What’s the difference between tires and wheels? It’s a question that might seem simple at first glance, but delving deeper reveals a fascinating world of intricate design, crucial function, and remarkable interaction. These two components, often seen as one, are in fact distinct entities playing vital roles in the smooth operation of any vehicle. From the rubber that grips the road to the metal that supports the weight, tires and wheels work in tandem to provide the foundation for safe and efficient travel.
Understanding the differences between tires and wheels goes beyond mere curiosity. It empowers drivers to make informed decisions about maintenance, upgrades, and even safety precautions. By examining their individual roles, materials, and designs, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate engineering that goes into every vehicle we drive.
The Core Components
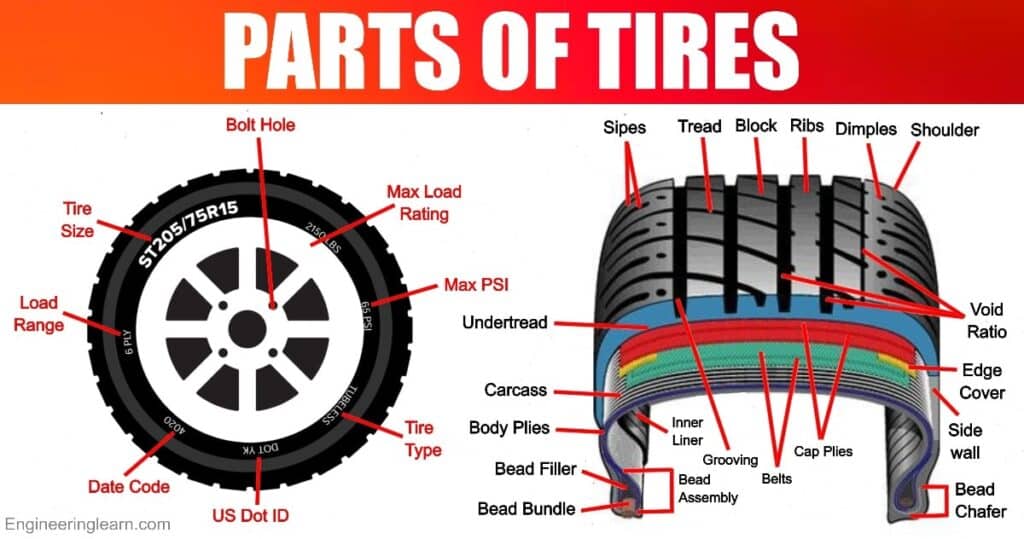
Imagine a car cruising down the road. It’s a smooth ride, thanks to the tires and wheels working in perfect harmony. While they seem like one unit, they are actually distinct components with unique roles. Let’s delve into the core of these essential parts and understand their individual functions.
Materials Used in Construction
The materials used to build tires and wheels play a crucial role in their performance and durability.
- Tires are primarily made of rubber, a material known for its flexibility and resilience. Natural rubber, extracted from rubber trees, provides elasticity, while synthetic rubber offers improved durability and resistance to wear.
- Steel belts, woven into the tire’s structure, provide strength and support, preventing the tire from collapsing under load.
- Nylon or polyester cords, forming the tire’s carcass, provide flexibility and allow the tire to deform under pressure.
- Wheels, on the other hand, are typically made of metal, usually steel or aluminum. Steel wheels are durable and affordable, while aluminum wheels are lighter and offer better heat dissipation.
Function and Interaction
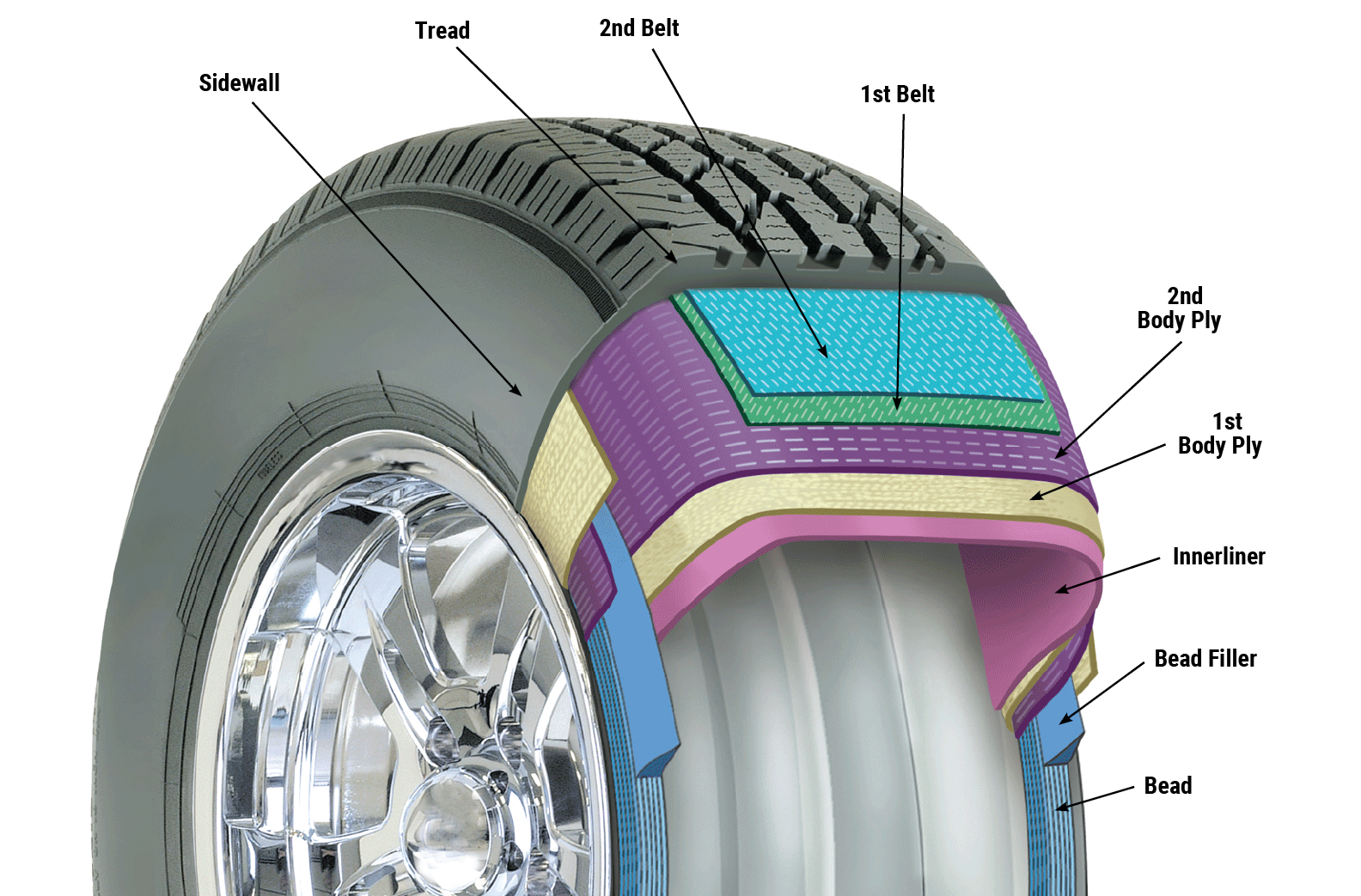
Imagine a car, its engine roaring with power, ready to take you on an adventure. But without tires and wheels, that adventure would never leave the garage. They are the crucial link between the car’s power and the road, allowing it to move forward, navigate turns, and conquer different terrains. Let’s delve into the intricate dance between these two essential components, understanding how they work together to make driving possible.
The Tire’s Role in Traction and Shock Absorption
Tires are the primary contact points between a vehicle and the road. Their unique design, featuring a tread pattern and rubber compound, plays a crucial role in providing traction and absorbing shocks.
- Traction: The tire’s tread pattern provides grip on the road surface, allowing the vehicle to accelerate, brake, and steer effectively. The grooves in the tread pattern help channel water away, preventing hydroplaning, a dangerous situation where tires lose contact with the road due to water accumulation.
- Shock Absorption: The tire’s flexible rubber construction acts as a spring, absorbing the impact of bumps and irregularities in the road surface. This cushioning effect protects the vehicle’s suspension system and improves ride comfort.
The Wheel’s Role in Movement and Weight Support
Wheels are the circular structures that support the vehicle’s weight and facilitate movement. Their primary functions are:
- Weight Support: Wheels bear the weight of the vehicle, distributing it evenly across the contact patch between the tire and the road. This distribution ensures stability and prevents uneven wear on the tires.
- Movement: Wheels rotate, allowing the vehicle to move forward, backward, and sideways. This rotation is achieved through the transmission of power from the engine to the wheels via the drivetrain.
Tire and Wheel Interaction, What’s the difference between tires and wheels
Tires and wheels are interconnected components that work together to enable vehicle operation. The wheel provides the structural support for the tire, allowing it to rotate and maintain its shape. The tire, in turn, provides the necessary traction and shock absorption for the wheel to perform its functions effectively.
The interaction between tires and wheels is crucial for vehicle stability, ride comfort, and overall performance.
Tire Types and Wheel Variations

Beyond the fundamental interaction between tires and wheels, the world of automotive engineering offers a vast array of tire types and wheel designs, each tailored to specific performance goals and driving conditions. Understanding these variations is crucial for optimizing vehicle handling, comfort, and fuel efficiency.
Tire Types
Tire types are classified based on their intended use and construction. Each type boasts unique tread patterns, rubber compounds, and sidewall designs to suit specific driving environments and performance demands.
- Passenger Car Tires: Designed for everyday driving on paved roads, these tires offer a balance of comfort, handling, and fuel efficiency. They feature a variety of tread patterns, from all-season to summer-specific, and are available in various sizes to fit different vehicle models.
- Light Truck Tires: Built for heavier vehicles and off-road adventures, these tires offer greater durability and load capacity. Their deeper tread patterns and reinforced sidewalls provide excellent traction on rough terrain and in challenging weather conditions.
- High-Performance Tires: Engineered for speed and precision handling, these tires feature a stiffer sidewall and a tread pattern optimized for grip and cornering. They often utilize specialized rubber compounds that offer excellent adhesion on dry and wet surfaces.
- Run-Flat Tires: Designed to maintain vehicle control even after a puncture, these tires have reinforced sidewalls that allow them to support the vehicle’s weight without air pressure. They are often used in luxury and high-performance vehicles.
- Winter Tires: Equipped with a unique tread pattern and rubber compound designed for cold temperatures and snow, these tires offer superior grip and traction on icy and snowy roads. They are typically used in regions that experience harsh winter conditions.
Wheel Designs
Wheel designs go beyond aesthetics, playing a significant role in vehicle performance, weight distribution, and overall aesthetics.
- Spoke Wheels: Characterized by their radial spokes extending from the center hub to the rim, spoke wheels offer a classic and elegant look. They are known for their lightweight construction, allowing for improved acceleration and handling.
- Mesh Wheels: Featuring a complex and intricate network of interwoven spokes, mesh wheels provide a modern and aggressive aesthetic. They offer excellent strength and rigidity, contributing to enhanced vehicle stability and performance.
- Forged Wheels: Crafted from a single piece of aluminum through a forging process, forged wheels are exceptionally strong and lightweight. They offer superior durability and resistance to bending, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
Impact of Tire and Wheel Combinations
The combination of tire type and wheel design significantly influences a vehicle’s performance characteristics.
- Handling and Cornering: Wider tires with a stiffer sidewall, coupled with lightweight forged wheels, provide superior grip and responsiveness, enhancing cornering stability and precision.
- Ride Comfort: Tires with a softer sidewall and a tread pattern designed for comfort, paired with spoke wheels, contribute to a smoother and more enjoyable ride experience.
- Fuel Efficiency: Lighter wheels and tires with a lower rolling resistance, such as those with a specific tread pattern and rubber compound, can improve fuel economy by reducing the energy required to move the vehicle.
Maintenance and Considerations: What’s The Difference Between Tires And Wheels
Maintaining your tires and wheels is crucial for a safe and enjoyable driving experience. Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance, extends the life of your tires, and protects your vehicle from potential damage.
Tire Pressure
Maintaining the correct tire pressure is essential for safe and efficient driving. Underinflated tires can lead to increased rolling resistance, which reduces fuel efficiency and increases wear and tear. Overinflation, on the other hand, can make the ride harsh and increase the risk of tire blowouts.
The recommended tire pressure for your vehicle can be found in your owner’s manual or on a sticker located on the driver’s side doorjamb.
- Impact on Handling: Underinflated tires can cause the vehicle to handle poorly, making it harder to steer and brake effectively. This is because the tire’s contact patch with the road surface is reduced, leading to a loss of grip.
- Fuel Efficiency: Underinflated tires require more energy to roll, leading to decreased fuel efficiency. Overinflating tires can also slightly reduce fuel efficiency, but the impact is less significant than underinflation.
- Tire Wear: Underinflation causes the tire to deform and wear out more quickly, especially on the outer edges. Overinflation can lead to uneven wear on the center of the tire.
Routine Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance practices for tires and wheels are essential for ensuring their longevity and performance. These practices include:
- Tire Rotation: Rotating tires regularly helps ensure even wear and tear. This involves moving the tires from one position to another on the vehicle, typically every 5,000 to 7,500 miles. This practice helps to distribute the wear and tear evenly across all tires, extending their lifespan.
- Wheel Alignment: Wheel alignment refers to the angle of the wheels relative to each other and the vehicle’s frame. Misaligned wheels can cause uneven tire wear, affect steering and handling, and increase fuel consumption. Wheel alignment should be checked every 6,000 to 8,000 miles or if you notice any changes in steering or handling.
- Tire Inspections: Regularly inspect your tires for signs of wear, damage, or other abnormalities. This includes checking for:
- Tread depth: The minimum tread depth required for safe driving is 2/32 of an inch. Use a tread depth gauge to measure the remaining tread depth.
- Cuts, punctures, or bulges: Any damage to the tire can compromise its integrity and should be repaired or replaced.
- Uneven wear: Uneven wear patterns can indicate issues with wheel alignment or tire pressure.
Choosing the Right Tires and Wheels
Selecting the right tires and wheels for your vehicle is crucial for optimal performance, safety, and comfort. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Vehicle Type: Different vehicle types require different tire sizes and types. For example, SUVs and trucks typically require tires with a higher load capacity and a more aggressive tread pattern than sedans.
- Driving Conditions: The type of driving you do will also influence your tire and wheel choices. For example, if you live in an area with heavy snowfall, you will need winter tires. If you frequently drive on rough terrain, you may need tires with a more rugged tread pattern.
- Personal Preferences: Ultimately, the choice of tires and wheels comes down to personal preference. Consider factors such as ride comfort, noise level, and aesthetics.
The relationship between tires and wheels is a testament to the ingenuity of engineering. They are two distinct components that, when combined, create a seamless system capable of navigating various terrains and carrying heavy loads. From the humble rubber compound that provides traction to the sturdy metal framework that bears the weight, each element plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth and safe ride.
Understanding their individual functions and the intricate way they interact allows us to appreciate the complexity and importance of these seemingly simple components. As we continue to explore the world of automobiles, it’s important to remember that even the most basic elements, like tires and wheels, hold a wealth of knowledge and intricate design that contribute to the overall functionality and safety of our vehicles.
Quick FAQs
What is the purpose of a tire?
A tire provides traction for the vehicle, absorbs shock from the road, and helps maintain stability.
What is the purpose of a wheel?
A wheel supports the weight of the vehicle and facilitates movement by rolling on the road.
What are some common types of tires?
Common tire types include all-season, summer, winter, and performance tires, each designed for specific driving conditions and preferences.
What are some common wheel designs?
Common wheel designs include spoke, mesh, and forged styles, each offering different aesthetic and performance characteristics.
How often should I rotate my tires?
Tire rotation is recommended every 5,000 to 7,500 miles to ensure even wear and tear.