A manufacturer is designing a two wheeled cart – A manufacturer is designing a two-wheeled cart, embarking on a journey to create a versatile and efficient tool. This endeavor involves careful consideration of design elements, functionality, and manufacturing processes to ensure a product that meets the needs of its intended users. The success of this design hinges on a balance between practicality, innovation, and user experience.
The cart’s design will be shaped by a range of factors, including its intended use, weight capacity, and maneuverability. The manufacturer will need to carefully select materials for the frame, wheels, and other components, taking into account factors such as durability, weight, and cost. The design will also incorporate features that enhance functionality, such as a folding mechanism, adjustable handle height, and built-in storage compartments.
Design Considerations
Designing a two-wheeled cart requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure functionality, safety, and user-friendliness. The design must balance weight capacity, maneuverability, stability, and ease of use, making it suitable for its intended purpose.
Material Selection
The choice of materials significantly impacts the cart’s performance, durability, and cost.
- Frame: Steel is a common choice for frames due to its strength and affordability. Aluminum is lighter and resists corrosion but is more expensive. For high-load applications, reinforced steel or specialized alloys might be preferred.
- Wheels: The material used for wheels influences their durability, rolling resistance, and noise levels. Solid rubber wheels are durable and low-maintenance but offer less cushioning. Pneumatic tires provide better shock absorption and a smoother ride but require inflation and are susceptible to punctures.
- Other Components: Handles, axles, and other components can be made from various materials like steel, aluminum, or even plastics. The selection depends on the desired strength, weight, and aesthetic appeal.
Wheel Types
Different wheel types offer distinct advantages and disadvantages.
- Solid Rubber Wheels: These wheels are robust, low-maintenance, and resistant to punctures. They are suitable for applications where durability and low rolling resistance are paramount, such as industrial settings or rough terrain. However, they offer less cushioning than pneumatic tires, resulting in a less comfortable ride.
- Pneumatic Tires: These tires provide better shock absorption and a smoother ride, making them ideal for transporting fragile goods or traversing uneven surfaces. They are also generally quieter than solid rubber wheels. However, they require inflation and are prone to punctures, which can be a concern in certain environments.
- Caster Wheels: Caster wheels are designed for maneuverability, allowing the cart to rotate freely. They are often used on carts that need to move easily in tight spaces. However, caster wheels can be less stable than other wheel types, especially when carrying heavy loads.
Functionality and Features
A two-wheeled cart is designed to facilitate the transportation of goods or materials, primarily serving as a mobile platform for moving objects efficiently. Its primary function is to simplify the process of moving items from one location to another, reducing the physical effort required for manual carrying. This section explores how design choices can enhance the functionality and features of the cart, making it more versatile and user-friendly.
Optimization of Primary Functions
The primary function of a two-wheeled cart is to transport goods or materials. To optimize this function, design choices should focus on factors such as:* Load capacity: The cart should be designed to handle the expected weight of the items it will carry. This requires careful consideration of the materials used for construction and the structural integrity of the frame.
Maneuverability
The cart should be easy to maneuver, especially in tight spaces. This can be achieved by using smooth-rolling wheels with appropriate bearings and by ensuring a stable wheelbase.
Stability
The cart should be stable and secure, preventing tipping or rolling over when loaded. This can be achieved through a low center of gravity, a wide wheelbase, and a well-designed frame.
Ease of loading and unloading
The cart should be designed to make loading and unloading easy and efficient. This can be achieved through features such as a low loading height, a wide platform, and secure attachments for holding items in place.
Innovative Features
Several innovative features can be incorporated into the cart to enhance its functionality, making it more versatile and user-friendly. Some examples include:* Folding mechanism: A folding mechanism allows the cart to be compactly stored when not in use, saving space. This is particularly useful for carts intended for home use or transportation in vehicles.
Adjustable handle height
An adjustable handle height allows users of different heights to comfortably operate the cart. This feature is particularly beneficial for users who may experience discomfort or strain when using a fixed-height handle.
Built-in storage compartments
Built-in storage compartments provide a dedicated space for storing small items, tools, or accessories. This feature is useful for organizing and keeping essential items within easy reach.
Integrated scales
Integrated scales provide an accurate measurement of the weight of the items being transported. This feature is particularly useful for applications where precise weight measurement is required.
Power-assisted steering
Power-assisted steering can make the cart easier to maneuver, especially when carrying heavy loads. This feature is particularly useful for carts used in industrial or commercial settings.
User Interface Design
A user-friendly interface is crucial for a two-wheeled cart, ensuring that users can easily operate and control the cart’s functionality. Design considerations for the user interface include:* Intuitive controls: The cart’s controls should be intuitive and easy to understand. This can be achieved by using clear and concise labeling, ergonomic design, and familiar control mechanisms.
Visual feedback
The cart should provide visual feedback to the user about its current state and operation. This can be achieved through the use of indicators, displays, or other visual cues.
Accessibility
The cart should be accessible to users with different abilities and disabilities. This can be achieved by considering factors such as the height of controls, the size of buttons, and the visibility of displays.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process for a two-wheeled cart involves a series of steps that transform raw materials into a functional and durable product. These steps include material sourcing, cutting, bending, welding, and assembly. The choice of manufacturing techniques can significantly impact the efficiency, cost, and quality of the final product.
Manufacturing Techniques
The choice of manufacturing technique depends on factors such as production volume, desired level of automation, and budget.
- Manual Assembly: This method involves assembling the cart by hand using tools and equipment. It is typically suitable for small-scale production runs or custom orders.
- Automated Assembly: This method utilizes robotic arms and other automated systems to perform repetitive tasks, such as welding, cutting, and assembly. Automated assembly is more efficient for large-scale production runs and can improve consistency and accuracy.
- 3D Printing: This technique uses a digital model to create a physical object layer by layer. It offers flexibility in design and allows for the production of complex geometries. However, 3D printing is currently less cost-effective for large-scale production of carts.
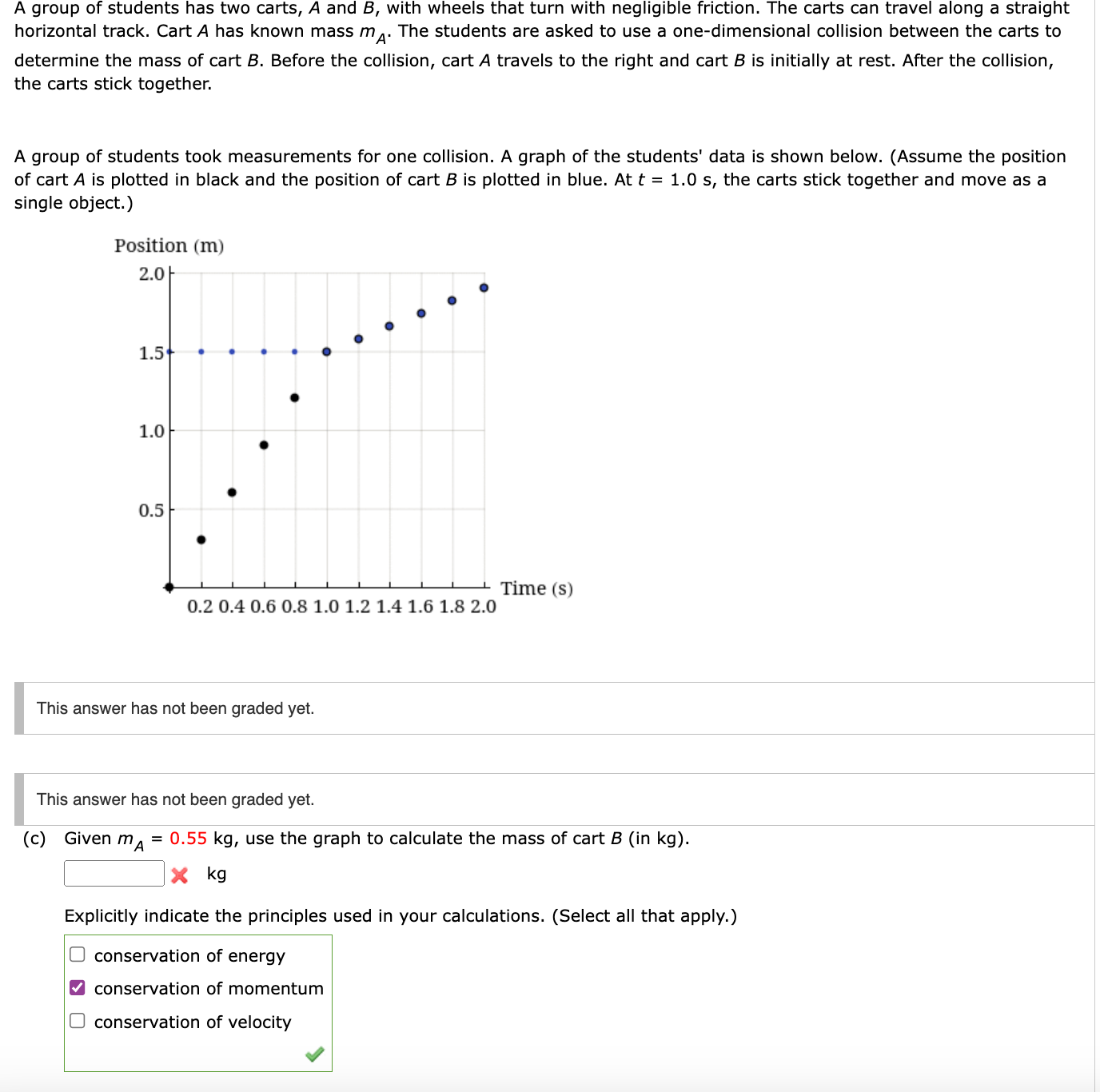
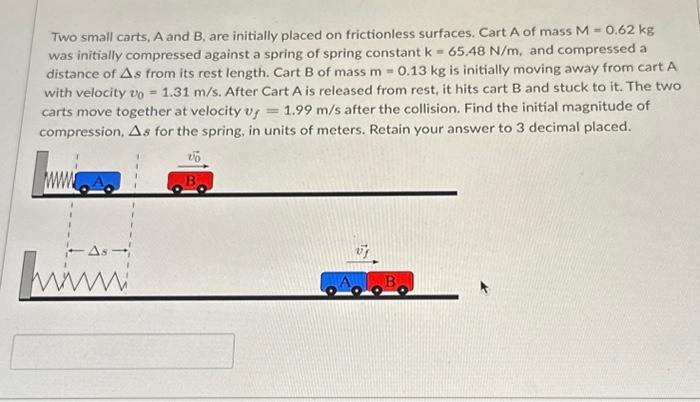
Quality Control Measures, A manufacturer is designing a two wheeled cart
Implementing rigorous quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process is crucial to ensure that the final product meets the desired standards of quality, safety, and performance.
- Material Inspection: Inspecting incoming materials for defects, such as cracks, scratches, or inconsistencies in dimensions, ensures that only high-quality materials are used in the manufacturing process.
- Process Monitoring: Monitoring the cutting, bending, welding, and assembly processes helps to identify any deviations from specifications and ensures that the manufacturing process is performed consistently.
- In-Process Inspection: Performing inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process allows for early detection of defects and prevents the propagation of errors to subsequent stages.
- Final Inspection: A thorough final inspection of the assembled cart ensures that it meets all design specifications and quality standards before it is shipped to the customer.
Target Market and Applications: A Manufacturer Is Designing A Two Wheeled Cart
The target market for a two-wheeled cart is vast and diverse, encompassing individuals, businesses, and organizations across various sectors. This versatility stems from the cart’s inherent functionality and adaptability to a wide range of needs and usage scenarios.
Target Market Demographics
The target market for two-wheeled carts can be broadly categorized based on demographics, needs, and usage scenarios.
- Individuals: Individuals seeking convenient and efficient solutions for transporting goods, groceries, or personal belongings. This includes homeowners, students, and individuals with mobility challenges.
- Businesses: Businesses across various industries, including retail, warehousing, hospitality, and construction, utilize two-wheeled carts for transporting goods, supplies, and equipment.
- Organizations: Non-profit organizations, schools, hospitals, and government agencies often require carts for transporting materials, supplies, and equipment.
Applications of Two-Wheeled Carts
Two-wheeled carts find applications in diverse sectors, offering efficient and practical solutions for various tasks.
- Retail: Retailers utilize carts for transporting merchandise, customer purchases, and inventory within stores, warehouses, and loading docks.
- Warehousing: Warehouses rely on carts for moving pallets, boxes, and other materials within the facility, streamlining logistics and warehouse operations.
- Transportation: Two-wheeled carts are used for transporting luggage, equipment, and supplies in airports, train stations, and other transportation hubs.
- Home Use: Individuals use carts for transporting groceries, gardening supplies, and other household items, simplifying tasks and improving efficiency.
- Construction: Construction sites use carts for transporting tools, materials, and equipment, facilitating construction activities.
- Hospitality: Hotels, restaurants, and other hospitality venues utilize carts for transporting luggage, room service items, and supplies.
Marketing Strategy
A successful marketing strategy for a two-wheeled cart should highlight its key features and benefits, targeting specific customer segments.
- Focus on Convenience and Efficiency: Emphasize the cart’s ability to simplify tasks, reduce effort, and increase productivity, highlighting its time-saving benefits.
- Highlight Durability and Reliability: Emphasize the cart’s sturdy construction and reliable performance, assuring customers of its longevity and dependability.
- Promote Versatility and Adaptability: Showcase the cart’s versatility in handling various loads and its adaptability to diverse applications, catering to a wide range of needs.
- Target Specific Customer Segments: Tailor marketing messages to specific customer segments, such as individuals, businesses, or organizations, highlighting features relevant to their needs and usage scenarios.
- Emphasize User-Friendliness: Highlight the cart’s ease of use and maneuverability, emphasizing its user-friendly design and intuitive operation.
- Offer Competitive Pricing: Position the cart competitively within the market, offering value for money and justifying its purchase.
Safety and Regulations
The safety of users and bystanders is paramount when designing and manufacturing a two-wheeled cart. Potential hazards must be identified and mitigated through appropriate design and manufacturing practices. This section will Artikel the relevant safety regulations and standards that apply to the design and manufacturing of two-wheeled carts, and will provide a comprehensive safety manual for the cart, outlining proper use, maintenance, and storage procedures.
Potential Safety Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
The potential safety hazards associated with using a two-wheeled cart can be categorized into three main areas:
- Stability and Tipping: Two-wheeled carts are inherently less stable than carts with four wheels, and can easily tip over if overloaded or if the load is not properly balanced. This can result in injuries to the user or damage to the load.
- Load Handling and Securement: Improper loading and securing of the load can lead to the load shifting during transport, potentially causing the cart to tip over or the load to fall off.
- Collision Hazards: Two-wheeled carts can be difficult to maneuver in tight spaces, increasing the risk of collisions with people or objects.
To mitigate these hazards, the following design and manufacturing practices should be considered:
- Wide Base and Low Center of Gravity: A wide base and a low center of gravity will increase the cart’s stability and reduce the risk of tipping.
- Load Capacity and Weight Distribution: The cart should be designed to handle the maximum anticipated load weight, and the load should be distributed evenly across the cart.
- Securement Mechanisms: The cart should be equipped with securement mechanisms, such as straps or clamps, to prevent the load from shifting during transport.
- Braking System: A reliable braking system should be incorporated to control the cart’s speed and prevent uncontrolled movement.
- Maneuverability and Visibility: The cart should be designed for easy maneuverability in tight spaces, and should incorporate features that enhance visibility, such as bright colors and reflective materials.
- Ergonomics and User Interface: The cart should be designed with ergonomics in mind, to minimize user fatigue and strain. The controls should be intuitive and easy to use.
Safety Regulations and Standards
The design and manufacture of two-wheeled carts are subject to various safety regulations and standards, which vary depending on the intended use and the jurisdiction. Some of the key regulations and standards that may apply include:
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): ASTM International develops and publishes voluntary consensus standards for materials, products, systems, and services. Relevant ASTM standards for two-wheeled carts include:
- ASTM F2113: Standard Consumer Safety Specification for Hand Trucks
- ASTM F2907: Standard Specification for Hand Trucks, Dollies, and Platform Trucks
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI): ANSI is a private non-profit organization that administers and coordinates the U.S. voluntary standardization system. Relevant ANSI standards for two-wheeled carts include:
- ANSI/ASME B56.1: Safety Standard for Powered Industrial Trucks
- ANSI/ASME B56.5: Safety Standard for Powered Platform Lifts
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA is a federal agency that sets and enforces standards for workplace safety and health. OSHA regulations related to two-wheeled carts include:
- 29 CFR 1910.178: Safety Requirements for Powered Industrial Trucks
- 29 CFR 1910.179: Safety Requirements for Cranes
It is important to note that these are just a few examples of the many safety regulations and standards that may apply to two-wheeled carts. Manufacturers should consult with relevant regulatory bodies and industry experts to ensure compliance with all applicable requirements.
Safety Manual
A comprehensive safety manual should be provided with each two-wheeled cart, outlining proper use, maintenance, and storage procedures. The manual should include the following information:
- Cart Specifications: This section should include the cart’s load capacity, dimensions, weight, and any other relevant specifications.
- Operating Instructions: This section should provide detailed instructions on how to operate the cart safely, including:
- Loading and Securing the Load: Explain how to properly load and secure the load to prevent shifting or falling off.
- Maneuvering the Cart: Describe how to safely maneuver the cart in different environments, including tight spaces and around obstacles.
- Using the Braking System: Explain how to use the braking system effectively to control the cart’s speed and prevent uncontrolled movement.
- Maintenance Procedures: This section should Artikel the recommended maintenance procedures for the cart, including:
- Regular Inspections: Describe how to inspect the cart for damage or wear and tear, and what to do if any issues are found.
- Lubrication: Explain how to lubricate the cart’s moving parts to ensure smooth operation.
- Cleaning and Storage: Provide instructions on how to clean the cart and store it properly to prevent damage.
- Safety Precautions: This section should highlight important safety precautions to follow when using the cart, such as:
- Avoiding Overloading: Emphasize the importance of not exceeding the cart’s load capacity.
- Proper Lifting Techniques: Provide guidance on proper lifting techniques to prevent injuries.
- Awareness of Surroundings: Encourage users to be aware of their surroundings and potential hazards.
- Using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): If necessary, recommend the use of PPE, such as safety shoes or gloves.
The safety manual should be written in clear and concise language, and should include illustrations and diagrams to enhance understanding. It should be readily accessible to all users of the cart, and should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect any changes in safety regulations or best practices.
As the manufacturer meticulously crafts this two-wheeled cart, they are not merely creating a product but a solution. This cart has the potential to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and simplify tasks across a variety of industries and applications. By embracing innovation and prioritizing user needs, the manufacturer aims to create a cart that is both practical and user-friendly, leaving a lasting impact on the world of transportation and logistics.
Essential Questionnaire
What are some common materials used for cart frames?
Common materials for cart frames include steel, aluminum, and plastic. Steel is durable and affordable, aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant, and plastic is lightweight and impact-resistant.
What are the different types of wheels commonly used for carts?
Cart wheels can be solid rubber, pneumatic tires, or caster wheels. Solid rubber wheels are durable and low-maintenance, pneumatic tires provide a smooth ride, and caster wheels allow for easy maneuverability in tight spaces.
What are some key considerations for safety when designing a cart?
Safety considerations include ensuring the cart is stable, has a secure load platform, and has a clear and visible handle. The cart should also be designed to avoid pinch points and sharp edges.