How long does it take to replace wheel bearings? This question arises frequently for car owners facing this common maintenance task. The answer, however, isn’t straightforward, as the time required can vary significantly depending on several factors. These factors encompass the type of wheel bearing, the vehicle’s make and model, the severity of the damage, and the complexity of the vehicle’s suspension system.
Understanding these factors is crucial for accurately estimating the time needed for wheel bearing replacement. Additionally, the choice between a professional mechanic and a DIY approach also influences the overall time frame. This article explores the intricacies of wheel bearing replacement, providing insights into the factors that affect time, the steps involved, and the advantages and disadvantages of professional versus DIY solutions.
Factors Influencing Wheel Bearing Replacement Time
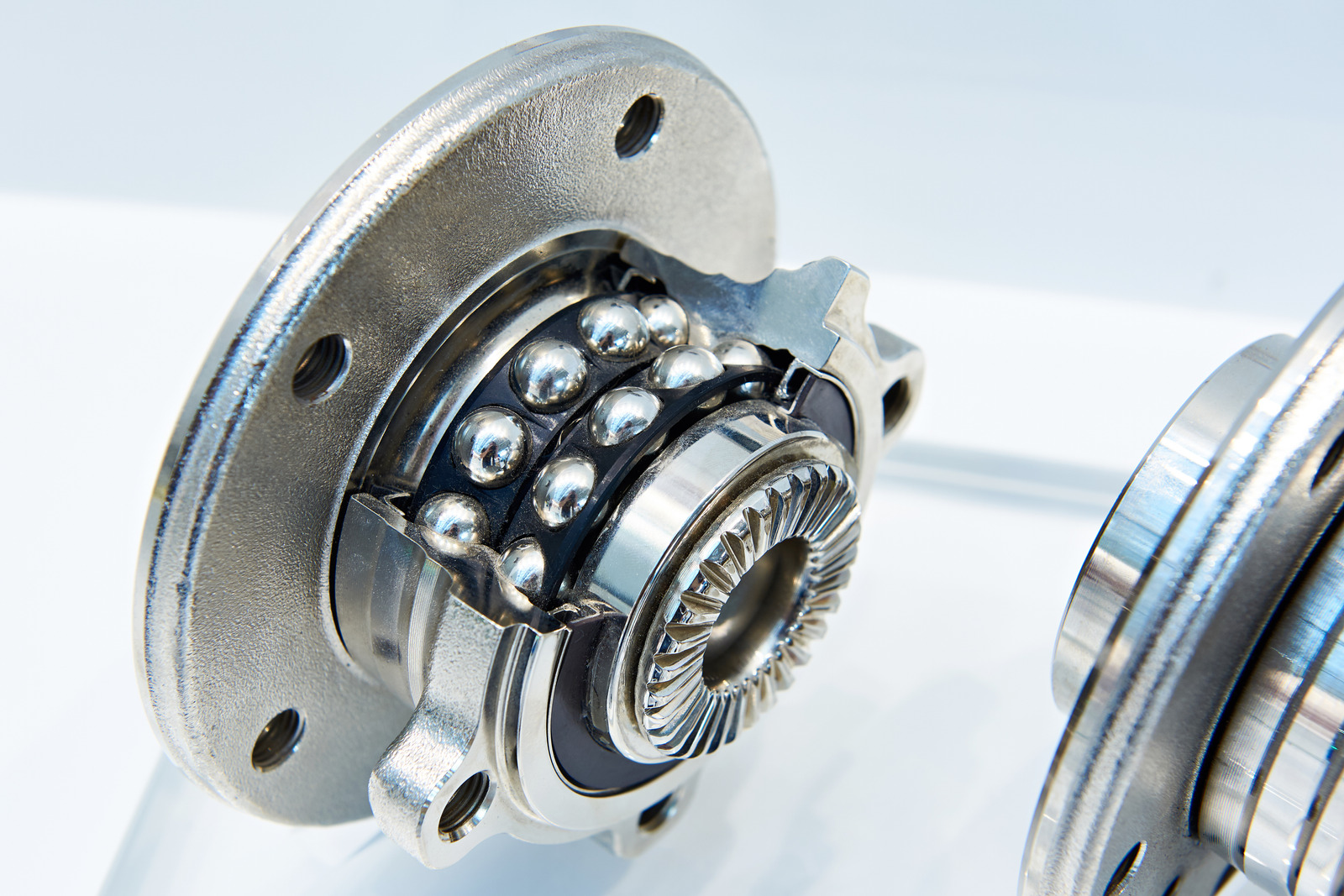
The time it takes to replace a wheel bearing can vary significantly depending on several factors. These factors influence the complexity of the repair, the time required for the job, and ultimately, the cost. Understanding these factors can help you better anticipate the duration of the repair and make informed decisions about your vehicle’s maintenance.
Types of Wheel Bearings
The type of wheel bearing used in a vehicle can have a considerable impact on the replacement time.
- Tapered Roller Bearings: These are the most common type of wheel bearing, found in a wide range of vehicles. They are relatively simple to replace, and the process typically involves removing the hub assembly, pressing out the old bearing, and pressing in the new one.
- Ball Bearings: These bearings are less common than tapered roller bearings but are used in some vehicles, particularly older models. They are more complex to replace, often requiring specialized tools and more time.
- Sealed Wheel Bearings: These bearings are becoming increasingly popular, especially in newer vehicles. They are pre-lubricated and sealed, eliminating the need for regular greasing. However, replacing sealed bearings can be more challenging, as the entire hub assembly often needs to be replaced.
Vehicle Make, Model, and Year
The make, model, and year of your vehicle can significantly influence the time required to replace a wheel bearing. Some vehicles have simpler suspension designs that make the repair easier, while others have more complex systems that require additional steps and time. For instance, replacing a wheel bearing on a compact car may be relatively straightforward, while a similar repair on a large SUV or truck may take longer due to the heavier components and more intricate suspension system.
Examples of Common Vehicle Models
- Honda Civic: A popular compact car with a relatively simple suspension design, making wheel bearing replacement relatively quick.
- Ford F-150: A popular pickup truck with a more complex suspension system, which can increase the time needed for wheel bearing replacement.
- Toyota Camry: A mid-size sedan with a moderately complex suspension system, making wheel bearing replacement time somewhat average.
Severity of Bearing Damage
The extent of the bearing damage can also influence the time required for replacement. If the bearing is only slightly damaged, the repair may be relatively quick. However, if the bearing is severely damaged, it may require more extensive repairs, such as replacing the entire hub assembly. In extreme cases, the damage may even affect other components of the suspension system, further increasing the repair time.
Complexity of the Vehicle’s Suspension System
The complexity of the vehicle’s suspension system can significantly impact the time required for wheel bearing replacement. Some vehicles have simple suspension systems that allow for easy access to the bearings, while others have more intricate designs that require more steps and time to disassemble and reassemble. For example, vehicles with independent rear suspensions often have more components to remove and reinstall compared to vehicles with solid rear axles.
Steps Involved in Replacing Wheel Bearings

Replacing a wheel bearing is a common automotive repair that requires careful attention to detail and adherence to safety procedures. Understanding the steps involved in this process will ensure a smooth and successful repair.
Diagnosing a Faulty Wheel Bearing
Diagnosing a faulty wheel bearing is essential before proceeding with replacement. This involves identifying the symptoms and performing an inspection to confirm the issue.
- Symptoms of a Faulty Wheel Bearing:
Common symptoms of a failing wheel bearing include:
- Grinding or roaring noise: This noise typically increases with vehicle speed and may be accompanied by a vibration.
- Wobble or shake in the steering wheel: This indicates a problem with the wheel bearing, causing instability in the steering.
- Uneven tire wear: A faulty wheel bearing can lead to uneven tire wear due to misalignment caused by the bearing’s failure.
- Play in the wheel: If there is excessive play or movement in the wheel when it is shaken, it could be a sign of a worn-out bearing.
- Inspection Methods:
To confirm a faulty wheel bearing, a thorough inspection is necessary. This can be done by:
- Visual inspection: Check for any visible signs of damage, such as cracks, rust, or excessive wear on the bearing race or seals.
- Jacking up the vehicle: Raise the vehicle and check for any play in the wheel by rocking it back and forth. Excessive movement indicates a worn-out bearing.
- Using a stethoscope: Listen for any unusual noises coming from the bearing area. A grinding or roaring sound is a clear indication of a faulty bearing.
Removing the Old Wheel Bearing
Once a faulty wheel bearing has been diagnosed, the next step is to remove it. This involves a series of steps that require specialized tools and careful handling.
- Preparing the Vehicle:
Before starting the removal process, ensure the vehicle is safely secured.
- Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake.
- Use wheel chocks to prevent the vehicle from rolling.
- Remove the wheel and tire from the affected side.
- Removing the Bearing Assembly:
The removal process will vary depending on the vehicle model and bearing type. However, it generally involves the following steps:
- Remove the brake caliper and rotor.
- Remove the hub nut and axle nut.
- Use a bearing race and seal puller to remove the bearing race and seal from the hub.
- Remove the old bearing from the hub using a bearing puller.
- Specialized Tools:
Replacing wheel bearings often requires specialized tools, including:
- Bearing race and seal puller: This tool is used to remove the bearing race and seal from the hub.
- Bearing puller: This tool is used to remove the old bearing from the hub.
- Torque wrench: This tool is essential for tightening the hub nut and other components to the correct specifications.
Installing the New Wheel Bearing, How long does it take to replace wheel bearings
Once the old wheel bearing has been removed, the new bearing can be installed. This process requires careful handling and adherence to safety procedures.
- Preparing the New Bearing:
Before installing the new bearing, ensure it is clean and free of any debris.
- Clean the hub and bearing seat thoroughly.
- Apply a thin layer of grease to the bearing race and inner bearing surface.
- Installing the Bearing:
The installation process involves carefully placing the new bearing into the hub and securing it in place.
- Install the new bearing into the hub, ensuring it is properly seated.
- Use a bearing race and seal installer to install the new bearing race and seal into the hub.
- Install the rotor and caliper, ensuring the brake pads are properly aligned.
- Safety Precautions:
When installing the new wheel bearing, it is crucial to follow safety precautions:
- Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris.
- Use gloves to protect your hands from grease and sharp edges.
- Ensure the vehicle is securely supported on jack stands.
- Do not use excessive force when installing the bearing.
Torqueing the Wheel Bearing and Related Components
After installing the new wheel bearing, it is essential to torque the hub nut and other related components to the correct specifications. This ensures proper fit and prevents loosening or damage.
- Torque Specifications:
The torque specifications for the hub nut and other components will vary depending on the vehicle model. Refer to the vehicle’s owner’s manual or a reputable repair manual for the correct torque values.
- Tightening the Hub Nut:
When tightening the hub nut, it is important to use a torque wrench to ensure the correct tension.
- Tighten the hub nut to the specified torque value.
- Do not overtighten the hub nut, as this can damage the bearing.
- Other Components:
Torque the other related components, such as the axle nut and caliper bolts, to the specified torque values.
Post-Installation Testing and Adjustments
After installing the new wheel bearing, it is essential to perform post-installation testing and adjustments to ensure the repair was successful.
- Road Test:
Take the vehicle for a test drive to evaluate the new bearing.
- Listen for any unusual noises.
- Check for any vibration or play in the steering wheel.
- Ensure the brakes are working properly.
- Adjustments:
If any issues are detected during the road test, make necessary adjustments. This may involve:
- Re-torquing the hub nut.
- Adjusting the brake pads.
- Checking for any loose components.
Professional vs. DIY Wheel Bearing Replacement

Deciding whether to tackle a wheel bearing replacement yourself or entrust it to a professional mechanic involves weighing several factors. This decision hinges on your mechanical aptitude, available tools, and the potential risks involved. This section delves into the advantages and disadvantages of each approach, shedding light on the cost implications and safety measures for DIY replacements.
Professional Wheel Bearing Replacement
Employing a professional mechanic offers several benefits, including:
- Expertise and Experience: Mechanics possess the specialized knowledge and experience to diagnose the problem accurately and perform the replacement efficiently. They are familiar with the intricacies of different vehicle models and can identify any underlying issues that might be contributing to the wheel bearing failure.
- Specialized Tools: Professionals have access to a wide range of tools and equipment specifically designed for wheel bearing replacement, ensuring a precise and efficient job. These tools might not be readily available to the average DIY enthusiast.
- Warranty: Many mechanics offer warranties on their work, providing peace of mind and covering any potential issues that may arise after the replacement.
- Safety: Professionals prioritize safety and have the training and equipment to handle potentially hazardous situations, such as working with heavy components or dealing with potential brake fluid leaks.
However, hiring a professional comes with a cost. The labor costs associated with wheel bearing replacement can vary depending on the mechanic’s experience, location, and the complexity of the job. Additionally, the mechanic might recommend additional services, such as brake inspections or tire rotations, which can further increase the overall cost.
DIY Wheel Bearing Replacement
Undertaking a DIY wheel bearing replacement can save you money on labor costs, but it requires a significant investment in tools and expertise.
- Cost Savings: The primary advantage of a DIY approach is the potential for cost savings on labor. However, it’s important to consider the cost of tools and parts, which might not be cheaper than the professional labor cost.
- Sense of Accomplishment: Many DIY enthusiasts enjoy the challenge and satisfaction of tackling automotive repairs themselves. Replacing a wheel bearing can be a rewarding experience for those with the necessary skills and tools.
However, DIY wheel bearing replacement comes with several risks and challenges:
- Technical Expertise: Replacing a wheel bearing requires a thorough understanding of automotive mechanics and the ability to use specialized tools. Lack of experience can lead to errors or incomplete repairs, potentially compromising safety.
- Tools and Equipment: DIY replacements necessitate a significant investment in tools, such as a hydraulic press, bearing race and seal drivers, and torque wrenches. These tools might be expensive and are often not readily available to the average homeowner.
- Safety Concerns: Working on a vehicle’s suspension system can be dangerous if proper safety precautions are not taken. Improper lifting or handling of heavy components can lead to injury. Additionally, working with brake fluid requires caution as it is hazardous and can damage paint.
Cost Comparison
The cost of professional and DIY wheel bearing replacement varies depending on factors such as vehicle make and model, parts cost, and labor rates. However, here’s a general estimate:
| Professional | DIY | |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Cost | $100 – $300 | $0 |
| Parts Cost | $50 – $150 | $50 – $150 |
| Tools Cost | $0 | $100 – $300 |
| Estimated Total Cost | $150 – $450 | $150 – $450 |
Note: The cost of tools for DIY replacement is a one-time expense. Subsequent repairs will only require the cost of parts.
Safety Measures for DIY Replacement
If you choose to replace the wheel bearing yourself, it’s crucial to prioritize safety:
- Use a Jack Stand: Never rely solely on a jack to support the vehicle. Always use jack stands to ensure stability and prevent the vehicle from falling.
- Chock the Wheels: Place wheel chocks on the remaining wheels to prevent the vehicle from rolling while working.
- Wear Protective Gear: Wear safety glasses, gloves, and sturdy shoes to protect yourself from potential hazards.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Use proper lifting techniques to avoid injury. If lifting heavy components, enlist assistance or use a hoist.
- Handle Brake Fluid Carefully: Brake fluid is hazardous and can damage paint. Use a designated container and wear gloves when handling it.
Maintaining Wheel Bearings for Longer Lifespan
Wheel bearings are critical components in your vehicle’s suspension system, ensuring smooth and safe driving. Neglecting their maintenance can lead to premature failure, resulting in costly repairs and potential safety hazards. By implementing a proactive approach to wheel bearing maintenance, you can significantly extend their lifespan and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspection of wheel bearings is crucial for early detection of any issues.
- Listen for unusual noises: A grinding, humming, or roaring sound, especially when turning or at higher speeds, can indicate worn-out bearings.
- Check for excessive play: Grab the tire at the 12 and 6 o’clock positions and try to move it back and forth. Excessive movement indicates worn bearings.
- Inspect for leaks: Look for signs of grease leaks around the bearing seals.
It is recommended to inspect your wheel bearings at least once a year or every 10,000 miles, whichever comes first.
Using High-Quality Lubricants and Greases
Using high-quality lubricants and greases is essential for optimal wheel bearing performance.
- Proper viscosity: The grease should have the correct viscosity to provide adequate lubrication under various temperatures and driving conditions.
- Corrosion resistance: The grease should be formulated to resist corrosion and protect the bearings from rust and wear.
- Extreme pressure (EP) additives: EP additives help to prevent premature wear and tear by reducing friction and heat buildup.
Using the wrong type of grease can lead to premature bearing failure, so always consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a trusted mechanic for the recommended grease type.
Impact of Driving Conditions
Driving conditions play a significant role in the lifespan of wheel bearings.
- Road surfaces: Rough roads and potholes can put extra stress on wheel bearings, leading to faster wear and tear.
- Driving habits: Aggressive driving, such as hard braking and cornering, can also contribute to premature bearing failure.
- Environmental factors: Extreme temperatures, moisture, and dirt can affect the performance and lifespan of wheel bearings.
By minimizing exposure to harsh driving conditions, you can help to extend the life of your wheel bearings.
Preventative Measures
Several preventative measures can help to prolong the lifespan of your wheel bearings.
- Regular lubrication: Properly lubricate your wheel bearings according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Avoid overloading: Overloading your vehicle can put extra stress on the wheel bearings.
- Maintain tire pressure: Properly inflated tires can help to reduce wear and tear on the bearings.
- Smooth driving: Avoid harsh acceleration, braking, and cornering.
These simple steps can significantly extend the life of your wheel bearings and prevent premature failure.
Common Causes of Wheel Bearing Failure and Prevention Methods
| Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|
| Lack of lubrication | Regular lubrication according to manufacturer’s recommendations |
| Contamination | Properly seal bearings and avoid driving in dusty or wet conditions |
| Overloading | Avoid exceeding the vehicle’s weight capacity |
| Improper installation | Ensure proper installation by a qualified mechanic |
| Damaged components | Replace damaged bearings, seals, and races promptly |
In conclusion, replacing wheel bearings is a necessary maintenance task that can vary in complexity and time depending on several factors. Understanding these factors and the steps involved in the process is crucial for making informed decisions regarding professional or DIY approaches. By prioritizing safety, using high-quality parts, and following proper procedures, you can ensure a successful wheel bearing replacement and extend the lifespan of your vehicle’s suspension system.
FAQ Insights: How Long Does It Take To Replace Wheel Bearings
Can I drive with a bad wheel bearing?
It is not recommended to drive with a bad wheel bearing. Doing so can lead to further damage to the bearing, suspension components, and even cause a loss of control. It’s best to have it repaired as soon as possible.
How often should I inspect my wheel bearings?
Regular inspections are crucial for early detection of any issues. It’s recommended to inspect your wheel bearings at least once a year or more frequently if you drive on rough roads or in harsh conditions.
What are the signs of a bad wheel bearing?
Common signs include grinding or roaring noises, especially when turning or driving at high speeds. You may also notice a vibration in the steering wheel or a feeling of looseness in the wheels.