Does TMJ cause ear ringing sets the stage for this exploration, delving into the complex relationship between the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) and a persistent ringing in the ears, known as tinnitus. The TMJ, located just in front of the ear, plays a crucial role in chewing, speaking, and yawning. While the exact mechanisms are still being studied, evidence suggests that TMJ dysfunction can indeed contribute to ear ringing, often through intricate pathways involving muscle tension, inflammation, or nerve compression.
This article examines the anatomical connections, common symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and various treatment options for managing TMJ-related ear ringing. It aims to shed light on the often-overlooked connection between these two seemingly disparate conditions, offering valuable insights for individuals experiencing this perplexing symptom.
TMJ and Ear Ringing
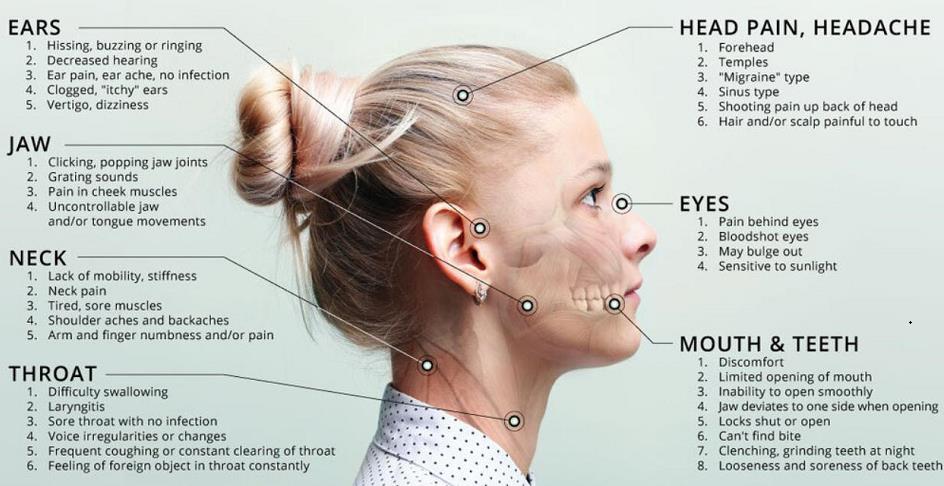
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ), located just in front of your ear, plays a crucial role in chewing, speaking, and swallowing. This complex joint connects your jawbone to your skull, and its proper functioning is essential for these everyday activities. Ear ringing, also known as tinnitus, is a common symptom that can be caused by a variety of factors, including TMJ dysfunction.
Understanding the anatomical relationship between the TMJ and the ear can help shed light on how these two seemingly unrelated conditions might be interconnected.
Anatomical Relationship Between TMJ and Ear
The close proximity of the TMJ to the ear makes it possible for dysfunction in the joint to affect the ear structures. The TMJ, ear canal, and middle ear are all situated within a confined space, and any changes in the TMJ can impact the surrounding structures, including the delicate nerves and blood vessels responsible for hearing.
Potential Pathways for TMJ Dysfunction to Impact Ear Structures
The connection between TMJ dysfunction and ear ringing can be attributed to several potential pathways:
Muscle Tension
The muscles surrounding the TMJ, such as the masseter and temporalis muscles, can become tense and tight due to stress, clenching, or grinding of the teeth. This muscle tension can put pressure on the nerves and blood vessels in the ear, leading to ear ringing.
Joint Inflammation
Inflammation of the TMJ, known as temporomandibular joint disorder (TMD), can also cause ear ringing. The inflammation can irritate the nerves and blood vessels in the ear, leading to pain, pressure, and ringing in the ears.
Nerve Compression
The trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for sensation in the face and jaw, passes through the TMJ region. Compression of this nerve due to TMJ dysfunction can lead to ear ringing, as well as other symptoms such as facial pain and numbness.
“TMJ dysfunction can cause ear ringing by affecting the nerves and blood vessels in the ear. This can happen due to muscle tension, joint inflammation, or nerve compression in the TMJ region.”
Examples of How TMJ Dysfunction Can Lead to Ear Ringing
Muscle Tension
A person who clenches their jaw during stressful situations might experience muscle tension in the TMJ region. This tension can put pressure on the nerves and blood vessels in the ear, leading to ear ringing.
Joint Inflammation
Someone with arthritis in the TMJ might experience inflammation and pain in the joint. This inflammation can irritate the nerves and blood vessels in the ear, leading to ear ringing and other symptoms.
Nerve Compression
A person with a displaced jawbone might experience compression of the trigeminal nerve. This compression can lead to ear ringing, as well as other symptoms such as facial pain and numbness.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and diagnostic process for TMJ disorders is crucial for proper treatment and management. Recognizing the signs and seeking professional evaluation can help alleviate discomfort and prevent complications.
Symptoms of TMJ Disorders
TMJ disorders can manifest in various ways, affecting the jaw, ears, and surrounding areas. Common symptoms include:
- Jaw pain: Aching, throbbing, or sharp pain in the jaw, often localized near the ear or temple. The pain may worsen with chewing, talking, or yawning.
- Clicking or popping: A noticeable clicking or popping sound when opening or closing the mouth, indicating a misalignment or dysfunction in the joint.
- Limited jaw movement: Difficulty opening the mouth wide, chewing, or speaking clearly due to stiffness or pain in the jaw joint.
- Ear ringing (Tinnitus): A persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing sound in the ear, which can be a symptom of TMJ disorders, particularly when the pain is located near the ear.
- Headaches: Frequent or intense headaches, often localized around the temples or forehead, can be associated with TMJ disorders.
- Facial pain: Pain in the face, especially around the cheeks or jaw, can also indicate a TMJ problem.
- Neck pain: Pain in the neck or shoulders can sometimes be linked to TMJ disorders, particularly if the jaw joint is misaligned.
Differentiating TMJ-Related Tinnitus from Other Causes
It’s important to differentiate TMJ-related tinnitus from other causes, as the treatment approach will vary. Here’s how to distinguish:
- TMJ-related tinnitus is often associated with jaw pain, clicking, or limited jaw movement. The ringing sound may be intermittent or persistent, and it may worsen with jaw movements.
- Other causes of tinnitus include:
- Exposure to loud noises: Prolonged exposure to loud music, machinery, or firearms can damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear, leading to tinnitus.
- Ear infections: Infections in the middle ear can cause inflammation and pressure, leading to tinnitus.
- Medications: Some medications, such as aspirin, antibiotics, and chemotherapy drugs, can cause tinnitus as a side effect.
- Underlying medical conditions: Conditions like high blood pressure, thyroid disorders, and cardiovascular disease can also contribute to tinnitus.
Diagnosis of TMJ Disorders
A comprehensive diagnostic process is essential to identify the underlying cause of TMJ-related symptoms and rule out other conditions.
- Physical examination: A thorough examination of the jaw joint, muscles, and surrounding areas helps assess range of motion, palpate for tenderness, and identify any clicking or popping sounds.
- Imaging studies: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs may be ordered to provide detailed images of the jaw joint, revealing any structural abnormalities or damage.
- Ruling out other conditions: A medical history review and physical examination are crucial to rule out other potential causes of ear ringing, such as ear infections, neurological disorders, or cardiovascular problems.
Treatment Options for TMJ-Related Ear Ringing: Does Tmj Cause Ear Ringing

If you’re experiencing ear ringing alongside TMJ symptoms, it’s crucial to seek professional help. There are various treatment options available to manage TMJ disorders and alleviate associated ear ringing. The approach will depend on the severity of your condition and underlying causes.
Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatments are often the first line of defense for TMJ disorders and associated ear ringing. These methods aim to reduce pain, inflammation, and muscle tension.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain and inflammation. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatory medications to reduce muscle tension and discomfort.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen jaw muscles, improve range of motion, and reduce pain. They may also recommend techniques like heat therapy or massage to relieve muscle tension.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making changes to your daily habits can help reduce strain on your jaw. These include:
- Avoiding chewing gum or hard candy.
- Eating softer foods that require less chewing.
- Practicing stress-reduction techniques like yoga or meditation.
- Maintaining good posture.
- Avoiding clenching or grinding your teeth, especially during sleep.
Dental Interventions
Dental interventions play a significant role in addressing TMJ-related ear ringing, particularly when misalignment or bite problems contribute to the disorder.
- Occlusal Adjustments: A dentist can adjust the fit of your teeth to improve the alignment of your bite. This can help reduce strain on the jaw joint and alleviate associated ear ringing.
- Bite Guards: Custom-made mouthguards, worn at night, can help prevent teeth grinding (bruxism), which can contribute to TMJ pain and ear ringing.
Injections
In some cases, injections may be used to manage TMJ-related ear ringing. These injections are typically used to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Corticosteroids are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that can be injected directly into the TMJ joint to reduce swelling and pain.
- Botox Injections: Botox injections can temporarily paralyze the muscles involved in jaw clenching and grinding, reducing pain and muscle tension. This can also help alleviate ear ringing associated with TMJ dysfunction.
Surgery
Surgery is generally considered a last resort for TMJ disorders. It may be recommended in cases where conservative treatments have failed to provide relief or when the TMJ joint is severely damaged.
- Arthroscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small camera and surgical instruments into the TMJ joint to repair or remove damaged tissue.
- Open Joint Surgery: This more invasive procedure involves making a larger incision to access the TMJ joint for more extensive repairs.
Research and Evidence
While the connection between TMJ disorders and ear ringing (tinnitus) is increasingly recognized, research on this specific relationship is still evolving. Several studies have explored this link, offering insights into the potential mechanisms and prevalence of this association.
Studies Supporting the Link Between TMJ Dysfunction and Tinnitus, Does tmj cause ear ringing
The existing research provides evidence supporting the link between TMJ dysfunction and tinnitus.
- A 2015 study published in the Journal of Oral & Facial Pain and Headache found that 78% of patients with TMJ disorders reported experiencing tinnitus. The study further indicated that the severity of tinnitus correlated with the severity of TMJ pain and dysfunction.
- Another study, published in the International Journal of Audiology in 2017, investigated the prevalence of tinnitus in patients with temporomandibular joint disorders (TMD). The researchers found a significantly higher prevalence of tinnitus in patients with TMD compared to a control group.
These studies suggest a strong correlation between TMJ dysfunction and tinnitus, indicating a potential causal relationship.
Limitations of Current Research and Areas for Further Investigation
Despite the growing body of evidence, there are limitations to current research on the relationship between TMJ disorders and ear ringing.
- Many studies are observational, meaning they cannot definitively prove a causal link between TMJ dysfunction and tinnitus. Further research is needed to establish a causal relationship and determine the specific mechanisms involved.
- The heterogeneity of TMJ disorders and tinnitus makes it challenging to conduct large-scale, controlled studies. Different types of TMJ disorders and tinnitus may have varying etiologies and characteristics, requiring further investigation to understand the specific relationships between these conditions.
- The precise mechanisms by which TMJ dysfunction might lead to tinnitus are not fully understood. More research is needed to explore potential mechanisms, such as muscle spasms, inflammation, and nerve compression, that may contribute to the development of tinnitus in individuals with TMJ disorders.
Further research is essential to address these limitations and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the relationship between TMJ disorders and ear ringing.
Patient Perspectives and Management

Living with TMJ-related ear ringing can be a challenging experience, and understanding the perspectives of individuals who have navigated this condition is crucial for effective management. These individuals offer valuable insights into the impact of ear ringing on daily life, the coping strategies they have employed, and the importance of seeking professional help.
Impact on Daily Life and Quality of Life
The constant presence of ear ringing can significantly disrupt daily life and impact quality of life. Individuals may experience:
- Difficulty concentrating: The persistent sound can make it challenging to focus on tasks, especially those requiring concentration, such as reading, studying, or working.
- Sleep disturbances: Ear ringing can interfere with sleep, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. This can lead to fatigue, irritability, and impaired cognitive function.
- Social isolation: The constant ringing can be embarrassing and make it difficult to engage in social situations, leading to feelings of isolation and withdrawal.
- Emotional distress: Ear ringing can trigger feelings of anxiety, frustration, depression, and even anger. The constant sound can be a constant reminder of the condition and its impact on their lives.
The intricate link between TMJ dysfunction and ear ringing underscores the importance of a holistic approach to diagnosis and treatment. While the exact mechanisms are still under investigation, the evidence suggests a strong connection, offering hope for effective management. By understanding the potential causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can navigate this challenging condition with greater awareness and seek appropriate care to alleviate ear ringing and improve overall well-being.
General Inquiries
Can TMJ cause permanent ear ringing?
While TMJ dysfunction can contribute to ear ringing, it’s not always permanent. Treatment often alleviates the ringing. However, if the underlying TMJ issue persists, the ear ringing may continue.
Is TMJ-related ear ringing common?
The prevalence of TMJ-related ear ringing is still being studied, but it’s considered a relatively common symptom among individuals with TMJ disorders.
Can stress worsen TMJ-related ear ringing?
Yes, stress can exacerbate TMJ disorders and potentially worsen ear ringing. Stress management techniques are often recommended as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.