What is a MIDI ring? Well, imagine a ring that lets you control your music like a conductor with a magic wand! It’s basically a high-tech piece of jewelry that uses sensors to pick up your hand movements and translate them into musical commands. Think of it as a tiny orchestra conductor sitting on your finger, ready to play those sweet, sweet melodies.
MIDI rings are like the coolest new gadget for musicians, letting you control virtual instruments, trigger samples, and even create unique sounds just by moving your hands. It’s like having a mini-DJ booth on your finger, but without the awkward dance moves. These rings use something called MIDI communication, which is basically a language that lets different musical instruments and software talk to each other.
So, when you move your fingers, the ring sends signals to your computer or music software, telling it what to do. It’s like sending a secret message to your music, telling it to play a note, change the volume, or even bend the pitch of a sound.
What is a MIDI Ring?
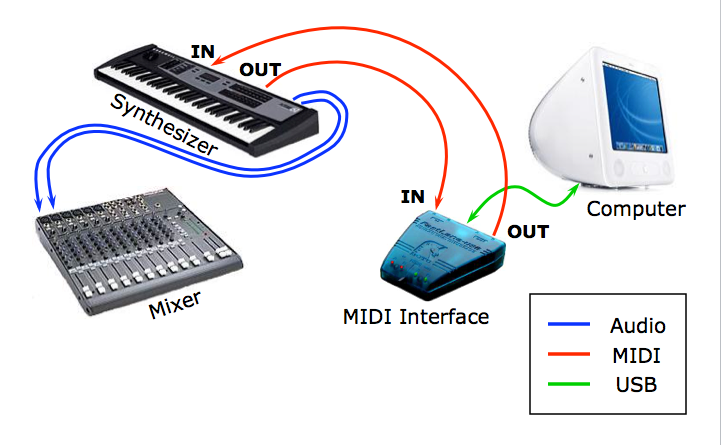
A MIDI ring is a wearable device that allows musicians to control musical instruments and software using hand gestures. It’s essentially a small, ring-shaped controller that utilizes sensors to track finger movements and translate them into MIDI signals. These signals can then be used to trigger notes, change instrument parameters, or manipulate other aspects of a musical performance.
MIDI Communication
MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a communication protocol that allows electronic musical instruments and computers to communicate with each other. It transmits data related to musical performance, such as note pitch, velocity, timing, and other musical parameters.
Advantages of Using a MIDI Ring
MIDI rings offer several advantages over traditional controllers:
- Portability: MIDI rings are small and lightweight, making them easy to carry and use in various settings.
- Intuitive Control: Using hand gestures to control music is a natural and intuitive way to interact with musical instruments.
- Versatility: MIDI rings can be used with a wide range of musical instruments and software, including synthesizers, drum machines, and music production software.
- Creative Possibilities: The freedom of movement and expressive control offered by MIDI rings can inspire new and innovative ways to create music.
Components and Functionality: What Is A Midi Ring
MIDI rings are fascinating devices that bridge the gap between the physical world and digital music creation. They use a combination of sensors and clever circuitry to translate hand gestures into musical data. This ability allows musicians to control their instruments and software in a way that feels intuitive and expressive.
Sensors and Circuitry
The heart of a MIDI ring lies in its sensors and circuitry. These components work together to detect and interpret hand movements, converting them into MIDI signals.
- Accelerometers: These sensors measure acceleration and tilt, allowing the ring to detect finger movements and hand gestures. They are often used to control parameters like pitch bend and volume.
- Gyroscopes: Gyroscopes measure rotational velocity, providing information about the ring’s orientation in space. This data can be used to control MIDI effects like modulation and panning.
- Magnetometers: These sensors detect magnetic fields, enabling the ring to track finger position and orientation relative to a magnetic field. This data can be used to control parameters like note selection and velocity.
- Microcontroller: The microcontroller acts as the brain of the ring, processing data from the sensors and converting it into MIDI signals. It also manages communication with external devices.
- Bluetooth or USB Connectivity: MIDI rings typically connect to computers or other devices via Bluetooth or USB, allowing them to transmit MIDI data.
Translating Hand Gestures into MIDI Data
The process of converting hand gestures into MIDI data is a fascinating combination of hardware and software.
- Gesture Recognition: The ring’s software analyzes the data received from the sensors, identifying specific hand gestures. These gestures are then mapped to specific MIDI commands.
- MIDI Data Conversion: Once a gesture is recognized, the ring’s software translates it into a corresponding MIDI message. This message contains information about the musical event, such as the note, velocity, or control change.
Types of MIDI Data Transmitted
MIDI rings can transmit a variety of MIDI data, allowing musicians to control various aspects of their musical performance.
- Note On/Off: These messages indicate when a note should be played or stopped. The ring can trigger notes by detecting finger taps or swipes.
- Velocity: Velocity represents the force with which a note is played, influencing its volume and intensity. The ring can control velocity by detecting the speed and force of finger movements.
- Pitch Bend: This message allows musicians to adjust the pitch of a note in real-time. The ring can control pitch bend by detecting the tilting or rotation of the hand.
- Control Change: These messages allow musicians to control various parameters, such as volume, panning, and effects. The ring can control these parameters by detecting different finger gestures.
Applications in Music Production

MIDI rings offer a novel and intuitive way to control music production software, expanding the possibilities for creative expression. Their gesture recognition capabilities, combined with the versatility of MIDI, allow musicians and producers to interact with their instruments and software in ways that were previously unimaginable.
Controlling Virtual Instruments
MIDI rings can be used to control a wide range of virtual instruments, such as synthesizers, samplers, and drum machines. By assigning different gestures to different parameters, such as pitch, volume, and effects, musicians can manipulate the sound of their instruments in real-time. This allows for a level of expressiveness and nuance that is difficult to achieve with traditional controllers.
For instance, a musician could use a ring to control the pitch of a synthesizer by simply moving their finger up and down, or they could use a combination of gestures to create complex and evolving soundscapes.
Triggering Samples, What is a midi ring
MIDI rings can also be used to trigger samples, allowing musicians to create beats, melodies, and sound effects with a simple gesture. This opens up new possibilities for creating music on the fly, as musicians can experiment with different sounds and rhythms without having to rely on traditional methods of sample triggering. Imagine a drummer using a MIDI ring to trigger different drum samples with their fingers, creating a dynamic and intricate beat.
Creating Expressive Performances
The gesture recognition capabilities of MIDI rings allow musicians to create expressive performances that are impossible to achieve with traditional controllers. By assigning different gestures to different MIDI messages, musicians can control the dynamics, articulation, and other expressive qualities of their performances. This allows for a more natural and intuitive way of playing music, as musicians can simply move their fingers in a way that feels natural to them.
“MIDI rings offer a new level of expressiveness and control, allowing musicians to create music in a way that feels more intuitive and natural.”
[Source
[Name of the source]]
Potential for Unique Musical Experiences
MIDI rings have the potential to revolutionize music production by creating unique and innovative musical experiences. Their ability to track multiple gestures simultaneously allows for complex and nuanced interactions with music software, opening up new possibilities for musical exploration. For example, a musician could use a ring to control multiple instruments at once, or they could use a combination of gestures to create complex and evolving sound textures.
Technical Considerations
MIDI rings, while innovative, come with specific technical considerations that impact their performance and usability. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed choices when selecting and using a MIDI ring for music production.
Data Transmission Protocols
The data transmission protocol used by a MIDI ring determines how it communicates with other devices and software. MIDI rings typically employ the MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) protocol, a standard communication language for musical instruments and electronic devices. This protocol allows the ring to send and receive data related to musical notes, timing, and other parameters.
- MIDI over Bluetooth: Some MIDI rings utilize Bluetooth technology for wireless communication. This offers convenience and flexibility, but it may introduce latency and limit the range of compatible devices.
- MIDI over USB: MIDI rings that connect via USB often provide a more stable and reliable connection with lower latency. This is particularly important for real-time music production, where precise timing is essential.
Latency
Latency refers to the delay between the time a user interacts with a MIDI ring and the time the corresponding data is received and processed by the software. This delay can be significant, especially in wireless connections or when using devices with limited processing power.
- Wireless Connections: Bluetooth connections often introduce higher latency compared to wired connections.
- Processing Power: Devices with limited processing power may struggle to process MIDI data quickly, leading to noticeable latency.
Compatibility
Compatibility with various software and hardware is a critical factor to consider when choosing a MIDI ring. Not all MIDI rings are compatible with every software and hardware combination.
- Software Compatibility: Ensure the MIDI ring is compatible with your preferred music production software, such as Ableton Live, Logic Pro X, or FL Studio. Check the manufacturer’s website or documentation for compatibility information.
- Hardware Compatibility: Verify that the MIDI ring connects to your computer or other devices using the appropriate ports and interfaces (e.g., USB, Bluetooth). Some MIDI rings may require specific drivers or software to function correctly.
Setting Up and Configuring
Setting up and configuring a MIDI ring with music production software typically involves the following steps:
- Connecting the MIDI Ring: Connect the MIDI ring to your computer or other devices using the appropriate cable or wireless connection.
- Installing Drivers: If necessary, install the required drivers for the MIDI ring. These drivers ensure that your computer recognizes the device and can communicate with it.
- Selecting the MIDI Input/Output: Open your music production software and select the MIDI ring as the input or output device. This will allow the software to receive and interpret data from the ring.
- Mapping Controls: Map the different controls on the MIDI ring to specific functions within your software. This can involve assigning gestures, movements, or pressure levels to various parameters, such as notes, volume, effects, or automation.
Comparison of MIDI Ring Models
The market offers various MIDI ring models with different features, specifications, and price points. Here’s a comparison of some popular options:
| Model | Data Transmission | Latency | Compatibility | Features | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roli Seaboard Block | Bluetooth, USB | Low latency | Compatible with various software and hardware | Pressure-sensitive surface, expressive control | $299 |
| Artiphon Instrument 1 | Bluetooth, USB | Moderate latency | Compatible with various software and hardware | Multi-touch surface, customizable controls | $399 |
| Sensel Morph | USB | Low latency | Compatible with various software and hardware | Pressure-sensitive surface, customizable layout | $299 |
Future of MIDI Rings
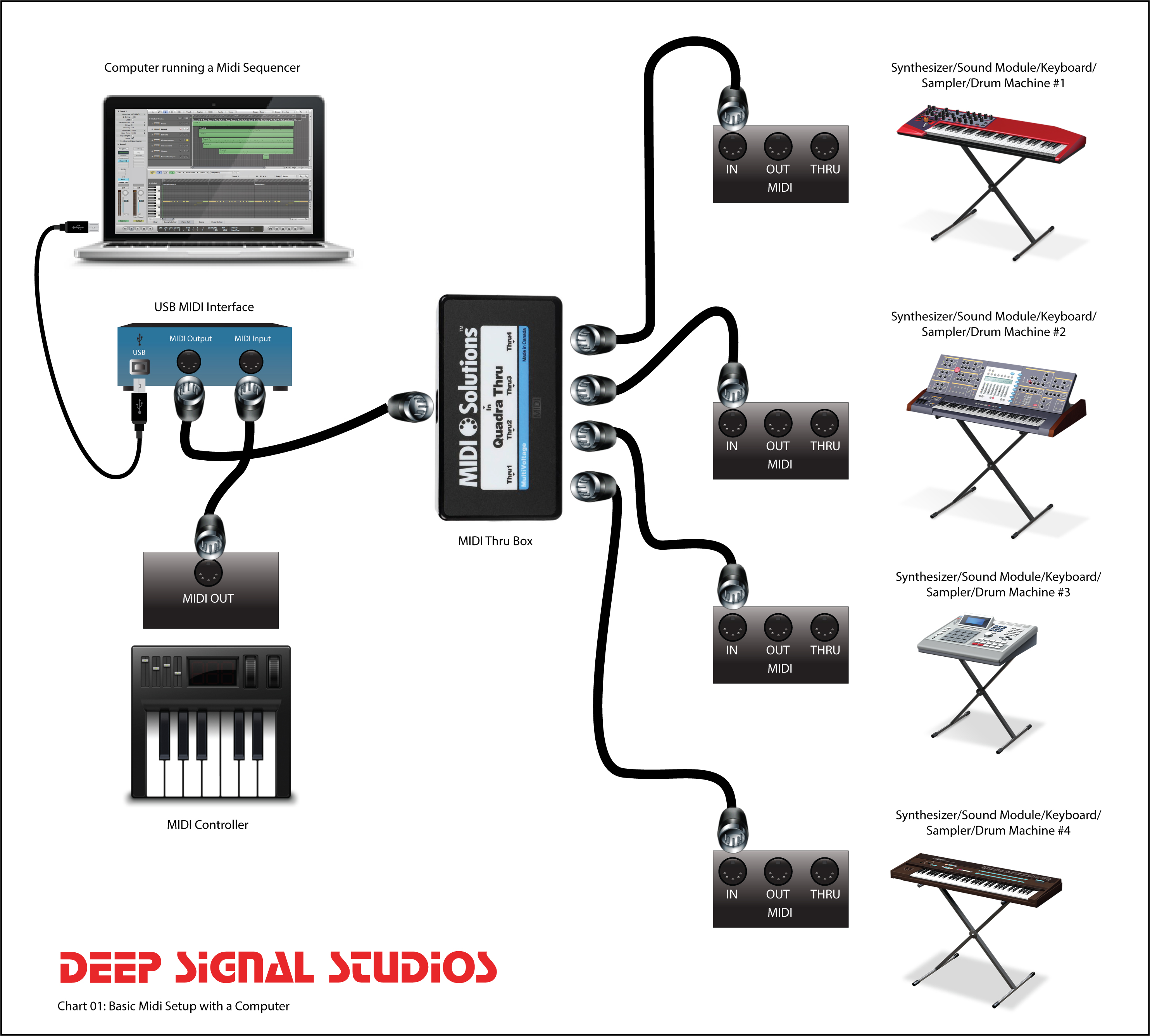
MIDI rings are still a relatively new technology, but their potential for revolutionizing music creation and performance is immense. As sensor technology and artificial intelligence continue to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and powerful MIDI rings emerge in the years to come.
Advancements in Sensor Technology
The capabilities of MIDI rings are directly tied to the sophistication of their sensors. Current MIDI rings utilize a variety of sensors, including accelerometers, gyroscopes, and pressure sensors, to track hand movements and gestures. However, future MIDI rings could incorporate even more advanced sensors, such as:
- EMG Sensors: These sensors detect electrical signals in muscles, allowing for more precise and nuanced control over musical parameters. For example, a musician could use EMG sensors to control the volume or pitch of a sound based on the subtle tension in their fingers.
- Haptic Feedback Sensors: These sensors provide tactile feedback to the user, allowing for a more immersive and interactive musical experience. For instance, a musician could feel the rhythm of a beat or the intensity of a chord through haptic feedback.
- Optical Sensors: Optical sensors could be used to track hand movements with even greater accuracy and precision than current sensor technology. This would allow for more complex and expressive musical gestures.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
AI has the potential to significantly enhance the capabilities of MIDI rings. AI algorithms could be used to:
- Predict and anticipate musical intentions: AI could learn a musician’s playing style and preferences, allowing it to predict and anticipate their musical intentions. This could enable more intuitive and responsive musical interaction with MIDI rings.
- Generate and compose music: AI could be used to generate musical ideas and compositions based on the user’s input. This could provide musicians with a powerful new tool for creativity and exploration.
- Personalize musical experiences: AI could be used to personalize the musical experience for each user. For example, a MIDI ring could automatically adjust its settings to match the user’s playing style and preferences.
Impact on Music Creation and Performance
The development of more advanced MIDI rings could have a profound impact on the future of music creation and performance. Here are some potential impacts:
- New musical possibilities: MIDI rings could open up new musical possibilities by enabling musicians to control a wider range of musical parameters with greater precision and expressiveness.
- More accessible music creation: MIDI rings could make music creation more accessible to people who are not traditionally trained musicians.
- Enhanced live performance: MIDI rings could enhance live performances by allowing musicians to interact with their instruments in new and innovative ways.
- Collaborative music making: MIDI rings could facilitate collaborative music making by allowing musicians to interact with each other’s instruments in real time.
So, there you have it! MIDI rings are a game-changer for musicians, allowing them to create music in ways that were previously unimaginable. It’s like having a secret weapon in your music arsenal, ready to unleash your inner maestro and create sonic masterpieces that would make even the most seasoned musician jealous. With their versatility and intuitive interface, MIDI rings are poised to revolutionize the way we make music, one finger movement at a time.
So, if you’re looking to add a touch of magic and innovation to your musical journey, maybe it’s time to put a ring on it!
Quick FAQs
What are some popular MIDI ring brands?
Some popular MIDI ring brands include Roli, Sensel, and ROLI Seaboard.
Are MIDI rings compatible with all music software?
Most MIDI rings are compatible with popular music production software like Ableton Live, FL Studio, and Logic Pro. However, it’s always best to check the manufacturer’s specifications for compatibility.
How much do MIDI rings cost?
The price of MIDI rings can vary depending on the brand, features, and technology used. They typically range from a few hundred dollars to over a thousand dollars.
Are MIDI rings difficult to use?
MIDI rings are designed to be user-friendly and intuitive. They often come with software that allows you to customize the ring’s settings and map your hand movements to specific musical actions.