Entry-Level (Under $500): Bikes in this range are ideal for casual riders and beginners. They typically feature aluminum frames, basic components, and simple designs. Examples include the Giant Contend 1 and the Trek Domane AL 2.
- Mid-Range ($500 – $1,500): Bikes in this range offer a balance of performance and affordability. They often feature aluminum or carbon fiber frames, upgraded components, and improved features. Examples include the Specialized Allez E5 and the Cannondale Synapse 105.
- High-End (Over $1,500): Bikes in this range are designed for serious riders and competitive cyclists. They feature high-quality carbon fiber frames, top-of-the-line components, and advanced technologies. Examples include the Trek Emonda SLR and the Giant TCR Advanced SL.
Riding Style and Needs
Your riding style and needs play a crucial role in choosing the right bike. Understanding your primary use for the bike will help you narrow down your options and select a model that best suits your requirements.
Riding Styles and Their Bike Choices
The type of riding you plan to do will significantly influence your bike selection. Here are some common riding styles and the corresponding bike types:
- Commuting: For daily commutes, a bike that is comfortable, durable, and efficient is essential. Consider a hybrid bike, which combines features of road and mountain bikes, offering a balance of comfort and speed. Other suitable options include city bikes, which prioritize comfort and stability, and gravel bikes, which can handle paved roads and light trails.
- Recreational Riding: If you enjoy leisurely rides on paved roads and bike paths, a road bike, with its lightweight frame and narrow tires, will provide a smooth and efficient ride. For a more versatile option, consider a hybrid bike, which can handle a variety of surfaces.
- Racing: Road bikes designed for racing prioritize speed and performance. They feature lightweight frames, aerodynamic designs, and components optimized for high-speed riding.
- Off-Road Riding: For adventures on trails and rough terrain, a mountain bike is the ideal choice. Its sturdy frame, wide tires, and suspension system provide the necessary traction and stability to navigate challenging terrain.
Comparing Bike Features and Benefits
Here’s a table comparing the features and benefits of bikes tailored to specific riding purposes:
| Riding Style | Bike Type | Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commuting | Hybrid, City, Gravel | Comfortable upright riding position, durable frame, wide tires, rack and fender mounts | Comfortable for long rides, versatile for different surfaces, practical for carrying cargo |
| Recreational Riding | Road, Hybrid | Lightweight frame, narrow tires, efficient drivetrain | Fast and efficient on paved surfaces, comfortable for long rides |
| Racing | Road | Lightweight frame, aerodynamic design, high-performance components | Maximum speed and performance on paved roads |
| Off-Road Riding | Mountain | Sturdy frame, wide tires, suspension system, disc brakes | Excellent traction and stability on rough terrain, capable of handling challenging obstacles |
Choosing the right bike is an investment in your health, fitness, and enjoyment. By carefully considering the factors Artikeld in this guide, you can make an informed decision that will lead to countless hours of pleasurable cycling. Remember, the best bike for you is the one that fits your needs, budget, and riding style, allowing you to explore the world on two wheels with confidence and ease.
Essential FAQs: What To Look At When Buying A Bike
What is the best brand of bike?
There is no single “best” brand, as quality and suitability vary depending on individual needs and preferences. Research different brands and models, read reviews, and consider your budget and riding style.
How often should I get my bike serviced?
Regular bike maintenance is essential for safety and performance. Aim for a service every 6-12 months or sooner if you notice any issues.
What kind of bike is best for commuting?
Hybrid bikes are a popular choice for commuting, offering a balance of comfort, speed, and durability. Consider a bike with fenders and a rack for carrying gear.