Does 4D mean 4 wheel drive? This question often arises when exploring the world of off-road vehicles and their capabilities. While the terms “4D” and “4WD” sound similar, they actually represent entirely different concepts. “4WD” stands for “Four-Wheel Drive,” a system that allows power to be distributed to all four wheels of a vehicle. This setup provides enhanced traction and handling, particularly in challenging terrains like snow, mud, or rough roads.
“4D” is not a recognized automotive term and is typically associated with other technologies, such as 4D cinema experiences, which involve immersive visual and auditory effects.
Understanding the nuances of 4WD, its benefits, and drawbacks is crucial for drivers seeking a vehicle that can conquer challenging terrains. This article delves into the intricacies of 4WD systems, exploring their functionalities, advantages, and disadvantages. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive grasp of 4WD, its applications, and whether it’s the right choice for your driving needs.
What is 4WD?

WD, short for four-wheel drive, is a type of drivetrain system used in vehicles, primarily off-road vehicles, SUVs, and pickup trucks. This system allows power from the engine to be distributed to all four wheels, providing increased traction and stability, especially on slippery or uneven surfaces.
Purpose of 4WD, Does 4d mean 4 wheel drive
The primary purpose of 4WD is to enhance a vehicle’s ability to handle challenging terrain and driving conditions. By engaging all four wheels, 4WD systems provide several benefits:
- Increased Traction: 4WD systems distribute power to all wheels, ensuring maximum grip on surfaces like mud, snow, sand, or gravel. This significantly improves traction and reduces the risk of wheel spin or getting stuck.
- Improved Stability: With all four wheels receiving power, 4WD vehicles experience enhanced stability, particularly when cornering or driving on uneven surfaces. This improved stability makes them safer and more controllable in challenging situations.
- Enhanced Off-Road Capability: 4WD systems are designed to handle rough terrain, allowing vehicles to navigate obstacles like rocks, hills, and deep mud with ease. This makes them ideal for off-road adventures and tasks requiring exceptional ground clearance and traction.
Difference Between 4WD and AWD
While both 4WD and AWD (All-Wheel Drive) systems provide power to all four wheels, they differ in their operation and intended use:
- 4WD: Typically designed for off-road use, 4WD systems are usually manually engaged by the driver. They offer superior traction and ground clearance for tackling difficult terrain. However, they can be less fuel-efficient than AWD systems and may not be as smooth on paved roads.
- AWD: Primarily designed for on-road use, AWD systems automatically distribute power to the wheels as needed. They provide improved traction and stability in slippery conditions but may not be as capable off-road as 4WD systems. AWD systems are typically more fuel-efficient and smoother on paved roads.
Examples of Vehicles with 4WD
Many vehicles commonly feature 4WD, particularly those designed for off-road capabilities or challenging driving conditions. Some popular examples include:
- SUVs: Jeep Wrangler, Toyota Land Cruiser, Ford Bronco
- Pick-up Trucks: Ford F-150, Chevrolet Silverado, Ram 1500
- Off-Road Vehicles: Land Rover Defender, Mercedes-Benz G-Class, Toyota Tacoma
How 4WD Works
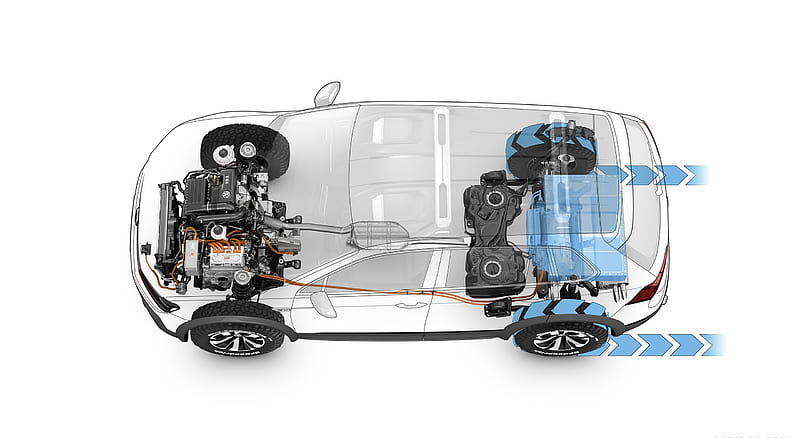
Four-wheel drive (4WD) systems are designed to enhance traction and off-road capability by distributing power to all four wheels. This allows vehicles to navigate challenging terrain, such as mud, snow, sand, and rocky surfaces, where two-wheel drive systems would struggle.
Components of a 4WD System
The core components of a 4WD system work together to transfer power from the engine to all four wheels. These components include:
- Transfer Case: The transfer case is a gearbox that sits between the transmission and the axles. It splits the engine’s power between the front and rear axles. The transfer case typically has a low-range gear, which provides increased torque for low-speed crawling and heavy loads.
- Differentials: Differentials are located in each axle and allow the wheels on that axle to rotate at different speeds. This is essential for turning, as the outside wheels need to travel a greater distance than the inside wheels.
- Axle Shafts: Axle shafts connect the differentials to the wheels, transmitting power from the transfer case to the wheels.
- Drive Shafts: Drive shafts connect the transfer case to the front and rear axles, transferring power from the transmission to the transfer case.
- Drivetrain Components: The drivetrain components, including the transmission, clutch, and torque converter, work together to deliver power from the engine to the transfer case.
Engaging and Disengaging 4WD
The process of engaging and disengaging 4WD varies depending on the type of system. In most vehicles, 4WD is engaged using a lever or switch located in the cabin.
- Part-time 4WD: In part-time 4WD systems, the driver can engage 4WD only when necessary, typically on slippery or off-road surfaces. When 4WD is not engaged, the vehicle operates as a two-wheel drive vehicle.
- Full-time 4WD: Full-time 4WD systems automatically engage 4WD all the time. These systems use a center differential to allow the front and rear axles to rotate at different speeds, even when driving on paved roads.
Types of 4WD Systems
Different types of 4WD systems offer varying levels of traction and off-road capability.
- Part-time 4WD: Part-time 4WD systems are the most common type of 4WD system. They offer a simple and affordable way to improve traction on slippery surfaces.
- Full-time 4WD: Full-time 4WD systems provide constant traction in all driving conditions. These systems are typically found in high-end SUVs and trucks.
- All-Wheel Drive (AWD): All-wheel drive (AWD) systems are similar to full-time 4WD systems, but they use a more sophisticated system to distribute power to the wheels. AWD systems are typically found in passenger cars and SUVs.
In conclusion, understanding the workings and benefits of 4WD is essential for drivers seeking to navigate challenging terrains or enhance their vehicle’s capabilities. Whether you’re venturing off-road, navigating snowy conditions, or towing heavy loads, 4WD provides the necessary traction and control to overcome obstacles with confidence. While 4WD offers significant advantages, it’s crucial to consider its drawbacks, such as increased fuel consumption and maintenance costs, before making a decision.
Ultimately, determining if 4WD is right for you depends on your individual driving needs and preferences.
FAQ: Does 4d Mean 4 Wheel Drive
What is the difference between 4WD and AWD?
4WD (Four-Wheel Drive) systems typically engage all four wheels for off-road use, while AWD (All-Wheel Drive) systems engage all four wheels automatically or on demand for improved traction in various conditions. 4WD systems are often designed for off-roading, while AWD systems are generally geared towards on-road performance and stability.
Is 4WD necessary for everyday driving?
For most drivers, 4WD is not necessary for everyday driving on paved roads. However, if you frequently encounter snowy or icy conditions, or if you frequently tow heavy loads, 4WD can provide additional traction and stability.
How often should I service my 4WD system?
It’s recommended to have your 4WD system inspected and serviced regularly, as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. This includes checking fluid levels, inspecting components for wear and tear, and ensuring proper operation of the system.
Can I use 4WD on paved roads?
While 4WD can be used on paved roads, it’s generally not recommended. Driving with 4WD engaged on paved roads can increase wear and tear on tires and drivetrain components, and it may also affect handling and fuel efficiency.