Should you replace wheel bearings in pairs? This question is a common one among car owners, and the answer isn’t always straightforward. While it might seem tempting to just replace the faulty bearing, there are several reasons why replacing both bearings simultaneously is often the best course of action. Wheel bearings are essential components that support the weight of your vehicle and allow your wheels to rotate smoothly.
They are subjected to constant wear and tear, and eventually, they will need to be replaced.
Understanding how wheel bearings work and the potential consequences of replacing only one bearing can help you make an informed decision about your vehicle’s maintenance. This article will delve into the intricacies of wheel bearing replacement, exploring the reasons why replacing them in pairs is often the most practical and cost-effective approach.
Understanding Wheel Bearings
Wheel bearings are essential components in a vehicle’s suspension system, playing a crucial role in supporting the weight of the vehicle and allowing the wheels to rotate smoothly. They are located within the wheel hub, acting as a critical interface between the wheel and the vehicle’s axle.
Types of Wheel Bearings
Wheel bearings are typically classified based on their design and construction.
- Tapered Roller Bearings: These bearings consist of a set of tapered rollers that are positioned between an inner and outer raceway. The tapered shape of the rollers allows for both radial and axial load support. Tapered roller bearings are commonly found in heavy-duty vehicles, trucks, and SUVs due to their high load-carrying capacity.
- Ball Bearings: Ball bearings utilize a set of hardened steel balls that rotate between inner and outer raceways. These bearings are primarily designed to handle radial loads and are often found in passenger cars and light-duty vehicles.
- Spherical Roller Bearings: These bearings feature a large spherical roller that rotates between inner and outer raceways. Spherical roller bearings excel in handling both radial and axial loads, making them suitable for applications where heavy loads and shock loads are expected.
Common Wheel Bearing Problems and Symptoms
Several factors can contribute to the deterioration and failure of wheel bearings.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the rolling elements and raceways within a wheel bearing can wear down due to friction and repeated stress. This wear can lead to increased noise, vibration, and reduced bearing life.
- Improper Lubrication: Insufficient or contaminated lubrication can cause premature wear and damage to wheel bearings. This can result from inadequate grease application, excessive heat, or contamination from road debris.
- Impact Loads: Severe impacts, such as hitting potholes or curbs, can damage wheel bearings, causing them to fail prematurely.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture, road salt, and other corrosive elements can lead to rust and corrosion, which can damage the bearings and affect their performance.
Wheel bearing problems often manifest through a variety of symptoms, including:
- Grinding or Rumbling Noise: A grinding or rumbling noise, especially when turning or driving over bumps, is a common indication of worn or damaged wheel bearings. The noise typically increases in severity as the bearing deteriorates.
- Vibrations: Vibrations in the steering wheel or the entire vehicle can be a sign of a failing wheel bearing. The vibrations may be more noticeable at higher speeds or when turning.
- Steering Wheel Play: Excessive play or looseness in the steering wheel can indicate a problem with the wheel bearings. This play may be accompanied by a clunking sound when turning the steering wheel.
- Uneven Tire Wear: If one or more tires wear unevenly, it could be a sign of a faulty wheel bearing. The bearing may not be supporting the wheel properly, leading to abnormal tire wear.
The Importance of Replacing in Pairs

Replacing wheel bearings in pairs is crucial for maintaining proper vehicle handling and preventing premature wear on other components. When only one bearing is replaced, the other side of the vehicle may experience uneven wear, leading to a variety of issues.
Uneven Wear and Its Consequences
Replacing only one wheel bearing can lead to uneven wear on the other side of the vehicle. This is because the new bearing will be tighter and have less friction than the older bearing. As a result, the vehicle will tend to lean towards the side with the newer bearing.
- Uneven tire wear: The leaning towards the newer bearing can cause uneven tire wear on the opposite side. This is because the tire on the side with the older bearing will be carrying more weight, causing it to wear out faster.
- Premature suspension component wear: Uneven wear can also put additional stress on other suspension components, such as control arms, tie rods, and ball joints. This can lead to premature wear and failure of these components.
- Reduced vehicle stability: Uneven wear can also affect the vehicle’s handling and stability. The vehicle may become harder to control, especially at higher speeds or in slippery conditions.
- Increased risk of accidents: Uneven wear can increase the risk of accidents, as the vehicle may be more prone to swerving or losing control.
Replacing wheel bearings in pairs is the best way to ensure that both sides of the vehicle are wearing evenly and that the vehicle is handling properly.
Factors Influencing the Decision

The decision to replace wheel bearings in pairs or individually involves a complex interplay of factors. While replacing only one bearing might seem like a cost-effective option initially, it can lead to complications and ultimately cost more in the long run. Understanding these factors is crucial for making an informed decision.
Several factors influence the decision to replace wheel bearings in pairs. These factors can be categorized into cost considerations, technical considerations, and safety concerns.
Cost Considerations
Replacing both wheel bearings at the same time, even if only one is showing signs of wear, can save money in the long run. This is because the labor cost for replacing both bearings is typically only slightly higher than replacing one, while the cost of parts is usually doubled. The cost savings come from avoiding the need for a second repair in the near future.
A second repair will require additional labor costs and potentially higher parts costs if the second bearing fails prematurely due to age or stress.
Benefits of Replacing Both Bearings
The decision to replace both wheel bearings is often influenced by the potential long-term benefits. Replacing both bearings simultaneously helps ensure that both sides of the axle remain balanced, reducing the risk of uneven wear and tear on the suspension components. This balance also contributes to a smoother ride and improved handling.
Comparing One Versus Two Bearing Replacement
| Factor | Replacing One Bearing | Replacing Both Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Long-Term Cost | Potentially higher due to the possibility of the other bearing failing prematurely | Lower due to the reduced likelihood of the other bearing failing prematurely |
| Labor Cost | Lower for the initial repair | Slightly higher for the initial repair |
| Suspension Balance | Can lead to uneven wear and tear | Ensures balanced suspension |
| Ride Quality | May experience unevenness or vibrations | Contributes to a smoother ride |
| Safety | Increased risk of failure of the other bearing | Enhanced safety due to the reduced risk of bearing failure |
Professional Recommendations
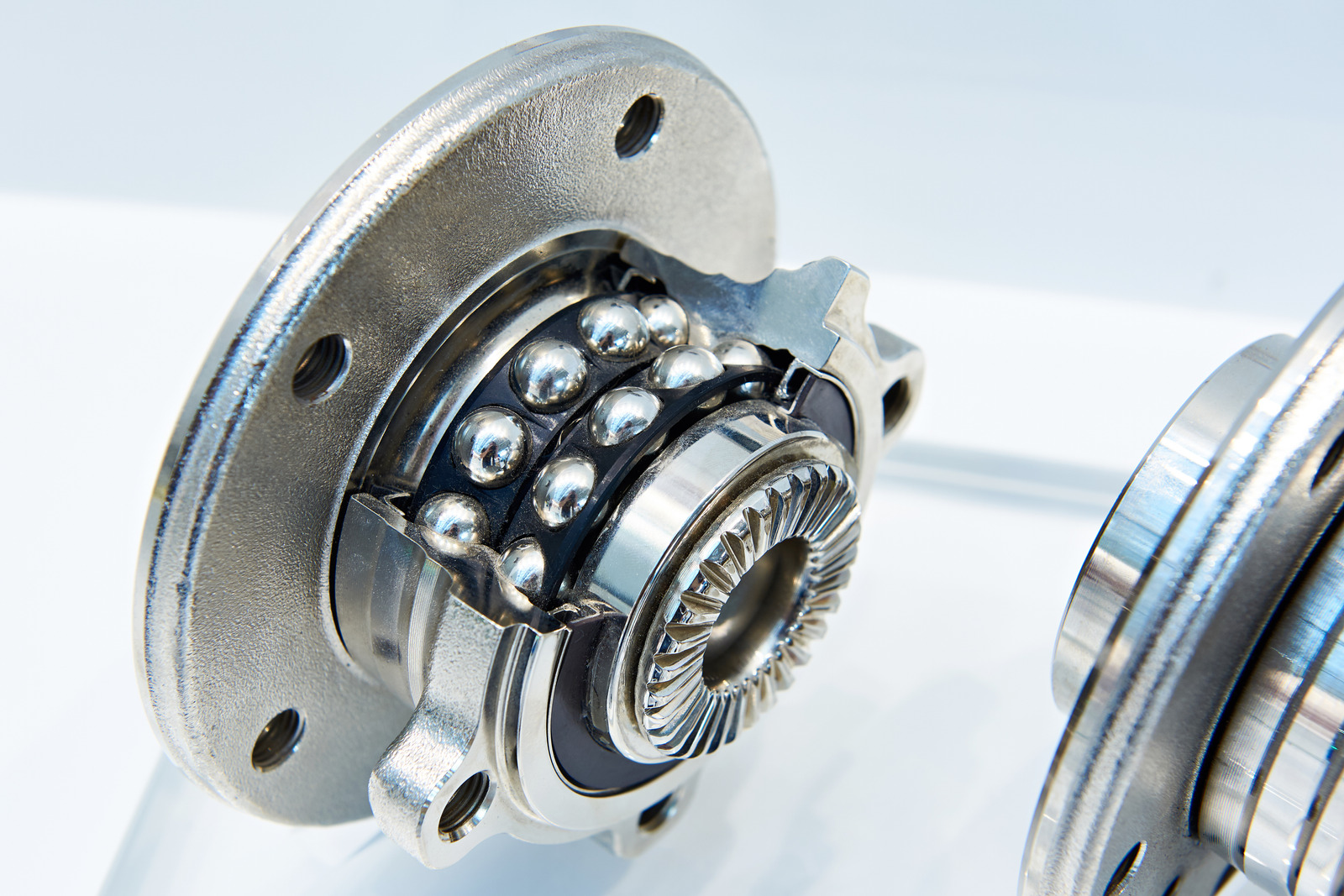
Automotive professionals generally recommend replacing wheel bearings in pairs, even if only one bearing exhibits signs of wear. This approach ensures balanced performance and extends the lifespan of the remaining bearing.
Resources for Professional Advice
Seeking professional advice from qualified mechanics is crucial for making informed decisions about wheel bearing replacement. Here are some resources that can provide valuable insights:
- Reputable Automotive Repair Shops: Consult with local mechanics or automotive repair shops known for their expertise and customer satisfaction.
- Vehicle Manufacturer’s Service Manuals: These manuals provide detailed specifications and recommendations for your specific vehicle model.
- Online Forums and Communities: Engage with online communities dedicated to automotive repair and maintenance. Seek advice from experienced mechanics and enthusiasts.
- Automotive Parts Suppliers: Contact reputable parts suppliers for technical assistance and recommendations on wheel bearing replacement.
Scenarios for Replacing Both Bearings, Should you replace wheel bearings in pairs
Several scenarios strongly suggest replacing both wheel bearings simultaneously:
- Significant Wear on One Bearing: If one bearing exhibits significant wear, it’s likely that the other bearing is also nearing the end of its lifespan. Replacing both bearings prevents premature failure of the remaining bearing and ensures balanced performance.
- Uneven Tire Wear: Uneven tire wear can indicate a problem with wheel bearings. If one bearing is worn, it can cause the wheel to misalign, leading to uneven tire wear. Replacing both bearings ensures proper alignment and even tire wear.
- Vehicle Age and Mileage: As vehicles age and accumulate mileage, wheel bearings are susceptible to wear and tear. Replacing both bearings proactively can prevent unexpected failures and costly repairs.
- Preventive Maintenance: Replacing both bearings during routine maintenance, such as brake pad replacement or suspension work, can extend the lifespan of the bearings and prevent future problems.
DIY vs. Professional Replacement: Should You Replace Wheel Bearings In Pairs
The decision to replace wheel bearings yourself or hire a professional mechanic is a significant one, influenced by factors such as your mechanical skills, available tools, and time constraints. Both approaches have advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right path depends on your individual circumstances.
This section delves into the comparison of DIY versus professional wheel bearing replacement, exploring the pros and cons of each approach, outlining a checklist to assess your capabilities, and discussing potential risks associated with DIY attempts.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The choice between DIY and professional replacement hinges on a careful evaluation of the benefits and drawbacks of each option.
- DIY Advantages:
- Cost Savings: DIY replacement can significantly reduce repair costs, as you eliminate labor charges. This is particularly attractive for budget-conscious individuals.
- Greater Control: Performing the replacement yourself gives you complete control over the process, allowing you to choose parts and ensure they are installed correctly.
- Learning Experience: DIY projects offer a valuable learning experience, enhancing your mechanical knowledge and skills.
- DIY Disadvantages:
- Technical Expertise: Replacing wheel bearings requires specialized tools and a good understanding of automotive mechanics. Lacking the necessary expertise can lead to improper installation, potentially causing further damage.
- Time Commitment: DIY replacement can be time-consuming, especially for beginners. It requires a significant amount of time for research, tool acquisition, and the actual repair process.
- Risk of Injury: Working on a vehicle can be hazardous, especially when dealing with heavy components and sharp tools. Improper handling can result in injuries.
- Potential for Damage: Incorrect installation or the use of low-quality parts can damage the wheel hub, axle, or other components, leading to further repairs.
- Professional Advantages:
- Expertise and Experience: Professional mechanics have extensive training and experience in automotive repair, ensuring proper installation and minimizing the risk of damage.
- Specialized Tools: Mechanics have access to specialized tools and equipment that are often necessary for efficient and accurate wheel bearing replacement.
- Warranty: Professional repairs usually come with a warranty, providing peace of mind in case of any issues after the replacement.
- Professional Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: Professional labor charges can significantly increase the overall cost of the repair compared to DIY.
- Limited Control: Hiring a mechanic means relinquishing control over the process, potentially leading to concerns about part quality or installation methods.
DIY Feasibility Checklist
Before attempting a DIY wheel bearing replacement, carefully assess your capabilities and resources by using this checklist:
- Mechanical Skills: Do you have experience working on vehicles and a good understanding of automotive mechanics, particularly suspension and wheel systems?
- Tools and Equipment: Do you have access to the necessary tools, including a hydraulic press, torque wrench, and specialized sockets?
- Time Availability: Are you willing to dedicate the necessary time to research, tool acquisition, and the actual repair process?
- Technical Resources: Do you have access to reliable repair manuals, online resources, or videos that can guide you through the process?
- Safety Precautions: Are you comfortable working with heavy components and sharp tools, and are you aware of necessary safety precautions?
Potential Risks and Challenges
Attempting a DIY wheel bearing replacement without proper knowledge and tools can lead to significant risks and challenges, including:
- Improper Installation: Incorrect installation can damage the wheel hub, axle, or other components, leading to further repairs or even accidents.
- Over-tightening or Under-tightening: Incorrect torque settings can cause premature bearing failure or damage to the wheel hub.
- Damage to Other Components: Improper handling of components during the replacement process can damage brake lines, suspension parts, or other surrounding components.
- Safety Concerns: Working on a vehicle without proper safety precautions can result in injuries, especially when dealing with heavy components and sharp tools.
- Warranty Issues: Attempting DIY repairs can void the vehicle’s warranty, potentially leading to expensive out-of-pocket expenses for future repairs.
In conclusion, replacing wheel bearings in pairs is generally recommended for a number of reasons. It promotes balanced wear and tear, prolongs the life of the new bearings, and helps prevent premature failure. While replacing just one bearing might seem like a cost-saving option in the short term, it could lead to additional repairs and expenses down the road. Consulting with a trusted mechanic can help you assess your specific situation and determine the best course of action for your vehicle.
FAQ Resource
What are the signs of a bad wheel bearing?
Common signs of a bad wheel bearing include grinding or roaring noises, especially when turning or driving at higher speeds, a vibration in the steering wheel, and a noticeable wobble or play in the wheel.
How long do wheel bearings typically last?
The lifespan of wheel bearings varies depending on factors such as driving conditions, vehicle weight, and maintenance practices. However, they typically last between 50,000 and 100,000 miles.
Can I replace wheel bearings myself?
Replacing wheel bearings can be a challenging task, requiring specialized tools and technical expertise. It’s generally recommended to have a qualified mechanic perform the replacement, especially if you lack experience with automotive repairs.