How does an energy recovery wheel work? This ingenious technology, quietly revolutionizing industries, taps into a hidden resource: waste heat. Imagine capturing the heat from a factory’s exhaust and using it to pre-heat incoming air, reducing energy consumption and lowering costs. This is the magic of energy recovery wheels, a marvel of engineering that transforms waste into a valuable asset.
Energy recovery wheels, also known as rotary heat exchangers, work by transferring heat between two airstreams. One stream, often hot and laden with waste heat, passes through the wheel’s porous core. The other stream, typically cooler and incoming, then passes through the same core, absorbing the heat from the previous stream. This clever heat exchange process allows for significant energy savings, making it a key player in sustainable practices.
Introduction to Energy Recovery Wheels
Energy recovery wheels are innovative devices that harness the waste heat generated in various industrial processes and convert it into usable energy. This technology plays a crucial role in reducing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact, making it a vital component in achieving sustainable operations.Energy recovery wheels operate on the principle of heat transfer, capturing the thermal energy from exhaust gases and transferring it to incoming fresh air.
This process involves rotating a wheel with a porous, heat-absorbing material, such as ceramic or metal, through the exhaust stream and then the fresh air stream. The wheel absorbs heat from the exhaust gases and releases it to the incoming fresh air, effectively preheating the air for use in various industrial applications.
The Significance of Energy Recovery
Energy recovery is essential for industries seeking to improve their energy efficiency and reduce operational costs. By capturing and reusing waste heat, businesses can significantly lower their energy consumption, leading to:
- Reduced energy bills: By utilizing recovered heat for preheating, drying, or other processes, industries can minimize their reliance on external energy sources, resulting in substantial cost savings.
- Lowered carbon footprint: By reducing energy consumption, energy recovery wheels contribute to a smaller carbon footprint, aligning with sustainability goals and environmental regulations.
- Enhanced process efficiency: Recovering waste heat can improve the efficiency of various processes, leading to higher productivity and output.
History of Energy Recovery Wheel Technology, How does an energy recovery wheel work
The concept of energy recovery wheels dates back to the early 20th century, with initial applications in the mining industry. Over time, the technology has evolved significantly, with advancements in materials, design, and control systems. Here’s a brief timeline of key milestones:
- Early 20th century: Initial energy recovery wheels were primarily used in mining operations to recover heat from exhaust gases, improving ventilation and worker comfort.
- 1950s-1960s: The development of more efficient materials, such as ceramic and metal, led to increased adoption of energy recovery wheels in various industries, including manufacturing, power generation, and food processing.
- 1970s-1980s: The energy crisis and growing environmental concerns spurred further innovation in energy recovery technology, resulting in the development of advanced control systems and more efficient wheel designs.
- 1990s-present: Continued advancements in materials science and computational modeling have led to the development of highly efficient and reliable energy recovery wheels with minimal energy consumption and extended service life.
Components and Working Principle
Energy recovery wheels are devices that transfer heat or moisture from an exhaust airstream to a fresh air stream, reducing energy consumption and improving indoor air quality. They achieve this through a rotating wheel with a porous material that absorbs and releases heat and moisture. The working principle of an energy recovery wheel involves the transfer of heat and/or moisture between two airstreams: the exhaust air and the fresh air.
As the wheel rotates, it passes through both airstreams, absorbing heat and moisture from the exhaust air and transferring it to the fresh air.
Types of Energy Recovery Wheels
Energy recovery wheels come in various types, each with its unique design and operating principles.
- Rotary Wheels: Rotary wheels are the most common type of energy recovery wheel. They consist of a large, rotating wheel with a porous material, typically made of aluminum or plastic. The wheel rotates continuously, passing through the exhaust air and fresh air streams. As the wheel rotates, it absorbs heat and moisture from the exhaust air and transfers it to the fresh air.
- Static Wheels: Static wheels are a newer type of energy recovery wheel that does not require a rotating wheel. Instead, they use a series of fixed plates with a porous material. The plates are arranged in a staggered pattern, allowing air to flow through them in a zig-zag pattern. This design helps to maximize heat and moisture transfer between the exhaust air and fresh air streams.
- Hybrid Wheels: Hybrid wheels combine the features of rotary and static wheels. They use a rotating wheel with a porous material, but they also have a series of fixed plates. This design helps to improve the efficiency of the wheel by increasing the surface area for heat and moisture transfer.
Types of Energy Recovery Wheels: How Does An Energy Recovery Wheel Work
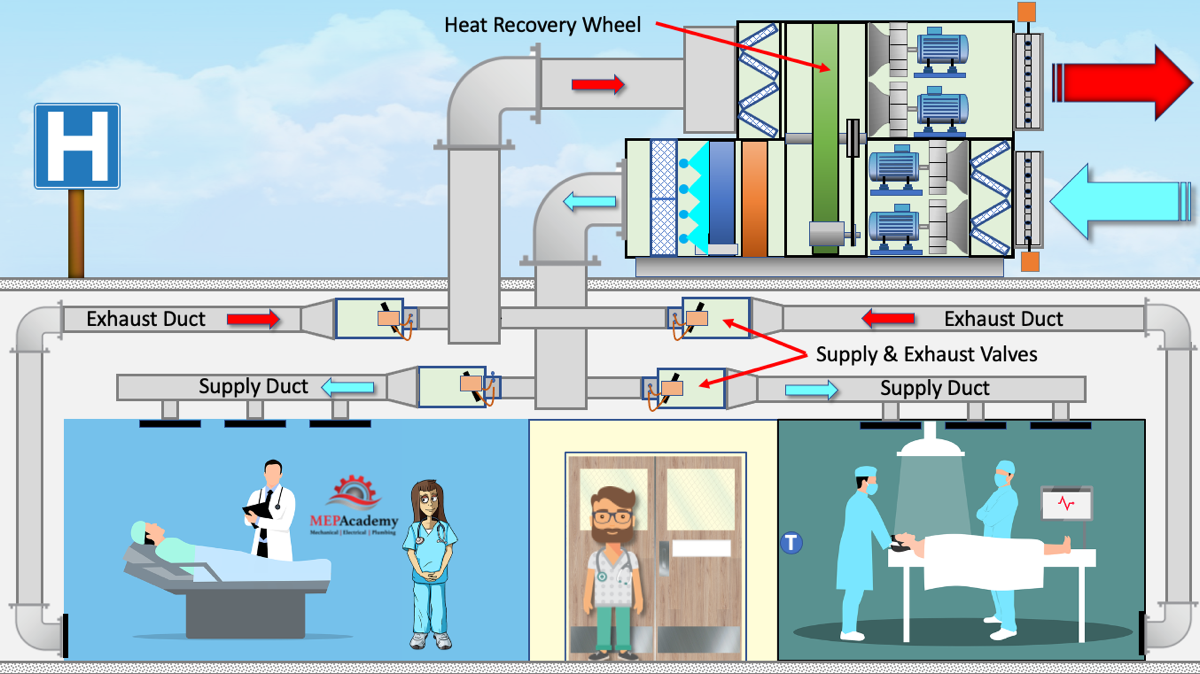
Energy recovery wheels are classified based on the type of energy they recover, primarily focusing on sensible heat, latent heat, or a combination of both. Each type offers unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications.
Sensible Heat Recovery Wheels
Sensible heat recovery wheels are designed to recover only the sensible heat from exhaust air. This type of wheel is commonly used in applications where the exhaust air contains minimal moisture, such as industrial processes involving dry materials. Sensible heat recovery wheels typically employ materials with high thermal conductivity, like aluminum or ceramic, to facilitate efficient heat transfer. The wheel rotates through the exhaust air stream, absorbing the sensible heat and transferring it to the incoming fresh air stream.
Applications
- Industrial Ventilation: In industries like manufacturing, warehousing, and food processing, where dry air is required for operations, sensible heat recovery wheels can reduce heating costs and improve energy efficiency.
- Commercial Buildings: Sensible heat recovery wheels are used in HVAC systems to preheat incoming fresh air, reducing the load on heating equipment and minimizing energy consumption.
- Data Centers: Data centers generate significant heat from servers and other equipment. Sensible heat recovery wheels can recover this heat and use it to preheat incoming fresh air, reducing energy consumption and cooling costs.
Advantages
- High Efficiency: Sensible heat recovery wheels can achieve high efficiency in recovering sensible heat from exhaust air.
- Low Maintenance: These wheels are relatively simple in design and require minimal maintenance.
- Cost-Effective: Sensible heat recovery wheels are generally less expensive than other types of energy recovery wheels.
Disadvantages
- Limited Moisture Recovery: Sensible heat recovery wheels do not recover latent heat, making them unsuitable for applications with high humidity.
- Potential for Frost Formation: In cold climates, condensation can occur on the wheel surface, leading to frost formation and reduced efficiency.
Latent Heat Recovery Wheels
Latent heat recovery wheels are designed to recover latent heat from exhaust air, primarily in the form of moisture. This type of wheel is commonly used in applications where the exhaust air contains significant moisture, such as swimming pools, greenhouses, and industrial processes involving wet materials.Latent heat recovery wheels typically employ materials with high moisture absorption capacity, like silica gel or zeolite.
The wheel rotates through the exhaust air stream, absorbing moisture and transferring it to the incoming fresh air stream.
Applications
- Swimming Pools: Latent heat recovery wheels can recover the latent heat from humid exhaust air from swimming pools, reducing the energy required to heat the pool water.
- Greenhouses: In greenhouses, latent heat recovery wheels can recover moisture from exhaust air and transfer it to the incoming fresh air, improving humidity levels and reducing the need for humidification.
- Food Processing: In food processing facilities, latent heat recovery wheels can recover moisture from exhaust air, reducing the energy required for drying and minimizing energy consumption.
Advantages
- High Moisture Recovery: Latent heat recovery wheels are highly effective in recovering moisture from exhaust air.
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: By recovering moisture, latent heat recovery wheels can help maintain optimal humidity levels, improving indoor air quality and comfort.
Disadvantages
- Lower Efficiency: Latent heat recovery wheels typically have lower efficiency than sensible heat recovery wheels.
- Higher Maintenance: Latent heat recovery wheels require more frequent maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
- Costly: Latent heat recovery wheels are generally more expensive than sensible heat recovery wheels.
Combined Heat and Moisture Recovery Wheels
Combined heat and moisture recovery wheels are designed to recover both sensible and latent heat from exhaust air. This type of wheel is commonly used in applications where both sensible heat and moisture recovery are required, such as hospitals, schools, and office buildings.Combined heat and moisture recovery wheels typically employ a combination of materials with high thermal conductivity and moisture absorption capacity.
The wheel rotates through the exhaust air stream, absorbing both sensible heat and moisture and transferring them to the incoming fresh air stream.
Applications
- Hospitals: Combined heat and moisture recovery wheels can recover both sensible heat and moisture from exhaust air in hospitals, reducing energy consumption and improving indoor air quality.
- Schools: In schools, combined heat and moisture recovery wheels can recover both sensible heat and moisture from exhaust air, reducing energy consumption and creating a more comfortable learning environment.
- Office Buildings: Combined heat and moisture recovery wheels are used in HVAC systems of office buildings to preheat and humidify incoming fresh air, reducing the load on heating and humidification equipment and minimizing energy consumption.
Advantages
- High Energy Efficiency: Combined heat and moisture recovery wheels offer high energy efficiency by recovering both sensible and latent heat.
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: By recovering both heat and moisture, these wheels can help maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels, improving indoor air quality and comfort.
Disadvantages
- Complex Design: Combined heat and moisture recovery wheels are more complex in design than other types of energy recovery wheels.
- Higher Maintenance: These wheels require more frequent maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
- Costly: Combined heat and moisture recovery wheels are generally the most expensive type of energy recovery wheels.
Applications and Benefits
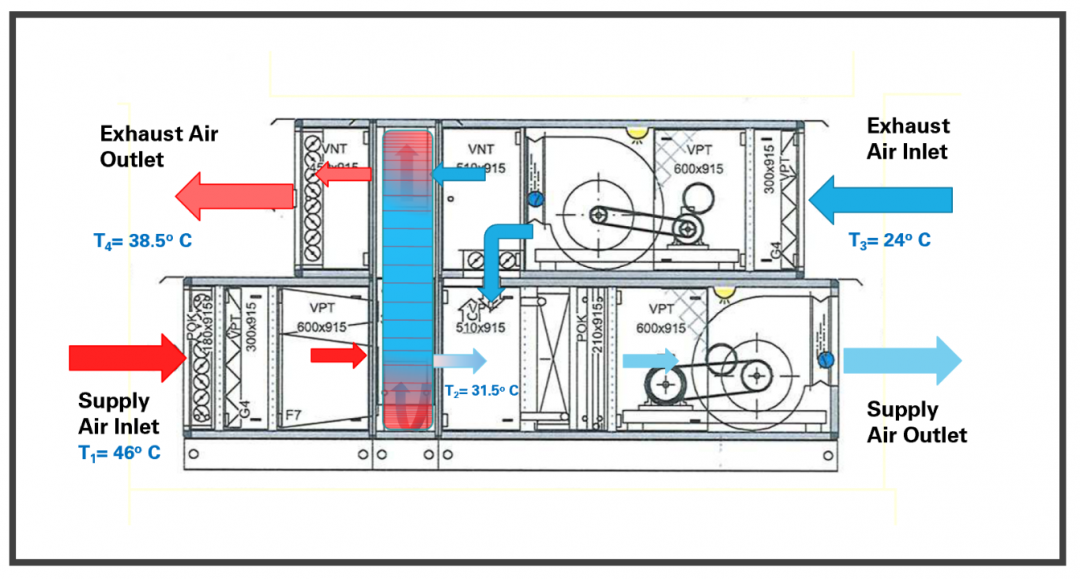
Energy recovery wheels find wide-ranging applications across various industries, significantly impacting energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. These devices harness the waste heat or cool air from exhaust streams to preheat or precool incoming air, resulting in substantial energy savings and reduced operational costs.
Industries Utilizing Energy Recovery Wheels
Energy recovery wheels are employed in a diverse range of industries, playing a crucial role in optimizing energy consumption and minimizing environmental impact.
- HVAC Systems: Energy recovery wheels are commonly used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to recover heat from exhaust air and preheat incoming fresh air. This preheating process reduces the load on heating systems, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs. For example, in commercial buildings, energy recovery wheels can significantly decrease heating energy requirements, resulting in substantial energy savings and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Industrial Processes: Energy recovery wheels are also widely used in industrial processes where large volumes of air are required for ventilation or process cooling. For instance, in manufacturing facilities, energy recovery wheels can recover heat from exhaust air generated by industrial ovens or furnaces, preheating incoming air for process applications. This heat recovery significantly reduces the energy needed for process heating, leading to substantial energy savings and reduced emissions.
- Power Generation: Energy recovery wheels are utilized in power generation plants to recover heat from exhaust gases and preheat incoming combustion air. This preheating process increases the efficiency of the combustion process, leading to improved power generation and reduced fuel consumption. In combined cycle power plants, energy recovery wheels play a critical role in capturing waste heat from the exhaust gases of gas turbines, preheating the air used for combustion in the steam turbine, resulting in significant energy savings and higher overall efficiency.
Benefits of Energy Recovery Wheels
The implementation of energy recovery wheels offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Energy recovery wheels significantly reduce energy consumption by capturing waste heat or cool air and utilizing it to preheat or precool incoming air. This reduces the load on heating and cooling systems, leading to substantial energy savings.
- Lower Operating Costs: By reducing energy consumption, energy recovery wheels contribute to lower operating costs, as less energy is required to heat or cool buildings or industrial processes. This translates to significant cost savings over the long term.
- Environmental Sustainability: Energy recovery wheels promote environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy consumption. By minimizing the need for fossil fuels, these devices contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable environment.
Real-World Examples of Energy Savings and Emission Reductions
- Commercial Building in New York City: A commercial building in New York City implemented an energy recovery wheel in its HVAC system. The energy recovery wheel captured waste heat from the building’s exhaust air and used it to preheat incoming fresh air. This resulted in a 30% reduction in heating energy consumption, leading to significant energy savings and reduced emissions.
- Manufacturing Facility in Germany: A manufacturing facility in Germany installed an energy recovery wheel to recover heat from exhaust air generated by its industrial ovens. The recovered heat was used to preheat incoming air for the ovens, reducing the energy needed for process heating by 25%. This resulted in substantial energy savings and reduced emissions from the facility’s operations.
- Combined Cycle Power Plant in Japan: A combined cycle power plant in Japan incorporated an energy recovery wheel to capture waste heat from the exhaust gases of its gas turbine. The recovered heat was used to preheat the combustion air for the steam turbine, increasing the overall efficiency of the power plant by 5%. This resulted in significant energy savings and reduced fuel consumption.
Design Considerations and Optimization
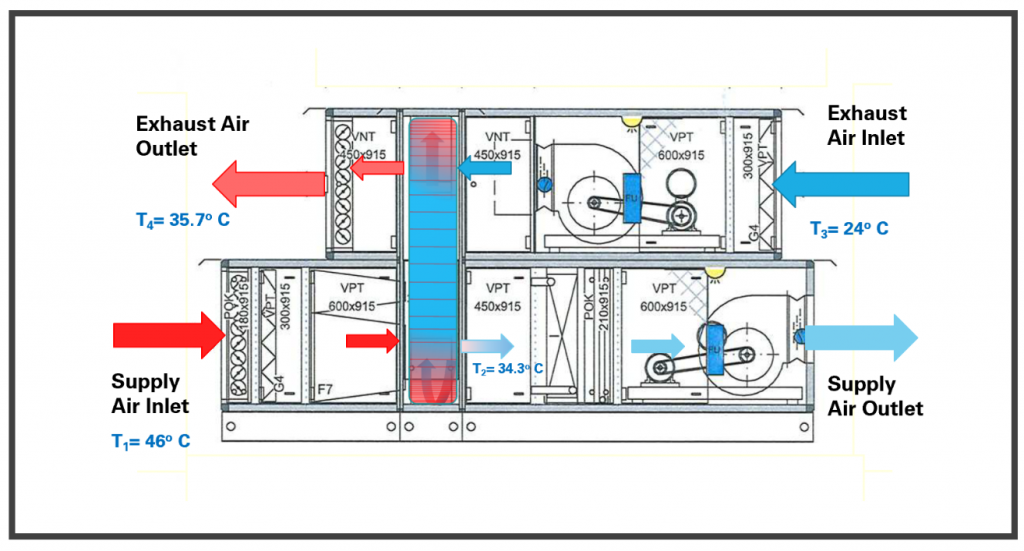
Designing and optimizing an energy recovery wheel system requires careful consideration of various factors to maximize energy recovery efficiency and ensure optimal performance. This involves balancing the airflow rate, temperature differential, and material selection, along with implementing optimization techniques such as adjusting wheel rotation speed and air flow control.
Airflow Rate and Temperature Differential
The airflow rate and temperature differential play a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of an energy recovery wheel. A higher airflow rate allows for greater heat transfer, leading to increased energy recovery. However, a higher airflow rate also increases pressure drop, potentially reducing the overall system efficiency. Conversely, a larger temperature differential between the exhaust and fresh air streams enhances the energy recovery potential.
However, a larger temperature differential may also lead to a higher risk of condensation and fouling on the wheel surface, hindering its performance.
Material Selection
The material selection for the energy recovery wheel is crucial for its performance and durability. Factors to consider include:
- Thermal Conductivity: High thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat transfer between the air streams. Materials like aluminum, stainless steel, and ceramics are commonly used for their excellent thermal conductivity.
- Resistance to Corrosion: The wheel material must be resistant to corrosion from the air streams, especially in applications involving corrosive gases or high humidity.
- Mechanical Strength: The wheel must be mechanically strong to withstand the stresses and vibrations associated with operation.
- Cost: The material cost is a significant factor in the overall system cost, and a balance must be struck between performance and affordability.
Optimization Techniques
Several optimization techniques can be employed to enhance the energy recovery efficiency of the system:
- Wheel Rotation Speed: Adjusting the wheel rotation speed allows for controlling the contact time between the air streams and the wheel surface. A higher rotation speed generally results in increased heat transfer, but it also increases power consumption.
- Air Flow Control: Optimizing the air flow distribution across the wheel surface ensures uniform heat transfer and reduces pressure drop. This can be achieved using baffles, louvers, or other flow control devices.
- Heat Exchanger Design: The design of the heat exchanger, including the number of plates, the spacing between plates, and the material of construction, significantly impacts the heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop. Optimizing these parameters can enhance energy recovery and minimize energy losses.
Impact of Operating Parameters
Various operating parameters can influence the energy recovery performance of the system.
- Exhaust Air Temperature: Higher exhaust air temperatures generally lead to increased energy recovery. However, exceeding the material’s temperature limit can cause damage to the wheel and reduce its lifespan.
- Fresh Air Temperature: Lower fresh air temperatures result in a larger temperature differential, enhancing energy recovery. However, very low fresh air temperatures may lead to condensation and fouling on the wheel surface.
- Humidity: High humidity can lead to condensation and fouling on the wheel surface, reducing its performance. Dehumidifying the air streams before they enter the wheel can mitigate this issue.
Maintenance and Operation
Proper maintenance and operation are crucial for maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of energy recovery wheels. Regular cleaning, filter replacement, and performance monitoring are essential for ensuring optimal performance and minimizing operational issues.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning is essential for maintaining the efficiency of energy recovery wheels. Dust, dirt, and other contaminants can accumulate on the wheel surface, reducing its effectiveness. The frequency of cleaning depends on the operating environment and the type of wheel. For example, wheels operating in dusty environments may require more frequent cleaning than those in cleaner environments.
- Cleaning Procedures: The cleaning procedure involves removing the wheel from the system and cleaning it with a suitable cleaning solution. The cleaning solution should be compatible with the wheel material and should not damage the wheel.
- Filter Replacement: Filters are used to protect the energy recovery wheel from dust and other contaminants. Filters should be replaced regularly according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Performance Monitoring: Performance monitoring involves tracking the energy recovery wheel’s performance over time. This can be done by monitoring the air flow rate, temperature difference, and pressure drop across the wheel.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Techniques
Energy recovery wheels can experience various issues, such as fouling, leakage, and reduced efficiency. These issues can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor maintenance, environmental conditions, and wear and tear.
- Fouling: Fouling occurs when contaminants accumulate on the wheel surface, reducing its efficiency. Fouling can be caused by dust, dirt, smoke, or other airborne particles.
- Leakage: Leakage occurs when air leaks from the wheel, reducing its efficiency. Leakage can be caused by damaged seals, worn bearings, or other mechanical issues.
- Reduced Efficiency: Reduced efficiency can be caused by fouling, leakage, or other factors.
To troubleshoot reduced efficiency, check the wheel for fouling, leakage, and other issues.
Best Practices for Long-Term Reliability and Optimal Performance
Following best practices can help ensure the long-term reliability and optimal performance of energy recovery wheel systems.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including cleaning, filter replacement, and performance monitoring, is essential for maintaining the efficiency and lifespan of the wheel.
- Proper Operation: Operating the wheel within its design parameters can help prevent premature wear and tear.
- Environmental Control: Controlling the environment in which the wheel operates can help minimize fouling and other issues.
- Training and Expertise: Ensure operators are properly trained on the operation and maintenance of the energy recovery wheel system.
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of energy recovery wheel technology is constantly evolving, driven by the need for more sustainable and efficient solutions for energy management. This section explores the emerging trends and innovations that are shaping the future of energy recovery wheels.
Advanced Materials
The development of advanced materials is playing a crucial role in enhancing the performance and efficiency of energy recovery wheels. These materials offer improved thermal conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion, leading to increased heat transfer efficiency and longer operational life.
- Ceramic materials: Ceramic materials, known for their high thermal conductivity and resistance to extreme temperatures, are being increasingly used in energy recovery wheel applications. They offer excellent heat transfer capabilities, enabling more efficient energy recovery.
- Composite materials: Composite materials, combining the strengths of different materials, are being explored for their ability to enhance the structural integrity and thermal performance of energy recovery wheels. These materials offer a balance of strength, lightweight, and thermal conductivity.
- Nanomaterials: Nanomaterials, with their unique properties, are being investigated for their potential to improve the heat transfer efficiency and durability of energy recovery wheels. These materials can enhance surface area, leading to improved heat transfer, and also provide enhanced resistance to wear and tear.
Improved Control Systems
Advanced control systems are being developed to optimize the performance of energy recovery wheels and maximize energy recovery efficiency. These systems use sophisticated algorithms and sensors to monitor and adjust the wheel’s operation in real-time, ensuring optimal performance under varying conditions.
- Adaptive control systems: Adaptive control systems can learn and adapt to changing environmental conditions, optimizing energy recovery efficiency. These systems can adjust the wheel’s speed, airflow, and other parameters to maximize energy recovery under different operating conditions.
- Predictive maintenance: Predictive maintenance systems use sensors and data analysis to anticipate potential problems and schedule maintenance before failures occur. This helps to ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime.
- Integration with Building Management Systems (BMS): Integration of energy recovery wheels with BMS allows for seamless control and monitoring of the system. This integration enables real-time adjustments based on building occupancy, weather conditions, and other factors, further enhancing energy efficiency.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
The integration of energy recovery wheels with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, offers significant potential for achieving net-zero energy buildings and sustainable industrial processes. By combining the energy recovery capabilities of wheels with renewable energy sources, it’s possible to create highly efficient and sustainable energy systems.
- Hybrid energy systems: Hybrid energy systems combine energy recovery wheels with renewable energy sources, creating a synergistic approach to energy management. The wheel can preheat or precool air, reducing the load on the renewable energy system and improving overall efficiency.
- Off-grid applications: Energy recovery wheels can be integrated into off-grid systems, providing a reliable and sustainable source of energy for remote locations. This can be particularly beneficial in areas with limited access to traditional energy sources.
- Microgrid integration: Energy recovery wheels can be integrated into microgrids, enhancing energy efficiency and resilience. By recovering waste heat and using renewable energy sources, microgrids can operate more efficiently and sustainably.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in energy recovery wheels are significantly impacting their cost-effectiveness and environmental impact. These advancements are leading to:
- Reduced operating costs: Improved efficiency and longer operational life translate into reduced operating costs, making energy recovery wheels a more attractive investment.
- Lower carbon footprint: Increased energy recovery efficiency leads to reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
- Enhanced sustainability: The integration of energy recovery wheels with renewable energy sources promotes sustainable energy practices and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Energy recovery wheels are a testament to the power of innovation, offering a practical solution to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact. By understanding their working principles, applications, and benefits, we can harness their potential to create a more sustainable future. As we move towards a greener tomorrow, energy recovery wheels will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping a world where efficiency and sustainability go hand in hand.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the different types of energy recovery wheels?
Energy recovery wheels can be categorized based on the type of heat transfer they facilitate: sensible heat recovery, latent heat recovery, and combined heat and moisture recovery. Sensible heat recovery wheels focus on transferring heat between airstreams, while latent heat recovery wheels capture and transfer moisture as well. Combined heat and moisture recovery wheels offer the benefits of both.
What are the common challenges associated with energy recovery wheels?
Common challenges include fouling, leakage, and reduced efficiency. Fouling occurs when dust and other particles accumulate on the wheel’s surface, reducing its heat transfer capabilities. Leakage can occur in the seals or air stream management system, leading to energy losses. Reduced efficiency can result from various factors, including improper maintenance, wear and tear, or environmental conditions.
How often do energy recovery wheels need maintenance?
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The frequency of maintenance depends on factors such as the type of wheel, operating conditions, and the environment. However, a general guideline is to inspect the wheel for fouling and leakage every few months and to replace filters and clean the wheel thoroughly at least once a year.