How to test an ABS wheel sensor sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The ABS wheel sensor, a crucial component of your vehicle’s braking system, plays a vital role in ensuring safe and controlled stopping. This guide will take you through the process of testing an ABS wheel sensor, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to diagnose potential issues and maintain the integrity of your vehicle’s braking system.
From understanding the sensor’s function and identifying common failure points to utilizing diagnostic tools and conducting practical tests, we’ll explore every step of the process in a clear and concise manner. We’ll delve into the world of ABS wheel sensors, uncovering their intricacies and empowering you to approach any potential issues with confidence.
Understanding the ABS Wheel Sensor

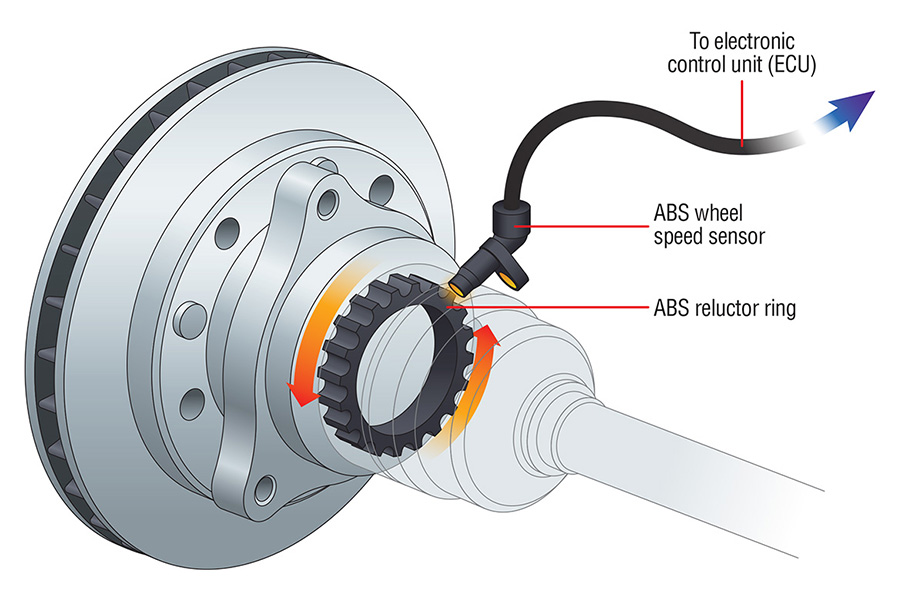
The ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) wheel sensor plays a crucial role in ensuring vehicle safety and stability during braking. It is an essential component of the ABS system, responsible for monitoring the wheel speed and transmitting this information to the ABS control module.
Types of ABS Wheel Sensors
The type of ABS wheel sensor used in a vehicle depends on the make and model. Here’s a breakdown of the common types and their working principles:
- Passive Magnetic Sensors: These sensors are the most common type and work on the principle of magnetic induction. They consist of a magnet and a coil of wire. As the toothed wheel rotates, the gaps between the teeth interrupt the magnetic field, inducing a voltage in the coil. This voltage is proportional to the wheel speed, which is then transmitted to the ABS control module.
- Hall Effect Sensors: These sensors utilize the Hall effect, which is the production of a voltage across a conductor when it is exposed to a magnetic field. A Hall effect sensor consists of a semiconductor material and a magnet. When the toothed wheel rotates, the gaps between the teeth change the magnetic field, generating a voltage in the sensor. This voltage is proportional to the wheel speed and is transmitted to the ABS control module.
- Optical Sensors: Optical sensors use a light source and a photodetector to measure the wheel speed. They consist of a light-emitting diode (LED) and a phototransistor. The LED emits light that is interrupted by the toothed wheel. The phototransistor detects the light pulses and converts them into an electrical signal, which is proportional to the wheel speed and transmitted to the ABS control module.
Causes of ABS Wheel Sensor Failure
Several factors can contribute to the failure of an ABS wheel sensor. These include:
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the sensor can wear down due to constant rotation and exposure to harsh environmental conditions. This can lead to a decrease in sensor sensitivity and accuracy, ultimately resulting in failure.
- Damage: The sensor can be damaged due to road debris, impacts, or other external forces. This damage can disrupt the sensor’s ability to detect the wheel speed, leading to failure.
- Corrosion: The sensor can be affected by corrosion, particularly in areas prone to moisture and salt exposure. Corrosion can interfere with the sensor’s electrical conductivity, causing it to malfunction.
- Wiring Problems: The wiring connecting the sensor to the ABS control module can become damaged or corroded, leading to a loss of communication and sensor failure.
- Toothed Wheel Damage: The toothed wheel itself can be damaged or worn, which can disrupt the magnetic field or light pulses detected by the sensor, resulting in inaccurate readings and sensor failure.
Visual Inspection and Basic Checks
Before diving into more complex diagnostics, it’s important to give your ABS wheel sensor a visual inspection. This initial step can reveal obvious issues that might be causing problems with your ABS system.
Think of it as a quick check-up for your car’s safety system, just like you’d give a quick look at your phone’s screen for cracks before using it.
Visual Inspection
A visual inspection helps you identify potential issues like damage, wear, or loose connections. Here’s what you need to do:
- Locate the ABS wheel sensor. It’s typically mounted near the wheel hub, usually on the inside of the brake rotor.
- Check for any visible damage, such as cracks, breaks, or corrosion on the sensor’s body or wiring.
- Examine the sensor’s tip, which is the part that detects the wheel’s rotation. Look for any signs of wear, dirt, or debris that could interfere with its operation.
- Inspect the wiring harness for any loose connections, broken wires, or signs of chafing. A loose connection or damaged wiring can interrupt the signal flow from the sensor to the ABS control module.
You’ll need a few basic tools for the visual inspection:
- A flashlight
- A small screwdriver
- A pair of gloves (optional)
Remember, if you find any visible damage or signs of wear, it’s best to replace the ABS wheel sensor to ensure proper ABS functionality.
Continuity Check
After the visual inspection, you can check the continuity of the ABS wheel sensor using a multimeter. This helps you confirm if the sensor is electrically connected and functioning properly.
Here’s how to check the continuity:
- Disconnect the ABS wheel sensor connector.
- Set your multimeter to the ohms (Ω) setting.
- Touch the multimeter’s probes to the sensor’s connector terminals.
- Check the multimeter reading. If the reading is close to zero ohms, it indicates good continuity, meaning the sensor is electrically connected.
- If the reading is infinite or very high, it suggests a broken wire or a faulty sensor.
Remember to consult your car’s service manual or an online repair guide for specific details on your vehicle’s ABS sensor and connector locations.
Diagnostic Tools and Procedures
Once you’ve completed the visual inspection and basic checks, it’s time to delve into the realm of diagnostic tools to pinpoint the issue with your ABS wheel sensor. These tools will provide you with valuable insights into the sensor’s functionality and help you determine the root cause of the problem.
Using an OBD-II Scanner
An OBD-II scanner is a must-have tool for any automotive enthusiast or mechanic. It allows you to access the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system (OBD) and retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to various components, including the ABS system.
- To use an OBD-II scanner, simply plug it into the OBD-II port located under the dashboard of your vehicle.
- Turn the ignition key to the “ON” position, but do not start the engine.
- Select “ABS” or “Body” from the scanner’s menu to access ABS-related codes.
- The scanner will display a list of DTCs, if any, stored in the vehicle’s memory.
Interpreting ABS Codes
ABS codes are standardized codes that provide information about specific faults within the ABS system. These codes can help you identify the specific sensor causing the issue.
- For example, a code like “C1222” might indicate a problem with the right front wheel speed sensor.
- Consult a repair manual or online database to interpret the specific codes you retrieve.
- Some common ABS codes related to wheel sensors include:
- C1221 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- C1222 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Open
- C1223 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Short to Ground
- C1224 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Short to Battery
Using a Digital Oscilloscope
A digital oscilloscope is a powerful tool that can provide a visual representation of the ABS sensor signal waveform. This waveform can reveal valuable information about the sensor’s health and functionality.
- Connect the oscilloscope probes to the ABS sensor wires.
- Observe the waveform displayed on the oscilloscope screen.
- A healthy ABS sensor signal waveform will typically have a specific frequency and amplitude.
- Any irregularities or abnormalities in the waveform can indicate a faulty sensor.
For example, a distorted or erratic waveform might indicate a damaged sensor or a problem with the wiring.
Testing the ABS Wheel Sensor Functionality
Testing the ABS wheel sensor functionality involves simulating the conditions the sensor encounters during normal operation. This process helps determine if the sensor is sending the correct signals and if its internal components are functioning as intended.
Testing the ABS Wheel Sensor Functionality
To test the ABS wheel sensor functionality, you will need a test bench or simulator that can generate the necessary input signals and measure the output signals from the sensor. This setup simulates the real-world conditions the sensor experiences, allowing you to analyze its performance.Here’s a step-by-step procedure for testing the ABS wheel sensor using a test bench or simulator:
- Connect the ABS wheel sensor to the test bench or simulator. This involves connecting the sensor’s electrical leads to the appropriate terminals on the test bench. Ensure a secure connection to avoid faulty readings.
- Apply a known input signal to the sensor. This signal can be a voltage, current, or frequency that simulates the rotation of the wheel. The test bench or simulator should have the capability to generate these signals accurately.
- Monitor the output signal from the sensor. This signal is typically a voltage or frequency that varies with the speed of the wheel. The test bench or simulator should have the ability to measure and display this output signal.
- Compare the output signal to the expected values. A healthy ABS wheel sensor will produce a specific output signal for a given input signal. This expected output signal is typically defined by the manufacturer’s specifications. The test bench or simulator can compare the measured output signal to the expected values to determine if the sensor is functioning correctly.
- Analyze the waveform of the output signal. The output signal from a healthy ABS wheel sensor should have a specific waveform, which can be analyzed using an oscilloscope. The waveform should be consistent with the expected signal for the sensor’s type and application. For example, a typical output waveform from an inductive ABS wheel sensor is a square wave with a frequency that increases with the speed of the wheel.
The expected output signal from a healthy ABS wheel sensor depends on the type of sensor and the application. For example, an inductive ABS wheel sensor typically produces a square wave with a frequency that increases with the speed of the wheel.
Expected Output Signals and Waveforms
The expected output signals and waveforms from a healthy ABS wheel sensor vary depending on the sensor type.
- Inductive ABS Wheel Sensor: The output signal from an inductive ABS wheel sensor is a square wave with a frequency that increases with the speed of the wheel. The frequency of the square wave is proportional to the speed of the wheel. The amplitude of the square wave should be consistent and within the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Hall Effect ABS Wheel Sensor: The output signal from a Hall effect ABS wheel sensor is a digital signal that changes state as the sensor detects the passage of a magnetic field. The frequency of the digital signal is proportional to the speed of the wheel. The amplitude of the digital signal should be consistent and within the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Magnetoresistive ABS Wheel Sensor: The output signal from a magnetoresistive ABS wheel sensor is a voltage that varies with the strength of the magnetic field. The voltage output is proportional to the speed of the wheel. The amplitude of the voltage output should be consistent and within the manufacturer’s specifications.
Comparing Test Results to Expected Values, How to test an abs wheel sensor
Once you have tested the ABS wheel sensor using a test bench or simulator, compare the measured output signal to the expected values. This comparison helps determine if the sensor is functioning correctly. If the measured output signal is significantly different from the expected values, it indicates that the sensor may be faulty.For example, if the output signal from an inductive ABS wheel sensor is not a square wave or if the frequency of the square wave does not increase with the speed of the wheel, it suggests that the sensor may be malfunctioning.In addition to comparing the output signal to the expected values, it’s important to analyze the waveform of the output signal.
The waveform should be consistent with the expected signal for the sensor’s type and application. If the waveform is distorted or irregular, it indicates that the sensor may be faulty.
Troubleshooting Common ABS Wheel Sensor Issues

Yo, let’s talk about the real deal – fixing those pesky ABS wheel sensor problems. Sometimes, your ABS system throws a fit, and you’re left scratching your head. But don’t worry, with a little knowledge and a few simple steps, you can get your ABS back in tip-top shape.
Identifying Common Symptoms of a Faulty ABS Wheel Sensor
A faulty ABS wheel sensor can cause a range of issues. Knowing the signs can help you quickly diagnose the problem and get your ABS back on track.
- ABS Warning Light: The most obvious sign is the ABS warning light on your dashboard. It’s like a flashing red flag screaming, “Hey, something’s wrong!”
- ABS System Malfunction: The ABS system might not function properly, meaning your brakes might lock up during hard braking. This is a serious safety concern, so pay attention!
- Uneven Braking: If one of your wheels is not being monitored by the ABS sensor, you might feel uneven braking, with one side braking harder than the other. This can make your car feel unstable and unpredictable.
Troubleshooting Techniques for Diagnosing ABS Wheel Sensor Issues
Okay, so you’ve noticed one or more of these symptoms. Now, it’s time to get your detective hat on and figure out what’s causing the problem. Here’s how to troubleshoot:
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the sensor itself. Look for any damage, corrosion, or loose connections. A damaged sensor is a dead giveaway!
- Resistance Check: Use a multimeter to check the resistance of the sensor. The resistance should fall within the manufacturer’s specifications. If it’s way off, you’ve got a faulty sensor.
- Voltage Check: You can also use a multimeter to check the voltage at the sensor. The voltage should be within a certain range. If it’s too low or too high, it could indicate a problem with the wiring or the ABS control module.
- Test Drive: Take your car for a test drive and pay close attention to how the ABS system is working. Does the warning light come on? Do the brakes feel uneven? This will give you more clues about the problem.
Potential Solutions and Repairs
So, you’ve diagnosed the problem. Now, it’s time to fix it! Here’s a checklist of potential solutions and repairs:
- Replace the Faulty Sensor: If the sensor is damaged or has failed the resistance check, you’ll need to replace it. Make sure you get a new sensor from a reputable supplier. Don’t try to cheap out on this one!
- Repair Wiring: If the wiring is damaged or corroded, you’ll need to repair or replace it. This might involve splicing in new wire or running new wire altogether.
- Inspect ABS Control Module: If the problem isn’t with the sensor or the wiring, the issue might be with the ABS control module itself. This requires more specialized testing and might need to be replaced by a qualified mechanic.
By following the steps Artikeld in this guide, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of how to test an ABS wheel sensor. You’ll be equipped to identify potential issues, troubleshoot effectively, and ensure the proper functioning of your vehicle’s braking system. Remember, a properly functioning ABS wheel sensor is critical for safe and reliable braking, so don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance if you encounter any difficulties or uncertainties.
FAQ Summary: How To Test An Abs Wheel Sensor
Can I test the ABS wheel sensor without using a diagnostic scanner?
While a diagnostic scanner provides valuable information, you can perform basic checks using a multimeter to test the sensor’s continuity and signal output.
What are the common symptoms of a faulty ABS wheel sensor?
Common symptoms include the ABS warning light illuminating, ABS system malfunctions, uneven braking, and a pulsating brake pedal.
How often should I test the ABS wheel sensor?
It’s recommended to test the ABS wheel sensor as part of regular vehicle maintenance or if you suspect any issues with the braking system.
Is it safe to drive with a faulty ABS wheel sensor?
While you can still drive with a faulty ABS wheel sensor, it’s not recommended as it can compromise the effectiveness of your braking system and increase the risk of accidents.