Knowing how to count bike chain links is an essential skill for any cyclist. This seemingly simple task can be the difference between a smooth ride and a frustrating experience. Whether you’re replacing a worn-out chain, adjusting the length for a new drivetrain, or simply trying to understand the mechanics of your bike, counting chain links is a fundamental step.
This guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools to confidently count your bike chain links, ensuring your bike runs efficiently and smoothly. We’ll explore various methods, discuss the importance of chain link count, and delve into the process of adjusting and maintaining your chain for optimal performance.
Understanding Bike Chain Links
A bike chain is a crucial component that transmits power from the pedals to the rear wheel, enabling the bike to move. It consists of a series of interconnected links, each playing a vital role in the chain’s functionality. Understanding the different types of links and their purpose is essential for proper chain maintenance and ensuring optimal bike performance.
Types of Bike Chain Links, How to count bike chain links
The construction of a bike chain involves different types of links, each serving a specific purpose. These links are designed to connect seamlessly and work together to form a continuous chain.
- Outer Links: These links form the outer edges of the chain and are responsible for engaging with the chainrings and sprockets. They have a plate on either side, creating a strong and durable connection.
- Inner Links: These links are located between the outer links and connect the chain plates. They have a pin that passes through the outer links, holding them together.
- Master Links: These are specialized links designed for easy chain assembly and disassembly. They typically have a special mechanism that allows them to be removed and reattached without the need for tools. Master links are often used to connect the chain ends when assembling a new chain or replacing a worn one.
Importance of Chain Link Count
The number of links in a bike chain is crucial for proper bike function and performance.
The chain length determines the chain’s overall length, which directly impacts the chain’s tension and the bike’s shifting performance.
- Correct Chain Length: A chain that is too short will be under excessive tension, leading to premature wear and tear on the chain, cassette, and chainrings. It can also cause difficulty shifting gears smoothly. On the other hand, a chain that is too long will be slack, resulting in poor power transfer and potential chain derailment.
- Chain Wear: As a chain wears down, the links stretch, increasing the chain’s overall length. This can lead to chain skipping, poor shifting, and ultimately chain failure. Regular chain maintenance, including cleaning and lubrication, is essential to minimize wear and extend the chain’s lifespan. When a chain reaches a certain level of wear, it needs to be replaced to prevent further damage to other drivetrain components.
Methods for Counting Chain Links
Accurately counting the number of links in a bicycle chain is crucial for determining its length, ensuring proper chain tension, and selecting the correct replacement chain. Several methods can be employed to achieve this task.
Counting Chain Links with a Ruler or Measuring Tape
This method involves measuring the overall length of the chain and then calculating the number of links based on the length of each individual link.
- Measure the Chain: Lay the chain out straight on a flat surface. Use a ruler or measuring tape to measure the total length of the chain in millimeters or inches.
- Determine Link Length: Measure the length of a single chain link, including the width of the pin and the space between the plates. The typical length of a bicycle chain link is around 1/2 inch (12.7 mm).
- Calculate the Number of Links: Divide the total chain length by the length of a single link. This will give you the approximate number of links in the chain.
Number of Links = Total Chain Length / Length of One Link
- Adjust for Overlap: Since the chain links overlap slightly, the calculated number of links may be slightly higher than the actual number. Subtract a few links (typically 1-2) from the calculated value to account for this overlap.
Counting Chain Links Using a Reference Point
This method relies on counting the number of links between two specific points on the chain.
- Select a Reference Point: Choose a recognizable feature on the chain, such as the master link or a specific link at the end of the chain.
- Count Links: Starting from the reference point, count the number of links until you reach another recognizable point on the chain, such as the master link or the end of the chain.
- Adjust for Overlap: As with the previous method, you may need to adjust the count slightly to account for the overlap between links.
Comparison of Counting Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Ruler or Measuring Tape |
|
|
| Reference Point |
|
|
Determining the Correct Chain Link Count

Determining the ideal chain link count for your bike is crucial for optimal performance and drivetrain longevity. The correct chain length ensures smooth shifting, prevents chain derailing, and minimizes wear and tear on your components. Several factors influence the ideal chain link count, including frame size, drivetrain components, and intended use.
Factors Influencing Chain Link Count
The ideal chain link count for a specific bike is determined by a combination of factors. These factors ensure that the chain is neither too short, causing tension and strain on the drivetrain, nor too long, leading to potential derailing or entanglement.
- Frame Size: Larger frames generally require longer chains to accommodate the increased distance between the chainrings and cassette. Conversely, smaller frames typically require shorter chains.
- Drivetrain Components: The number of gears on your cassette and chainrings influences the chain length. A larger cassette or chainring requires a longer chain to accommodate the increased travel distance.
- Intended Use: Bikes designed for aggressive riding, such as mountain bikes, often have shorter chain lengths to minimize chain slack and improve pedaling efficiency. Road bikes, on the other hand, may have longer chains to accommodate a wider range of gear combinations.
Recommended Chain Link Counts for Various Bike Types
The following table Artikels recommended chain link counts for various bike types, providing a general guideline for determining the appropriate length. These recommendations are based on typical configurations and may vary depending on the specific components and frame size.
| Bike Type | Recommended Chain Link Count |
|---|---|
| Road Bike | 110-116 |
| Mountain Bike | 106-112 |
| Hybrid Bike | 108-114 |
| Cruiser Bike | 104-110 |
Note: These are just general recommendations, and the ideal chain link count for your bike may vary. Always consult your bike’s user manual or a qualified bike mechanic for specific recommendations.
Adjusting Chain Link Count: How To Count Bike Chain Links
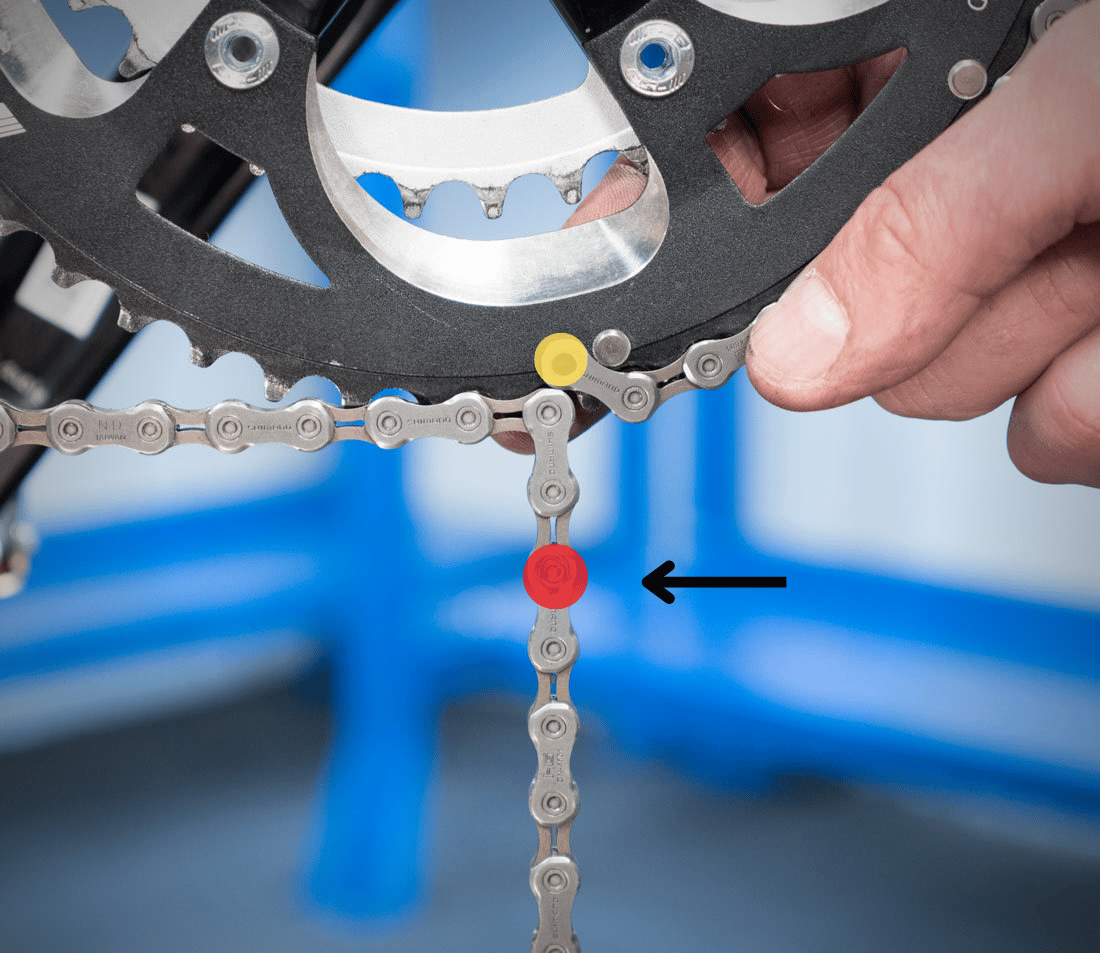
After determining the correct chain link count for your bike, you might need to adjust the existing chain length. This involves either adding or removing links to achieve the desired length.
Chain Link Adjustment Process
The process of adjusting the chain link count involves removing or adding links using a chain tool. This tool is specifically designed for this purpose and is essential for maintaining the integrity of the chain.
Using a Chain Tool
A chain tool is a specialized tool used to remove and add links to a bicycle chain. It consists of a handle, a pin punch, and a chain breaker. The pin punch is used to drive out the chain pins, and the chain breaker is used to compress the chain links together.
- Identify the Chain Link to Remove: Determine the link that needs to be removed. To shorten the chain, remove links from the section that is slack.
- Position the Chain Tool: Place the chain tool on the chain link to be removed. Align the pin punch with the chain pin.
- Drive Out the Chain Pin: Use the pin punch to drive out the chain pin. Apply even pressure to avoid damaging the chain.
- Remove the Link: Once the pin is removed, separate the two links.
- Repeat for Additional Links: If you need to remove more links, repeat steps 2-4.
- Adding Chain Links: To add a link, use a new chain link and a chain tool. Align the new link with the existing chain and use the chain tool to press the chain pin into the link.
Securing Chain Links After Adjustment
After adjusting the chain link count, it’s important to secure the chain links properly. This ensures the chain remains intact and functions correctly.
- Check for Proper Tension: Once the chain is adjusted, ensure it has the correct tension. It should be taut but not overly tight.
- Reinstall the Chain: After adjusting the chain, reinstall it on the rear derailleur and cassette.
- Lubricate the Chain: After reinstalling the chain, lubricate it with a bicycle chain lubricant. This helps to prevent rust and wear.
Importance of Chain Link Maintenance

A well-maintained bike chain is crucial for smooth and efficient riding. Neglecting chain maintenance can lead to premature wear and tear, reduced performance, and even potential damage to other components.
Regular Chain Cleaning and Lubrication
Regular cleaning and lubrication are essential for extending the life of your bike chain. Dirt, grime, and debris accumulate on the chain links, hindering smooth movement and increasing friction. This can cause excessive wear on the chain, sprockets, and other drivetrain components.
- Cleaning: Use a chain cleaning tool or a soft-bristled brush to remove dirt and grime. A degreaser can be used to remove stubborn grease and oil.
- Lubrication: After cleaning, apply a thin layer of chain lubricant. Avoid over-lubrication, as it can attract dirt and grime.
- Frequency: The frequency of cleaning and lubrication depends on riding conditions. For regular use on paved surfaces, cleaning and lubrication every 100-200 miles is recommended. In dusty or muddy conditions, more frequent maintenance is necessary.
Identifying Signs of Worn or Damaged Chain Links
A worn or damaged chain can significantly affect your bike’s performance. Identifying these issues early on can prevent further damage and ensure smooth riding.
- Stretching: As a chain wears, the links become stretched, causing the chain to become longer. This can be identified by measuring the chain length or observing a noticeable gap between the chain and the cassette.
- Bent or Broken Links: Inspect the chain for any bent or broken links. These can cause shifting issues and damage to the sprockets.
- Excessive Wear: Examine the chain for signs of excessive wear on the rollers and pins. Worn rollers and pins can cause a clunking sound when pedaling and hinder smooth chain movement.
Replacing a Worn-Out Chain
When a chain becomes excessively worn, it’s essential to replace it. A worn chain can damage the sprockets and increase friction, leading to reduced performance and potential mechanical failures.
- Measuring Chain Wear: Use a chain wear tool to measure the chain’s elongation. If the chain exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended wear limit, it should be replaced.
- Choosing the Right Chain: Select a chain compatible with your bike’s drivetrain. Ensure the chain width and number of speeds match your cassette and crankset.
- Installation: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installing the new chain. Ensure the chain is properly tensioned and aligned.
By mastering the art of counting bike chain links, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of your bike’s mechanics and be equipped to handle common maintenance tasks with ease. Remember, a well-maintained chain is crucial for optimal performance, efficiency, and longevity. With the right knowledge and tools, you can keep your bike running smoothly for miles to come.
FAQ Section
Why is it important to count bike chain links?
Counting chain links helps ensure the chain is the correct length for your bike’s drivetrain, preventing issues like chain skipping, derailleur problems, and excessive wear on components.
How often should I check my chain link count?
It’s a good practice to check your chain link count whenever you replace your chain or make significant changes to your drivetrain components.
What if I don’t have a chain tool?
While a chain tool is ideal for adjusting chain links, you can use a strong pair of pliers or a chain breaker tool if necessary. Be cautious and ensure you’re using the right tools for the job.