Which is better all wheel or front wheel – Which is better: all-wheel or front-wheel drive? This age-old question has sparked debates among car enthusiasts and everyday drivers alike. Both systems have their unique strengths and weaknesses, making the choice a matter of personal preference and driving needs. But fear not, we’re here to break down the intricacies of these two drive systems, helping you navigate the world of traction, handling, and fuel efficiency.
From the early days of automobiles, engineers have been experimenting with different ways to transfer power to the wheels. Front-wheel drive, first introduced in the early 20th century, gained popularity for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. All-wheel drive, on the other hand, emerged as a solution for tackling challenging terrain and improving overall stability, especially in slippery conditions. Today, both systems are widely used in a variety of vehicles, from compact cars to rugged SUVs.
All-Wheel Drive vs. Front-Wheel Drive: Which is Better?

Choosing the right vehicle for your needs often involves weighing the pros and cons of different drivetrain systems. Two of the most common are all-wheel drive (AWD) and front-wheel drive (FWD). This article will delve into the differences between these systems, exploring their history, key features, and how they perform in various driving conditions.
Understanding Drive Systems: A Historical Perspective
AWD and FWD systems have a long history, with each evolving to meet the demands of different driving environments and technological advancements.
- Front-wheel drive (FWD): This system, where power is delivered to the front wheels, first emerged in the early 20th century. Early FWD vehicles were known for their simplicity and fuel efficiency, but they often lacked the traction and handling of rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles. Over time, FWD technology has advanced, with modern systems offering better traction and handling capabilities.
- All-wheel drive (AWD): AWD systems, which deliver power to all four wheels, have been around for decades, but their popularity has surged in recent years. Initially, AWD systems were primarily found in off-road vehicles, but they have become increasingly common in passenger cars and SUVs, offering improved traction and stability in various weather conditions.
Key Terminology
To understand the differences between AWD and FWD, it’s essential to define some key terms:
- Traction: This refers to the grip between the tires and the road surface. Good traction is crucial for accelerating, braking, and maintaining control, especially in slippery conditions.
- Handling: This describes how a vehicle responds to steering input and its overall stability. Good handling is essential for maneuvering safely and comfortably.
- Fuel Efficiency: This measures how much fuel a vehicle consumes per unit of distance traveled. FWD systems are generally more fuel-efficient than AWD systems due to their simpler design and lower weight.
- Cost: AWD systems are generally more expensive than FWD systems due to the added complexity of the drivetrain. However, this higher cost can be offset by improved traction and safety in challenging conditions.
All-Wheel Drive (AWD)

All-wheel drive (AWD) systems offer numerous advantages over front-wheel drive (FWD) and rear-wheel drive (RWD) vehicles, especially in challenging driving conditions. By distributing power to all four wheels, AWD systems enhance traction, handling, and stability, making them a popular choice for drivers seeking increased capability and peace of mind.
Types of AWD Systems, Which is better all wheel or front wheel
AWD systems are designed to provide power to all four wheels, but the way they distribute power varies depending on the system’s type. Different types of AWD systems cater to different driving needs and preferences.
- Full-Time AWD: Full-time AWD systems continuously send power to all four wheels, regardless of road conditions. These systems are typically found in luxury SUVs and performance vehicles, where consistent grip and handling are paramount. They offer exceptional stability and traction in various weather conditions, including snow, rain, and slippery surfaces.
- Part-Time AWD: Part-time AWD systems engage the rear wheels only when necessary, usually when the front wheels lose traction. This type of system is often found in trucks and SUVs designed for off-roading or light-duty towing. It provides a balance between fuel efficiency and off-road capability.
- On-Demand AWD: On-demand AWD systems use sensors to detect wheel slip and engage the rear wheels only when needed. These systems are typically found in passenger cars and crossovers, offering improved traction in slippery conditions without compromising fuel economy.
Advantages of AWD
AWD systems provide a range of benefits that enhance vehicle performance and safety, particularly in challenging driving conditions.
- Enhanced Traction: By distributing power to all four wheels, AWD systems provide superior traction, especially on slippery surfaces like snow, ice, or wet roads. This improved traction helps drivers maintain control and avoid skidding, ensuring a safer driving experience.
- Improved Handling: AWD systems improve handling, particularly during cornering. The increased grip from all four wheels allows drivers to maintain control and navigate corners with greater confidence.
- Increased Stability: AWD systems enhance stability, especially during acceleration, braking, and cornering. The balanced distribution of power helps maintain control and prevent the vehicle from swaying or losing traction.
Examples of Vehicles with AWD Systems
AWD systems are widely used in various vehicle types, each offering specific benefits for different driving needs.
- Subaru Outback: The Subaru Outback is a popular wagon known for its ruggedness and off-road capabilities. Its symmetrical AWD system provides exceptional traction and handling in various conditions, making it suitable for both on- and off-road adventures.
- Audi Q5: The Audi Q5 is a luxury crossover that offers a refined driving experience. Its quattro AWD system provides exceptional handling and stability, making it a comfortable and capable vehicle for daily commutes and weekend getaways.
- Ford F-150: The Ford F-150 is a popular pickup truck known for its towing and hauling capabilities. Its optional 4×4 system provides enhanced traction and off-road performance, making it suitable for heavy-duty tasks and challenging terrain.
Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is a type of drivetrain system where the engine’s power is transmitted to the front wheels, which are responsible for propelling the vehicle. This system is widely used in many cars, especially in smaller and more fuel-efficient models.
Advantages of FWD Systems
FWD systems offer several advantages over other drivetrain configurations, making them a popular choice for many vehicles.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: FWD vehicles generally have better fuel efficiency compared to AWD vehicles. This is because FWD systems require less power to operate, as they only need to drive two wheels instead of four. For example, a compact car with FWD might achieve a combined fuel economy of 35 mpg, while a similar AWD model could get 28 mpg.
- Lower Manufacturing Cost: FWD systems are less complex to manufacture than AWD systems, resulting in lower production costs. This lower cost can be passed on to consumers, making FWD vehicles more affordable. For instance, a basic sedan with FWD might cost $20,000, while an equivalent AWD model could cost $25,000.
- Increased Interior Space: FWD vehicles often have more interior space than AWD vehicles. This is because FWD systems do not require a driveshaft to transmit power to the rear wheels, allowing for a more spacious cabin. For example, a mid-size FWD sedan might have a cargo volume of 15 cubic feet, while an AWD model of the same size might have only 12 cubic feet.
Working Principle of FWD Systems
FWD systems work by transmitting power from the engine to the front wheels through a transmission and a driveshaft. The transmission is responsible for changing gears, while the driveshaft transmits power from the transmission to the front wheels.
The power from the engine is first transferred to the transmission, which then directs the power to the front wheels via a driveshaft.
Examples of Vehicles with FWD Systems
FWD systems are used in a wide range of vehicles, from small city cars to larger sedans and even some SUVs.
- Honda Civic: The Honda Civic is a popular compact car that offers a comfortable ride, good fuel economy, and a spacious interior. It is available with both FWD and AWD drivetrains, but the FWD model is the most popular due to its lower price and better fuel efficiency.
- Toyota Camry: The Toyota Camry is a mid-size sedan known for its reliability, comfort, and fuel efficiency. The Camry is available with both FWD and AWD drivetrains, but the FWD model is the most popular due to its lower price and better fuel economy.
- Subaru Outback: The Subaru Outback is a popular wagon that offers a blend of car-like handling and SUV-like capability. The Outback is available with both FWD and AWD drivetrains, but the FWD model is the most popular due to its lower price and better fuel economy.
Comparing AWD and FWD
Choosing between all-wheel drive (AWD) and front-wheel drive (FWD) can be a tough decision, as both systems offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. While FWD is generally more fuel-efficient and affordable, AWD provides superior traction and handling in challenging conditions. Understanding the nuances of each system can help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and driving habits.
Performance Characteristics
The key difference between AWD and FWD lies in how power is distributed to the wheels. In FWD systems, the engine drives the front wheels, while AWD systems send power to all four wheels. This fundamental difference leads to distinct performance characteristics in terms of traction, handling, fuel efficiency, and cost.
- Traction: AWD systems excel in providing superior traction, especially on slippery surfaces like snow, ice, or wet roads. The additional grip from the rear wheels enhances stability and reduces the risk of wheel spin. FWD systems, on the other hand, can struggle to maintain traction in such conditions, leading to wheel slip and potential loss of control.
- Handling: AWD systems generally offer better handling, particularly in corners and during aggressive maneuvers. The balanced power distribution improves stability and reduces understeer, a phenomenon where the front wheels lose grip and the vehicle fails to turn as intended. FWD systems can experience understeer more readily, especially when cornering aggressively.
- Fuel Efficiency: FWD systems are typically more fuel-efficient than AWD systems. This is because they have fewer components and require less power to operate. The added weight and complexity of AWD systems can negatively impact fuel economy, especially in urban driving conditions.
- Cost: FWD systems are generally more affordable than AWD systems. This is due to the simpler design and fewer components involved in the drivetrain. AWD systems require additional components, such as a transfer case and rear differential, which contribute to a higher price tag.
Trade-offs in Choosing Between AWD and FWD
Choosing between AWD and FWD involves considering various factors, including driving conditions, vehicle usage, and budget.
- Driving Conditions: If you frequently drive in challenging conditions, such as snow, ice, or heavy rain, AWD offers a significant advantage in terms of traction and handling. The additional grip provided by all four wheels can significantly improve safety and control in such situations.
- Vehicle Usage: If you primarily drive in urban areas or on paved roads, FWD is likely a better choice due to its fuel efficiency and affordability. However, if you frequently tow heavy loads or engage in off-road driving, AWD offers greater capability and peace of mind.
- Budget: FWD vehicles are typically more affordable than AWD vehicles. If budget is a primary concern, FWD might be the more sensible option. However, if you prioritize safety and performance in challenging conditions, the added cost of AWD may be justified.
Comparison Table
Here’s a table summarizing the key features of AWD and FWD systems across different categories:
| Feature | AWD | FWD |
|---|---|---|
| Traction | Excellent, especially in challenging conditions | Good on dry surfaces, can struggle in slippery conditions |
| Handling | Generally better, especially in corners and aggressive maneuvers | Can experience understeer, particularly when cornering aggressively |
| Fuel Efficiency | Typically less fuel-efficient than FWD | Generally more fuel-efficient |
| Cost | More expensive than FWD | More affordable |
Applications and Considerations
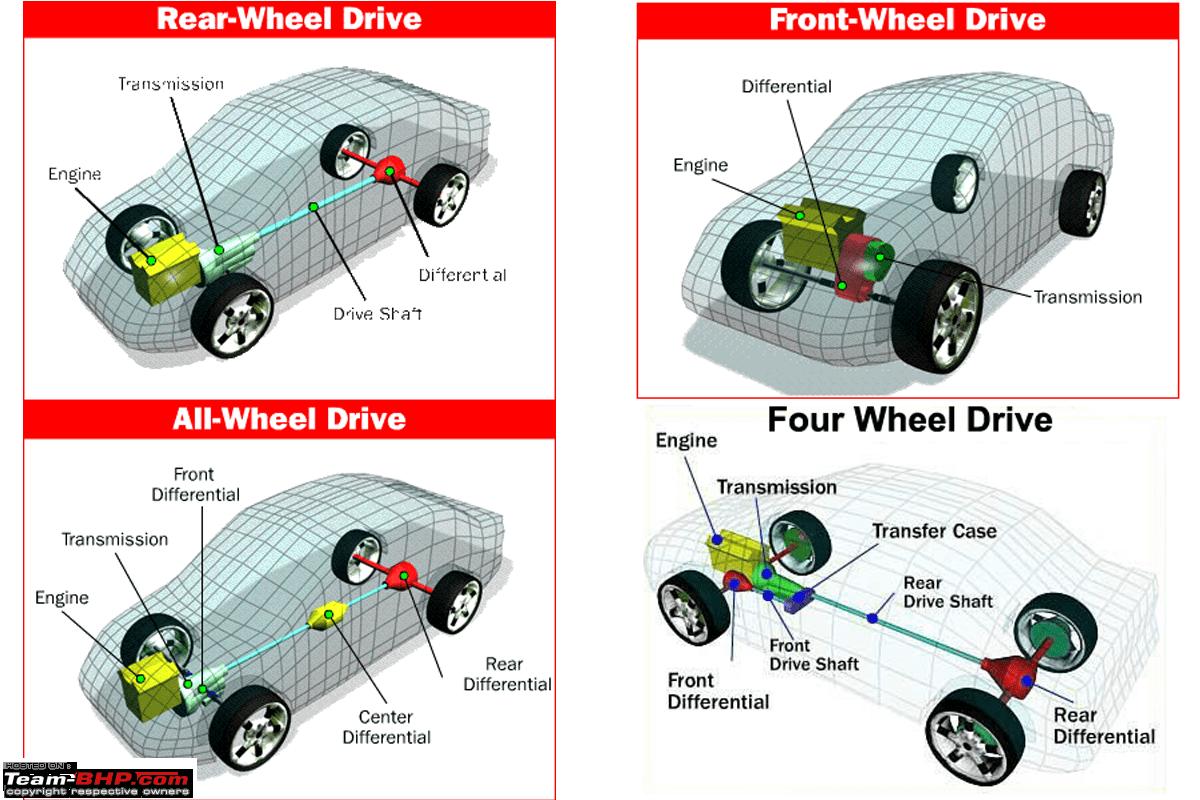
Choosing between AWD and FWD depends on various factors, including the type of vehicle, intended use, and driving conditions. Both systems offer advantages and disadvantages, and understanding their applications and considerations is crucial for making an informed decision.
Applications in Different Vehicle Types
AWD and FWD systems are designed for different types of vehicles, each offering specific benefits.
- Sedans: FWD is commonly used in sedans due to its cost-effectiveness and efficiency. AWD is less common but offers improved traction and handling in challenging conditions.
- SUVs: AWD is prevalent in SUVs, providing superior off-road capability and enhanced traction on slippery surfaces. FWD SUVs are also available, offering a more affordable option with decent fuel economy.
- Trucks: AWD is a standard feature in many trucks, especially those designed for off-road use. FWD trucks are less common, primarily found in smaller pickup models.
- Sports Cars: AWD is gaining popularity in sports cars, providing better acceleration and handling, particularly on slippery surfaces. FWD sports cars are still common, offering a lighter and more nimble driving experience.
Performance in Different Driving Scenarios
The performance of AWD and FWD systems varies depending on the driving conditions.
- Off-Road Driving: AWD provides superior traction and stability on rough terrain, making it ideal for off-road adventures. FWD vehicles struggle in off-road conditions, often losing traction and requiring additional modifications.
- City Driving: Both FWD and AWD perform well in city driving, offering good maneuverability and fuel efficiency. FWD is generally preferred due to its lower cost and better fuel economy.
- Highway Driving: FWD and AWD offer similar performance on highways, with AWD providing a slight advantage in slippery conditions or during sudden maneuvers.
Impact on Vehicle Weight, Fuel Consumption, and Maintenance Costs
AWD systems typically add weight to a vehicle, impacting fuel consumption and performance. FWD systems are generally lighter and more fuel-efficient.
- Weight: AWD systems involve additional components like a transfer case and driveshafts, increasing the overall weight of the vehicle.
- Fuel Consumption: The added weight and complexity of AWD systems can lead to lower fuel economy compared to FWD vehicles.
- Maintenance Costs: AWD systems require more frequent maintenance, including fluid changes and inspections of the transfer case and driveshafts, which can increase maintenance costs.
Conclusion: Which Is Better All Wheel Or Front Wheel
Choosing between AWD and FWD ultimately boils down to your individual needs and driving conditions. While AWD offers superior traction and handling in challenging conditions, FWD provides a more fuel-efficient and affordable option for everyday driving. This comparison has highlighted the strengths and weaknesses of each drive system, helping you make an informed decision based on your priorities.
Situations Where AWD is Preferred
AWD excels in situations where traction and stability are paramount. Here are some examples:
- Off-roading: AWD provides the necessary grip and power to navigate uneven terrain, mud, snow, and other challenging surfaces.
- Snowy or icy conditions: AWD’s superior traction significantly enhances safety and control during winter driving.
- Towing or hauling heavy loads: AWD distributes power to all wheels, providing more stability and control when towing or hauling heavy objects.
- Performance driving: AWD systems can improve acceleration and handling on dry surfaces, especially for vehicles with high horsepower.
Situations Where FWD is Preferred
FWD is a cost-effective and fuel-efficient option for everyday driving. Here are some scenarios where FWD might be the better choice:
- Urban driving: FWD is generally more fuel-efficient than AWD, making it a suitable choice for city driving with frequent stop-and-go traffic.
- Cost-consciousness: FWD vehicles are typically less expensive to purchase and maintain than AWD vehicles.
- Fuel efficiency: FWD vehicles tend to have better fuel economy than AWD vehicles, especially in everyday driving conditions.
- Front-heavy vehicles: FWD is often preferred for front-heavy vehicles, as it helps distribute weight more evenly.
Future Trends in AWD and FWD Technology
Advancements in technology are continuously improving both AWD and FWD systems, leading to enhanced fuel efficiency and performance.
- Electric AWD: Electric vehicles (EVs) with AWD systems are becoming increasingly popular. These systems provide excellent traction and performance, while also offering the benefits of electric powertrains, such as lower emissions and higher efficiency.
- Active AWD: Advanced AWD systems, such as active AWD, can dynamically adjust power distribution to individual wheels based on driving conditions. This technology optimizes traction and stability while enhancing fuel efficiency.
- Lightweight materials: Using lighter materials in AWD and FWD systems helps improve fuel efficiency and performance. For example, using lightweight aluminum or carbon fiber components can reduce the overall weight of the vehicle.
Ultimately, the decision between all-wheel drive and front-wheel drive boils down to your individual priorities. If you prioritize fuel efficiency and affordability, front-wheel drive is often the better choice. But if you crave the added confidence and capability of all-wheel drive, especially in challenging conditions, then it might be the way to go. Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, and the best drive system for you depends on your unique driving needs and lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between AWD and FWD?
AWD systems send power to all four wheels, while FWD systems only send power to the front wheels.
Is AWD always better than FWD?
Not necessarily. AWD offers better traction in slippery conditions but comes with a higher price tag and reduced fuel efficiency.
Does AWD improve fuel economy?
Generally, no. AWD systems require more power to operate, leading to slightly lower fuel efficiency compared to FWD.
Is AWD necessary for daily driving?
If you live in an area with frequent snow or ice, AWD can be beneficial. However, for most daily driving, FWD provides sufficient traction.